The Revenue Streams part of the business model focuses on how the overall business will generate sales.
In simple terms, there are two main types of revenue streams. The first is based on transaction-based revenue and the second generating recurring revenue.
In this section, you will learn about the different types of revenue streams, pricing mechanisms and methods used by leading businesses to generate money.
Table of Contents
What Is a Revenue Stream?

A revenue stream is a distinct source of income that can come from either be recurring revenue, transaction-based or service revenue.
A revenue stream is a critical part of the business model that influences strategy, business planning and investment. A revenue stream represents the economic value customers are willing to pay for the products and services offered. However, a revenue stream is not a business model, but it does influence how a business model works.
In short, revenue streams are the total sales of all products and services. However, in accounting terms, it is often called net sales.
You can see from the image below that Amazon reports its total revenue as net sales.
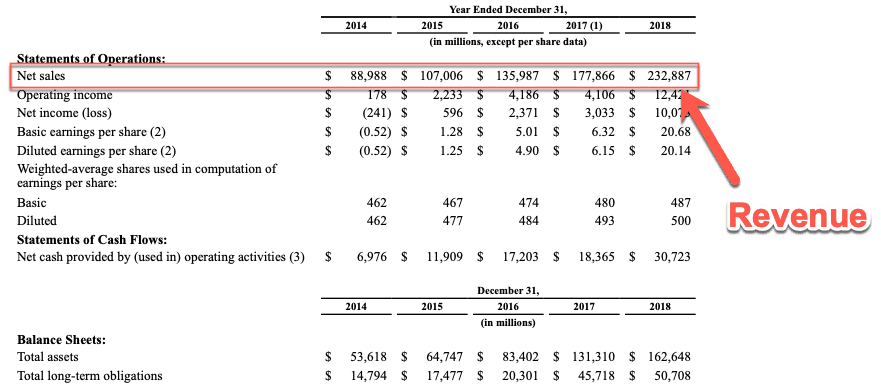
What Is The Difference Between A Revenue Model, Revenue Stream And A Business Model
A revenue stream is easily confused with a revenue model which, in turn, is often confused with a business model.
Definition of a Revenue Stream
A revenue stream is a distinct source of income that can come from either be recurring revenue, transaction-based or service revenue. A business can have a single source of revenue or multiple sources depending on its business model(s).
Definition of a Revenue Model
A revenue model is a framework for generating revenues. Essentially it is the strategy and plan for how a business generates income from either a single or multiple revenue streams. As a strategy, it involves consideration of what value to offer, how to price the value, and who pays for the value.
Definition Of A Business Model
A business model is a framework for optimizing long-term value by systematically analysing how to deliver value to customers profitably.
The business model takes all aspects of your business into account, including your revenue model and all your revenue streams, and examines how well the different parts of the business work together.
Business Model Revenue Streams
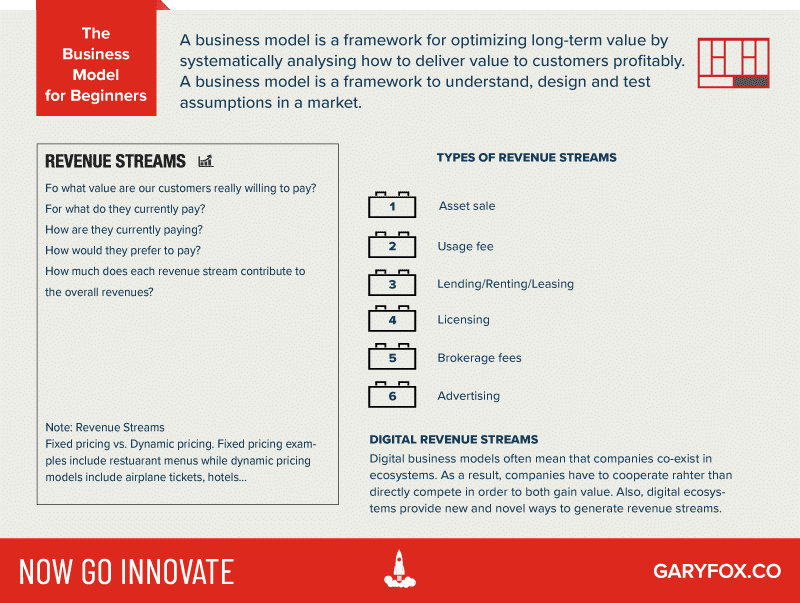
There are lots of different ways to generate revenue from products and services. Many markets have been disrupted by changes to revenue models.
As an example, by going digital the music industry was transformed and new revenue models appeared in the form of subscriptions (recurring revenue) rather than buying a song or album (transactions).
What are the different types of revenue streams?
