The visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk created the Tesla business model. Under his leadership, Tesla has become a symbol of innovation and a driving force behind the global shift towards electric mobility.
The trailblazing electric vehicle manufacturer has disrupted the automotive industry with its cutting-edge technology, sleek designs, and unwavering commitment to sustainability.
In this article, I delve into Tesla’s business model and uncover some of the strategies it employs to disrupt the car market.
Table of Contents
How Does Tesla’s Business Work?
Tesla’s business model revolves around the design, manufacture, and sale of high-performance electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and solar products.
The company operates on a direct-to-consumer sales approach, forgoing the traditional dealership model and selling its vehicles directly to customers through its showrooms and online platform.
Tesla also generates revenue by selling regulatory credits, which it earns by producing zero-emission vehicles and selling them to other automakers who need to offset their carbon footprint.
Key Facts About Tesla
Interesting Fact: Elon Musk is the longest-tenured CEO of any automotive manufacturer globally.
TESLA, Inc.
Elon Musk, Martin Eberhard, JB Straubel, Marc Tarpenning, Ian Wright
June 22. 2012 Tesla Model S launch
2003
Elon Musk
Palo Alto, California
TSLA
(FY 2023): $96.773 Billion
(FY 2023): $14.999 billion
(April, 2023): $516.20 billion
Useful Links for Tesla
A Brief History of Tesla
Tesla was founded in 2003 by a group of engineers who shared a vision of creating a world powered by sustainable energy. The company’s journey began with the development of the Tesla Roadster, the first all-electric sports car launched in 2008. Since then, Tesla has expanded its product lineup, introduced groundbreaking technologies, and established itself as a leader in the electric vehicle market.
Key milestones in Tesla’s history include:
- 2008: Launch of the Tesla Roadster, the company’s first all-electric sports car
- 2010: Tesla goes public on the NASDAQ stock exchange
- 2012: Introduction of the Tesla Model S, a premium all-electric sedan
- 2015: Launch of the Tesla Model X, an all-electric SUV with distinctive falcon-wing doors
- 2016: Acquisition of SolarCity, expanding Tesla’s offerings to include solar energy products
- 2017: Unveiling of the Tesla Model 3, the company’s first mass-market electric vehicle
- 2018: Opening of the Gigafactory 1 in Nevada, the world’s largest lithium-ion battery factory
- 2019: Unveiling of the Tesla Cybertruck, an all-electric pickup truck with a futuristic design
- 2020: Tesla becomes the world’s most valuable automaker by market capitalization
- 2021: Opening of Gigafactory Berlin and Gigafactory Texas, expanding Tesla’s global manufacturing footprint.
Note: Elon Musk also transformed the Space industry – see the SpaceX business model.
Who Owns Tesla?
Tesla is a publicly traded company whose shares are listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the ticker symbol TSLA. The company’s ownership structure includes a mix of institutional investors, individual shareholders, and insiders.
As of 2021, Elon Musk, the co-founder and CEO of Tesla, holds a significant portion of the company’s shares and wields considerable influence over its strategic direction.
Other notable shareholders include major institutional investors such as Baillie Gifford & Co., Capital World Investors, and Fidelity Management & Research.
Tesla Mission Statement
Tesla’s mission statement is “to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.”
How Tesla Works

Tesla’s business model is built on several key pillars that set it apart from traditional automakers:
- Electric vehicle focus: Tesla is dedicated solely to designing and producing electric vehicles, allowing it to channel all its resources and expertise into developing cutting-edge EV technologies.
- Direct-to-consumer sales: Tesla sells its vehicles directly to customers, bypassing the conventional dealership model. This approach enables the company to maintain greater control over the sales process, build stronger customer relationships, and optimize its inventory management.
- Vertical integration: Tesla has a vertically integrated business model with in-house design, manufacturing, and software development capabilities. This allows the company to achieve greater control over its supply chain, improve efficiency, and foster a culture of innovation.
- Software and technology leadership: Tesla strongly emphasizes software development and over-the-air updates, continuously enhancing the performance and features of its vehicles even after they have been sold.
- Charging infrastructure: Tesla has invested heavily in building its network of Supercharger stations, which provide fast and convenient charging options for its customers and address one of the main concerns associated with electric vehicle ownership.
