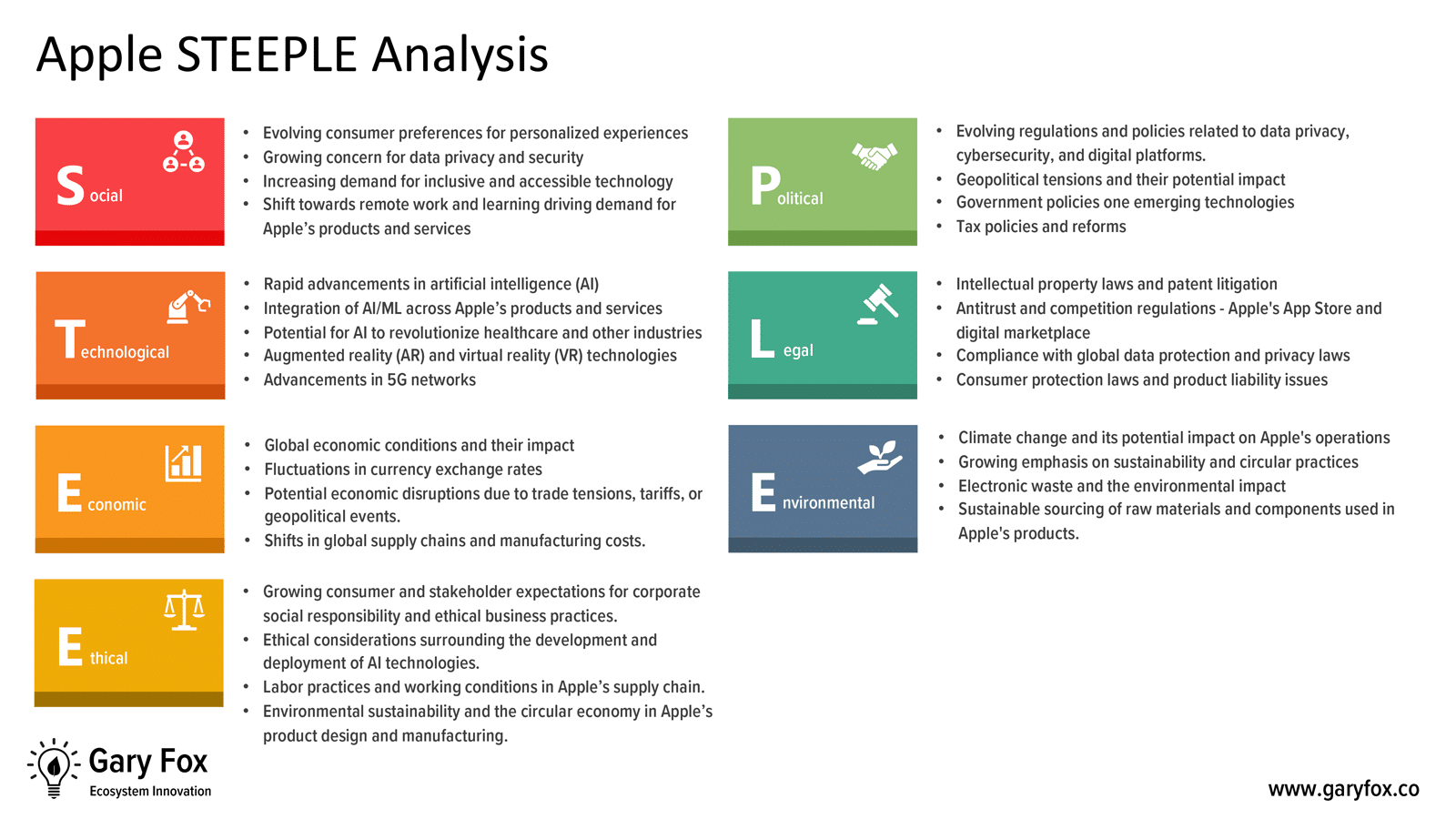
The Apple PESTLE analysis demonstrates that there are some significant trends and challenges for Apple to navigate.
Apple faces complex issues such as US-China trade tensions and increasing scrutiny over its App Store practices, which could reshape its business model. Economically, it must adapt to the current rise in inflation (globally) which could affect consumer spending.
Innovations in AI and AR present growth opportunities. Also, sustainability is becoming a more dominant trend which needs attention to address use and reuse of materials and ethical sourcing.