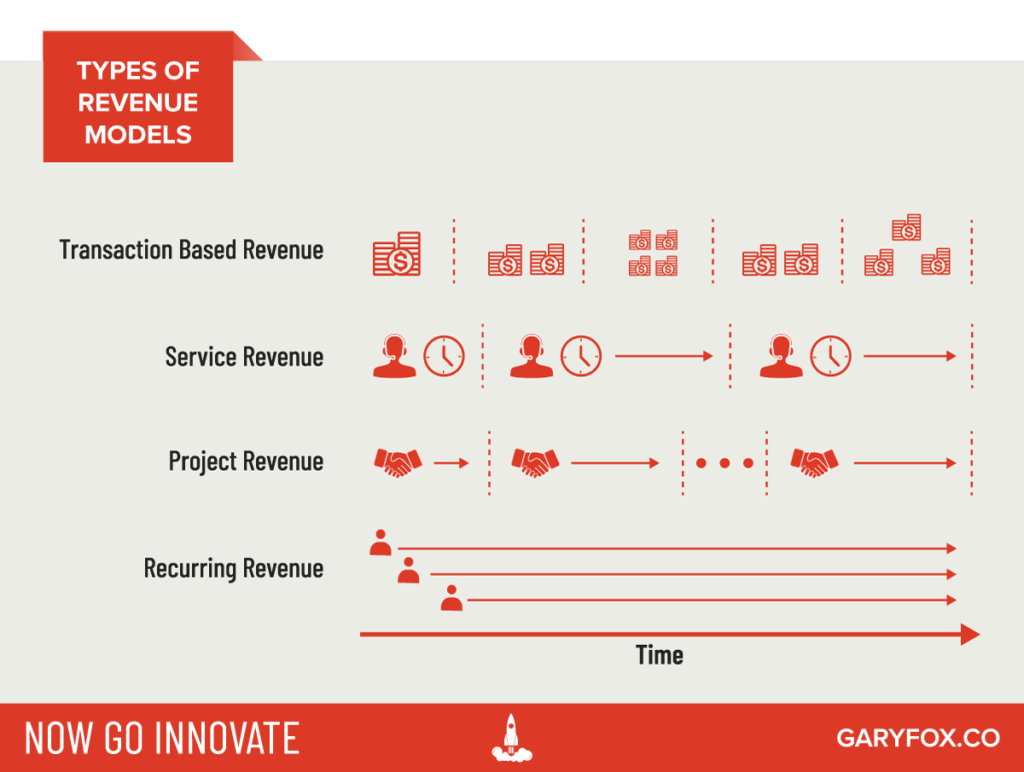
The two main types of revenue streams are:
- Transaction-based revenues – revenue is earned from customers making a one-time payment of your product or service.
- Recurring revenues – continuous payments for the delivery of products or services.
Why understanding revenue streams matters?
1. Revenue is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) for all businesses
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measure that aligns to the overall business strategy. Generally, you find that financial KPI’s link to revenue and profits but can also involve further measures such as cash flow and liquidity.
Whether you’re a startup or large corporation revenue is a key measure for all stakeholders.
2. Performance prediction differs between different revenue streams
What everyone wants to see or be able to predict is how much sales will be generated in the future. An investor will want to understand this because they have a vested interest in the future of the company. Shareholders will want to know or understand what a business is forecasting to understand its overall health.
Recurring revenue is the most predictable income because the cash inflow remains consistent with a stable customer base. In contrast, transaction-based and service revenues tend to fluctuate with customer demand and often is also affected by seasonality.
#3 Different forecasting models are needed for different revenue models
Depending on the type of revenue models a company employs, a financial analyst develops different forecasting models and carries out different procedures to obtain necessary information when performing financial forecasting. For companies with a recurring revenue stream, a forecast model should have a uniform structure and a similar pattern in revenue predictions.
Why Testing For Revenue Streams Is Important
Digital technologies have enabled new ways to test products and services in a market to understand if customers are actually willing to buy – in other words if they understand see the value in the new product or service.
Many growth hackers and successful entrepreneurs have had their fair share of failure as well as success. Often, entrepreneurs have had to change either their product, service, customer segment or value proposition to succeed.
The reason is often that they couldn’t get customers to take even the simplest of actions like signing up for an email, let alone paying for the new product.
Is generating the most important part of a business? Of course, it is but there have been some notable delays where a business doesn’t generate users and instead captures part of the market.
Often digital business models, platforms, require populating a platform prior to revenue generation. Facebook for years didn’t generate revenue, but then introduced ads.
Another example is when the revenue is not obvious. To some, it might seem that Google is free, and it is indeed for people that search, but Google then sells the search data and the ability to advertise as a method of generating revenue.
Often revenue models can seem complex as a result of digital business models, digital ecosystems and other digital technologies.
What are examples of revenue streams?