- Expansion into energy storage and solar: Tesla has diversified its business by offering energy storage solutions, such as the Powerwall and Powerpack, as well as solar panels and solar roofs through its subsidiary, Tesla Energy.
- Brand power and ecosystem: Tesla has cultivated a strong brand identity associated with innovation, luxury, and sustainability. The company’s ecosystem of products and services, including its vehicles, charging network, and energy solutions, creates a compelling value proposition for customers.
How Tesla Makes Money
The Revenue Model of Tesla
The revenue model of the Tesla business model consists of the overall sales and multiple streams it generates.
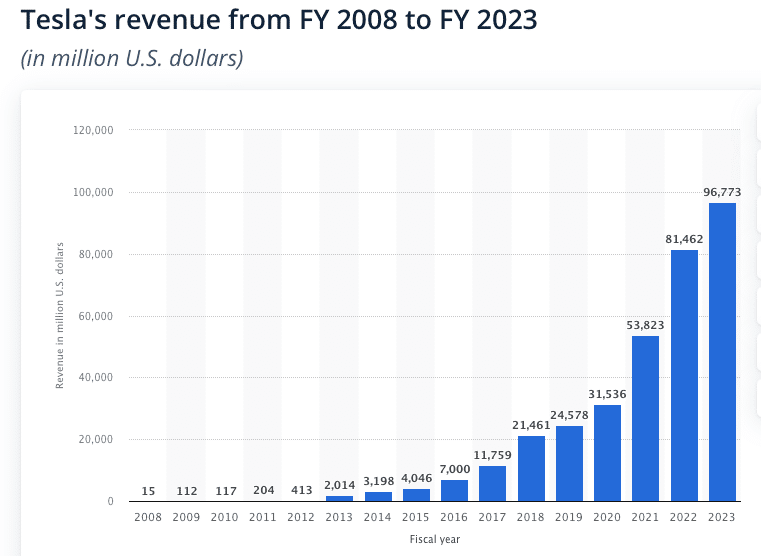

Tesla generates revenue through several key streams:
- Electric vehicle sales: Tesla’s primary source of revenue comes from the sale of its electric vehicles, including Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y.
- Regulatory credits: Tesla earns regulatory credits by producing and selling zero-emission vehicles, which it can then sell to other automakers who need to offset their carbon footprint to meet government regulations.
- Energy products and services: Tesla generates revenue from the sale of its energy storage systems, solar panels, and solar roofs, as well as from the installation and maintenance services associated with these products.
- Automotive leasing: Tesla offers vehicle leasing options, generating revenue from lease payments and the eventual sale of used vehicles.
- Other services: Tesla also generates revenue from other services, such as its in-car internet connectivity, premium vehicle features, and extended service plans.
Bloomberg estimates that all of Tesla’s chargers raked in around $1.74 billion of charging revenue in 2023, or around 17% of the “Services & Other” segment that Tesla accounts for in its earnings.
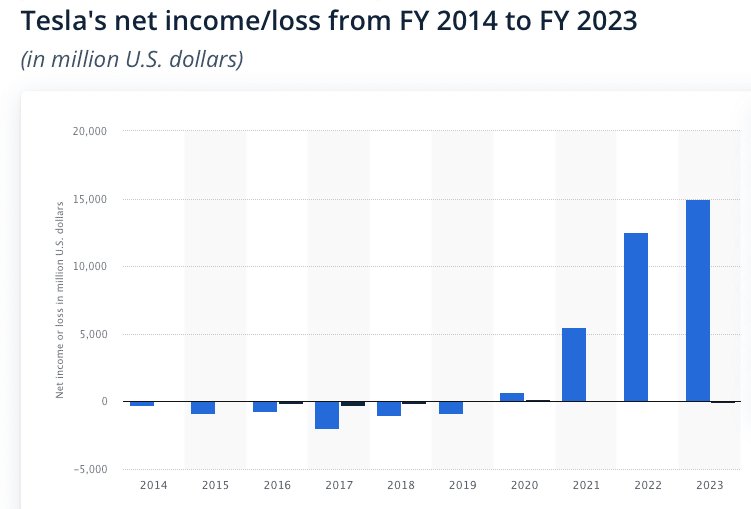
What is Tesla’s Business?