Also, ethical challenges include labour conditions in its supply chain and maintaining strict privacy standards.
Table of Contents
Overview of PESTLE ADN STEEPLE as a framework
When analyzing the external factors that influence a company’s operations and performance, two common frameworks are often used – PESTLE and STEEPLE.
PESTLE is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors, while STEEPLE adds further dimension to the analysis – Ethical factors.
In this article, I examine the external factors shaping Apple’s business environment using an Apple PESTLE analysis.
Using the PESTLE framework, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of Apple’s challenges and opportunities in each of these areas.
However, it is essential to note that an Apple PESTLE analysis does not explicitly address the ethical considerations that are increasingly important in today’s business landscape, which is where the STEEPLE framework can provide additional insights.
The Apple PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
The following political factors shape the overall Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- US-China Trade Relations: Ongoing trade tensions between the US and China have significant implications for Apple, particularly in terms of tariffs and supply chain disruptions, as a large proportion of its manufacturing is based in China. BBC
- Regulatory Pressures in the EU: The European Union’s stringent regulations on digital markets and privacy (e.g., GDPR) challenge Apple to comply with complex legal requirements, potentially increasing operational costs. Reuters
- Antitrust Scrutiny: Apple faces growing antitrust scrutiny in the US and Europe over its App Store practices, which may result in significant changes to its business model or fines. The Guardian
- Government Influence on Supply Chain: The US government’s initiatives to bring more technology manufacturing back to the US could affect Apple’s supply chain strategy, forcing it to consider domestic manufacturing options. The Washington Post
- Geopolitical Risks: The global geopolitical landscape, including tensions between Taiwan and China, could disrupt Apple’s supply chain, particularly in semiconductors, which are critical to its products. Financial Times
Economic Factors
The following economic factors affect the overall Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Global Economic Slowdown: The potential for a global economic slowdown, exacerbated by high inflation and rising interest rates, could reduce consumer spending power, impacting sales of high-end products like iPhones. Bloomberg
- Currency Fluctuations: As a multinational company, Apple is exposed to currency fluctuations that can affect its revenue when converting foreign profits back into US dollars. This is particularly significant in volatile markets like Latin America. CNBC
- Supply Chain Costs: Rising labour and material costs, particularly in Asia, could squeeze Apple’s profit margins if not managed effectively. This is compounded by potential shifts in global supply chains. The Economist
- Consumer Spending Trends: Trends in consumer spending, particularly in premium segments, are crucial for Apple. A shift towards more budget-conscious spending could impact the demand for Apple’s premium products. Forbes
- Impact of Inflation: Persistent global inflation can erode consumer purchasing power, potentially leading to reduced demand for non-essential luxury items like those offered by Apple. Reuters
Social Factors
The following social factors and treends are important to the overall Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Changing Consumer Preferences: There is a growing consumer preference for sustainable and ethically produced products. Apple has made efforts to align with this trend, but ongoing scrutiny of its supply chain practices, particularly around labour conditions, could impact its brand image. The Guardian
- Health and Wellness Trends: The increasing consumer focus on health and wellness presents an opportunity for Apple, as seen with the Apple Watch and its health-monitoring features. These products tap into the growing market for health-related technology. Harvard Business Review
- Brand Loyalty: Apple benefits from strong brand loyalty, but this also sets high expectations. Any missteps in product quality, customer service, or ethical practices could lead to a significant backlash from its dedicated consumer base. Fortune
- Youth Market Engagement: Engaging with younger demographics is critical for Apple’s long-term success. The company must continue to innovate in ways that resonate with younger consumers who value technology that is not just functional but also expressive of their identities. Business Insider
- Shift to Remote Work: The shift towards remote work and learning has increased demand for Apple’s products, particularly MacBooks and iPads. However, this demand could stabilise as the world adjusts to hybrid working models. The Verge
Technological Factors
The following technological factors shape the overall Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Innovation in AI and AR: Apple is heavily investing in artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR), which are expected to be significant growth areas. These technologies could define the next generation of consumer electronics and create new revenue streams. Wired
- 5G Adoption: The widespread adoption of 5G technology offers Apple an opportunity to capitalise on faster mobile internet speeds with its iPhone models, potentially boosting sales as consumers upgrade their devices. TechCrunch