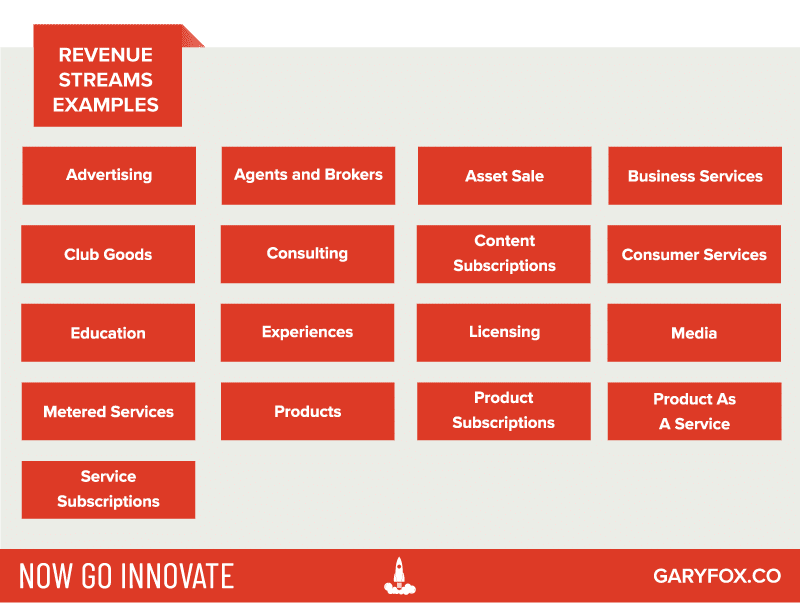
Advertising
Advertising involves being paid to communicate to an audience about a product or service.
Agents and Brokers
Agents and brokers act as intermediaries and take a percentage fee for their services.
Asset Sale
An asset sales is usually a one-off transaction involving an asset owned by either a person or a company.
Business Services
Business services can have a variety of revenue types depending on the type of service. As an example, a website built for a business can involve a transaction initially but then may move to a subscription for maintenance.
Club Goods
Cinemas and theme parks are examples of Club goods and involve a fee for entrance.
Consulting
Consulting companies such as McKinsey, PWC, Deloitte and Bain work on both a project and retainer basis. The retainer can be thought of as a subscription for a set number of hours and level of service. Projects are normally defined in terms of a start date and end date with a set outcome.
Content Subscriptions
Digital technologies disrupted and transformed the media industry. Newspapers used to rely on a regular set of customers buying a physical copy of their entire output. Now they are often online and customers pay a subscription to access the full content. Several bloggers have also moved to this type of arrangement.
Consumer Services
Consumer services range from restaurants to hairdressers and other forms of services aimed at consumers.
Education
Education consists of both services and products that educate either companies or individuals. Training can be either online, eLearning, face to face learning (e.g. as a workshop or in a classroom) or a blend of the two (blended learning).
Experiences
The experience economy has grown massively over the last 10 years. This includes real-world experiences such as travel, war games, parachuting, paragliding and many more.
Licensing
Intellectual Property can be licensed to create a recurring revenue stream.
Media
Sales of media is a common revenue stream for businesses such as production companies that make movies, documentaries, TV shows.
Metered Services
Many services are now being metered such as electricity, gas and water. A business will then gain revenue by charging for use or consumption.
Products
Products have been around for aeons and represent one of the oldest and more traditional revenue streams. They are mostly transactional involving a buyer and seller.
Product Subscriptions
A WordPress plugin is a good example of a product (digital) that is purchased downloaded and installed. Most premium WordPress plugins then work on an annual subscription model. Other products offer different timeframes for the payment terms.
Products As A Service
Some products such as wearable devices often also come linked with services. These product-service systems are present in consumer goods and B2B product-service systems e.g. aircraft engines.
Service Subscriptions
Web hosting services are an example of how some companies create revenue streams. Different pricing points take into account a range of customer segments and how the different requirements for each e.g. web developer vs. agency vs. a small business.
Revenue Formula
How do you calculate revenue streams?
Calculating revenue can be simple or complicated depending on the business.
As an example, if many companies periodically offer promotional codes, often with a different value. A product that has an original price of $100 could be discounted down by 10% – $90, 20% – $80 and so on. As a result, the total revenue will be a mix of all the sales at each price point.
Product A Revenue
| Units sold | Price | Discount | Sale Price | Total Revenue |
| 20 | $100 | None | $100 | $2,000 |
| 20 | $100 | 10% | $90 | $1,800 |
| 20 | $100 | 20% | $80 | $1,600 |
| Net Revenue (Sales) | $5,400 | |||
| Average Price Sold | $90 |
For product sales, it is calculated by taking the average price at which goods are sold and multiplying it by the total number of products sold. For service companies, it is calculated as the value of all service contracts, or by the number of customers multiplied by the average price of services.
What is the formula for revenue? An example of how you can calculate sales revenue.
Revenue = No. of Units Sold x Average Price
or
Revenue = No. of Customers x Average Price of Services
Revenue Forecast
Below is an example of a company’s forecast based on many drivers, including:
- Website traffic.
- Conversion rates.
- Product prices.
- Volume of different products.
- Discounts.
- Return and refunds.