The Tesla business model operates in the electric vehicle and clean energy sectors, offering products and services promoting sustainable transportation and renewable energy solutions.
The company primarily designs, manufactures, and sells high-performance electric vehicles, targeting the premium and mass-market segments. Tesla differentiates itself from competitors through its advanced technology, software-driven approach, and direct-to-consumer sales model.
The company’s competitive advantages include its:
- strong brand recognition
- cutting-edge EV technology
- extensive charging infrastructure
- continuous improvement of its vehicles through over-the-air software updates.
Key Features of Tesla’s Business Model
- Focus on electric vehicles and clean energy solutions
- Direct-to-consumer sales approach, bypassing traditional dealerships
- Vertical integration with in-house design, manufacturing, and software development
- Strong emphasis on software and technology leadership, including over-the-air updates
- Investment in charging infrastructure through the Tesla Supercharger network
- Diversification into energy storage and solar products through Tesla Energy
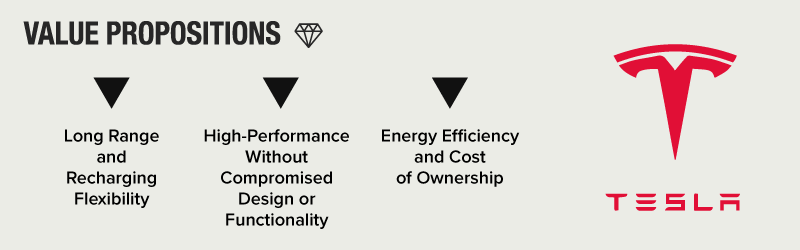
Clean Eco-Friendly Value Proposition
Electric storage technology is a final key part of the Tesla business model and one of the most important.
Tesla continues to lead the industry in energy storage. As a result, Tesla cars deliver the most extended range and fastest performance of any electric car on the market.
Tesla Business Model Patterns
The Tesla Ecosystem
The Tesla Range of Vehicles
The value proposition of the Tesla business model rests on the incredible design, status and performance of these electric vehicles.
As an example, the Tesla Roadster is the fastest car in the world – going from 0 to 60 mph in 1.9s.

Tesla, Inc., known for its innovative approach in the electric vehicle market, offers a range of models, each with distinctive launch dates and pricing tailored to various segments of the consumer market in the United States. Here’s an overview of the current range of Tesla cars available, along with their launch dates and costs:

- Tesla Model S
- Launch Date: June 2012
- Cost: Starting at approximately $94,990 USD for the Long Range model, and $114,990 USD for the Plaid model.
- Tesla Model 3
- Launch Date: July 2017
- Cost: Starting at approximately $43,990 USD for the Rear-Wheel Drive model, $51,990 USD for the Long Range model, and $58,990 USD for the Performance model.
- Tesla Model X
- Launch Date: September 2015
- Cost: Starting at approximately $109,990 USD for the Long Range model, and $119,990 USD for the Plaid model.
- Tesla Model Y
- Launch Date: March 2020
- Cost: Starting at approximately $54,990 USD for the Long Range model, and $57,990 USD for the Performance model.
- Tesla Cybertruck (upcoming)
- Announced Date: November 2019
- Expected Launch Date: Production has been delayed several times with the latest updates suggesting a potential start in late 2023.
- Estimated Cost: Starting at approximately $39,900 USD for the Single Motor RWD, $49,900 USD for the Dual Motor AWD, and $69,900 USD for the Tri Motor AWD.
- Tesla Roadster (upcoming)
- Announced Date: November 2017
- Expected Launch Date: Initially slated for 2020, its release has been postponed to likely after 2023.
- Estimated Cost: Starting at approximately $200,000 USD for the base reservation, and $250,000 USD for the Founder’s Series.
The Next Big Shift in the Tesla Business Model

Tesla’s forthcoming lorry, the Tesla Semi, is an all-electric Class 8 truck that has garnered significant interest for its potential to revolutionize the heavy-duty trucking industry with its sustainable technology. Here are the key details:
- Announcement Date: The Tesla Semi was initially unveiled in November 2017.
- Expected Launch Date: Production of the Tesla Semi has faced multiple delays. Initially expected to start production in 2019, the latest updates from Tesla suggest that production began in late 2022, with the first deliveries commencing by the end of that year.