- Cybersecurity Threats: As Apple continues to expand its ecosystem, particularly in services like iCloud and Apple Pay, it must remain vigilant against cybersecurity threats that could damage its reputation and consumer trust. The Guardian
- Supply Chain Technology: Apple’s investment in advanced supply chain technologies, such as robotics and automation, helps mitigate risks associated with manual processes and improves efficiency in its production lines. Financial Times
- Environmental Technology: Apple’s commitment to environmental sustainability is evident in its use of recycled materials and energy-efficient technologies, aligning with global trends towards greener technology solutions. Bloomberg
Legal Factors
TThese legal factors are most pressing in determinng the Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Intellectual Property Rights: Apple’s success relies heavily on its intellectual property (IP) portfolio, and it must continuously protect its patents and trademarks from infringement by competitors and counterfeiters. Forbes
- App Store Litigation: Apple faces several legal challenges related to its App Store policies, particularly regarding anti-competitive practices. These legal battles could force Apple to alter its App Store business model. The Verge
- Privacy Laws Compliance: With increasing global emphasis on data privacy, Apple must ensure compliance with varying privacy regulations, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, which can affect its data handling practices. TechCrunch
- Employee Rights and Labour Laws: Apple’s global workforce and supply chain partners are subject to different labour laws across regions. Compliance with these laws is critical to avoid legal sanctions and maintain its reputation. The Guardian
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with environmental regulations, such as those concerning electronic waste disposal and carbon emissions, is increasingly important for Apple as it positions itself as a leader in sustainability. Bloomberg
Environmental Factors
The environmental factors are becoming a more critical part of the Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Climate Change Impact: Apple’s operations and supply chain are increasingly impacted by climate change, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather events, which could disrupt production and logistics. The Guardian
- Sustainability Initiatives: Apple has committed to achieving carbon neutrality across its entire business by 2030, including its supply chain and product life cycle. This commitment aligns with global environmental concerns and enhances its brand reputation. Apple
- Electronic Waste Management: The growing concern over electronic waste (e-waste) places pressure on Apple to enhance its recycling programmes and develop products that are easier to repair and recycle. BBC
- Energy Consumption: Apple’s focus on reducing energy consumption in its products and operations is crucial for meeting global environmental standards. The company has made significant strides by powering all its facilities worldwide with renewable energy, but it continues to face challenges in ensuring its entire supply chain follows suit. Apple
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Apple’s global supply chain must adhere to increasing environmental regulations, including those related to carbon emissions and sustainable sourcing of materials. This requires significant investment and collaboration with suppliers to meet these stringent standards. The Guardian
Ethical Factors
These ethical factors are an important part of overall Apple PESTLE analysis as follows:
- Labour Practices and Working Conditions: Apple has faced criticism over the years regarding labour practices in its supply chain, particularly in factories in China. Issues such as poor working conditions, excessive working hours, and low wages have been highlighted, and Apple must continue to ensure its suppliers adhere to ethical labour standards to maintain its reputation. BBC
- Environmental Responsibility: Apple’s commitment to environmental sustainability is not just a business strategy but also an ethical responsibility. The company’s initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint, use recycled materials, and ensure responsible sourcing are crucial for maintaining its ethical stance. However, it faces the challenge of ensuring these practices are consistent across its global operations. Bloomberg
- Product Transparency and Consumer Privacy: Apple has positioned itself as a champion of consumer privacy, often highlighting its commitment to safeguarding user data. This ethical stance on privacy differentiates it from competitors, but the company must continually navigate complex global privacy laws and maintain its commitment in the face of potential pressures to compromise on these principles. The Guardian
- Corporate Governance and Ethical Leadership: Apple’s leadership is under constant scrutiny to act ethically, particularly in how it handles issues such as executive compensation, corporate tax strategies, and shareholder relations. Ensuring transparent and ethical corporate governance practices is vital for maintaining stakeholder trust and long-term success. Harvard Business Review
- Human Rights Advocacy: Apple’s global presence means it must be mindful of human rights issues wherever it operates. This includes ensuring that its products are not linked to human rights abuses, such as those related to conflict minerals or forced labour, and that it actively promotes human rights within its supply chain and corporate practices. Amnesty International
Summary of the Apple PESTLE Analysis
The image below is a summary of the overall Apple PESTLE analysis
More resources: Apple Business Model, Apple SWOT Analysis, Who Owns Apple