- Key Features: The Tesla Semi promises several innovative features:
- Range: The truck is expected to be available in two versions with different ranges from 300 and 500 miles on a single charge, addressing major range anxiety concerns in long-haul trucking.
- Performance: Capable of accelerating from 0 to 60 mph in about 20 seconds, even when fully loaded with 80,000 pounds of cargo. It also boasts energy recovery systems through regenerative braking.
- Safety and Autonomy: Equipped with Tesla’s Enhanced autopilot system, the Semi aims to provide semi-autonomous driving capabilities, including automatic emergency braking, lane keeping, and lane departure warnings.
- Economics: Tesla claims the Semi will significantly reduce the cost of cargo transport, citing fuel savings of over USD 200,000 compared to diesel trucks over a million miles.
- Cost: Tesla initially advertised the expected pricing as $150,000 USD for the 300-mile-range version and $180,000 USD for the 500-mile-range version. However, these prices are subject to change given the shifting dynamics of production costs and market conditions.
- Current Status: According to the latest information, Tesla has started limited production and has begun making deliveries to customers, including high-profile orders from companies like PepsiCo.
The Tesla Semi represents a significant step forward in electrifying commercial vehicles, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and operational costs associated with freight transport. As production scales up, the impact of the Tesla Semi will become more evident in the logistics and transportation sectors.
What Makes Tesla So Different Than Its Competitors.
Digital Technolgy
The Tesla car is a computer on wheels.
Unlike other car manufacturers, Telsa is born digital. Because of that digital focus, Tesla has some fundamental differences built into its DNA.
When Elon Musk started Tesla, he approached the car industry with a different mindset – technology first.
As an entrepreneur and technologist, he started the design of Tesla with technology as the start. As an example, the system software receives software updates.
This contrasts with other manufacturers whose tech and infotainment quickly become dated when you own the car. With a Tesla, it keeps getting better!
Right from its infancy, Tesla has focused on offering the best technology to go into a car. The result is a frictionless and easy-to-use experience with such features as:
The TESLA Strategic Focus
Tesla manufactures, distributes and sells the following products:
- Automobiles
- Electric vehicle powertrain components
- Batteries, energy storage
- Solar panels

It looked like the car market already had enough players. Let’s face it the amount of investment needed to compete in the car industry presents a significant barrier to entry.
Infrastructure, technology, production plants, and distribution networks aren’t something you can conjure up on a whim.
Yet, Tesla had the vision to transform the industry by producing electric cars. Their goal was to leapfrog rivals who were rigidly committed to cars fuelled by petrol/diesel. At a time when electric batteries were nowhere near the performance level of today that was a brave vision to pursue.
They faced significant technological barriers but overcame them and now they have the worlds most efficient electric car is the Tesla Model Y.
Tesla benefits from having fewer parts than an internal combustion vehicle making the total cost of Tesla ownership is significantly lower. There’s no need for expensive tune-ups and replacements.
In the US, Tesla charge points to account for 30 to 40 per cent of all charge points. This not only creates broader brand awareness but also improves the customer experience, reduces friction when making a purchase decision, and provides a physical infrastructure footprint.
With more and more competitors playing catch-up to Tesla it is not to say that the Tesla Business model will not face competition. However, Tesla is creating unique defensible strategies to maintain its lead in electric vehicles.
Tesla’s Corporate Mission and Vision
To create an entire sustainable energy ecosystem, Tesla also manufactures a unique set of energy solutions, Powerwall, Powerpack and Solar Roof, enabling homeowners, businesses, and utilities to manage renewable energy generation, storage, and consumption.
Tesla
TESLA Business Model Canvas
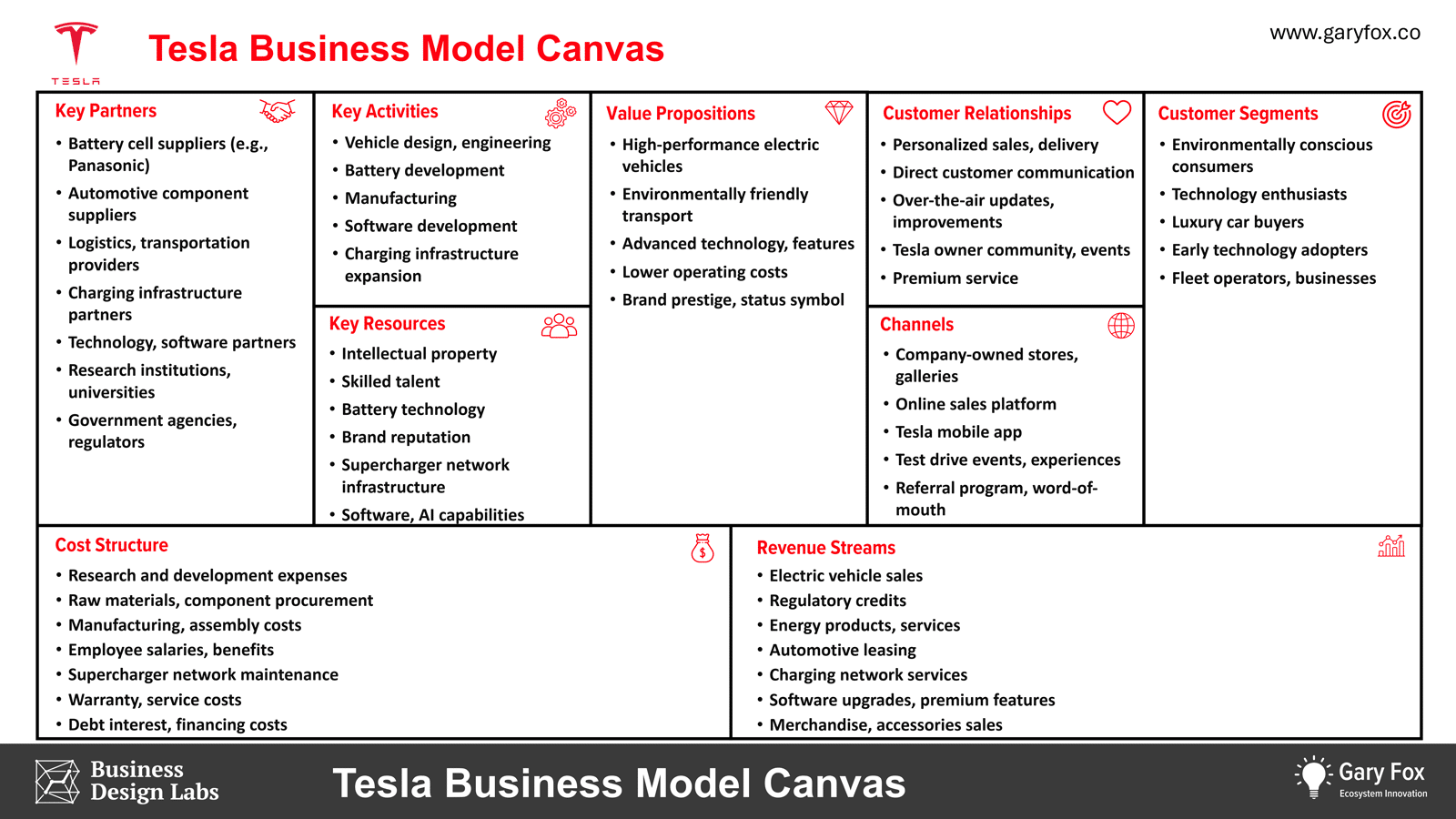
The Tesla Business Model
Tesla Customer Segments
The Tesla business model caters to a specific set of customer segments:

Tesla Value Proposition
The Tesla business model value proposition has recently expanded to include the forthcoming Tesla Semi, which, although not released, shifts Tesla into the commercial vehicle/heavy-duty truck market.
Tesla’s electric vehicles offer high performance, instant torque, and a thrilling driving experience, appealing to technology enthusiasts and luxury car buyers. The company’s focus on environmental sustainability attracts consumers who value eco-friendly transportation options. Tesla’s vehicles feature advanced technology, such as Autopilot and over-the-air updates, providing cutting-edge features and continuous improvements. Lower operating costs, due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, make Tesla’s vehicles an attractive long-term investment. Additionally, owning a Tesla is often seen as a status symbol, appealing to customers who value brand prestige and innovation.

Tesla Channels

The following are Tesla’s main channels:
Tesla Customer Relationships
Tesla establishes and maintains customer relationships that align with its innovative and direct-to-consumer approach. These relationships are designed to foster loyalty, engagement, and advocacy among customers. Tesla’s customer relationships include:
Tesla Key Activities
Tesla business model key activities are essential for smooth operations. Tesla’s key activities include:
Tesla Key Resources
Tesla business model relies on key resources to create and deliver its value propositions. These resources are crucial for the company to remain competitive. Tesla’s key resources include:
Tesla Key Partners
The Tesla business model involves multiple collaborations with key partners to create and deliver its value propositions. These partnerships are crucial for the company’s business model and contribute to its success. Tesla’s key partners include:
Tesla Revenue Streams
The Tesla business model generates revenue through various streams which includes:

Tesla Cost Structure
The Tesla business model model cost structure relate to the company’s operations. Tesla’s key costs include:
Final Notes on the Tesla Business Model
11 Ways The Tesla Business Model Model Disrupts The Automotive Industry
- Direct to the consumer: Unlike other car manufacturers who sell through franchised dealerships, Tesla uses direct sales.
- Service: Tesla has combined many sales centres with service centres. They believe that opening a service centre in a new area corresponds with increased customer demand. Customers can charge or service their vehicles at the service centres or the Service Plus locations.
- Electric vehicle performance: Tesla has the fastest car in the market and delivers the longest driving range from a full battery charge.
- Charging station ecosystem: Tesla has a network of superchargers that charge 4X faster than normal chargers. They are also partnering with EVgo to create a bigger network of charge points.
- Design: Tesla has invested heavily in the aesthetics and engineering of its EVs, resulting in a striking and unique brand identity and look.
- Sustainable energy: Tesla’s mission statement aligns with the global need for more sustainable sources of energy. Tesla’s cars and broader ecosystem are helping to lower CO2 emissions.
- R&D investments: Tesla invests heavily in both hardware and software. However, its focus on digital technologies has given it an advantage in the industry. Unlike other manufacturers, the Tesla infotainment system, like apps on your iPhone, gets updated and continually improves.
- Software: Tesla collects data from all its cars and charge points to further innovate and develop new technologies and value propositions.
- Autonomous driving: Tesla is the leading driver of autonomous and assisted vehicles.
- Partners: Tesla has a powerful network of partners, including several governments, that are supporting its production plants and infrastructure. Most governments have signed up to international agreements to lower carbon emissions, and so Tesla aligns with their goals to achieve this.
- Elon Musk: The enigmatic serial entrepreneur continues to be controversial, but nobody can deny his incredible talent for pushing the boundaries of innovation and creating headlines in the press—essentially free publicity.
TESLA Channels
Tesla cuts out the middlemen. Buying a Tesla is relatively simple through the online shop. Compare this to buying other vehicles and you have layers of complexity and negotiation – dealers with sales teams who you have to negotiate with to get the final price (often not the one advertised).
The Future of the Tesla Business Model
As Tesla continues to lead the electric vehicle revolution, its business model is poised for further growth and evolution. The company’s focus on innovation, vertical integration, and customer-centric approach will remain key drivers of its success. Tesla’s ongoing expansion into new markets, such as energy storage and solar products, will provide additional revenue streams and synergies with its core automotive business.
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles worldwide, driven by government regulations and shifting consumer preferences, presents significant opportunities for Tesla to scale its operations and capture a larger market share. The company’s investments in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and software development will be critical in maintaining its competitive edge and delivering superior value to customers.
However, Tesla will also face challenges as traditional automakers ramp up their electric vehicle offerings and new entrants emerge in the market. The company will need to continue innovating, optimizing its cost structure, and ensuring a reliable and efficient supply chain to maintain its leadership position.
As Tesla expands its product portfolio, enters new geographic markets, and explores additional revenue streams, the Tesla business model will likely evolve to accommodate these changes. Partnerships, strategic collaborations, and potential mergers and acquisitions could play a role in Tesla’s future growth strategy.
Overall, Tesla business model is well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable transportation and clean energy solutions. By staying true to its mission, fostering customer loyalty, and continuously pushing the boundaries of technology and innovation, Tesla has the potential to reshape the automotive industry and contribute to a more sustainable future.