The Microsoft business model has created one of the most powerful companies in the world.
In this article, you’ll discover how the Microsoft business model has changed, evolved and what the future of this tech giant looks like.
Did you know Microsoft is worth over $1400 billion dollars!
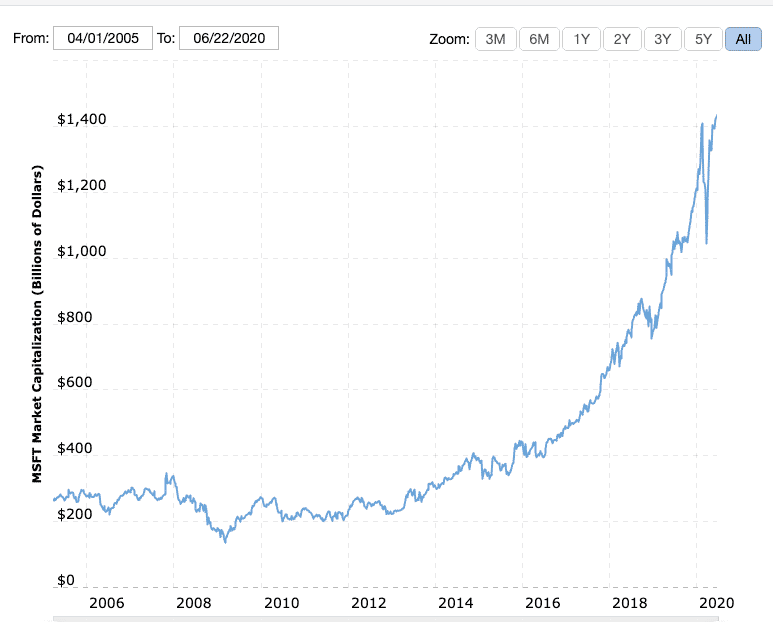
You can see from the market capitalization chart that there have been ups and downs in how investors viewed the future potential of Microsoft.
However, Microsoft went through some remarkable changes and has regained its position as a leading technology company.
We’ll explore how the Microsoft business model fundamentally changed as we go through the article.
What is Microsoft?
The First Few Years To Success
In 1975, a youthful 20-year-old Bill Gates and his friend Paul Allen formed Microsoft, the company that we all know today.
Back in those early days, computing was in its infancy and the internet was just a small and largely unknown network mostly used by academic institutions (very limited).
Bill Gates and Paul Allen spotted an opportunity to produce basic operation system (interpreter to be exact) for the Altair 8800.

By the early 1980’s MS-DOS, a simple operating system became the go-to operating system for computers. But it was Windows that was the breakthrough, a visual interface that quickly captured the market.
In 1986, Microsoft was launched on the stock market creating billionaires and multiple millionaires.
After that, Microsoft had the money and resources to build its empire and consolidate its position as the main operating system used in PC’s.
However, other entrepreneurs like Steve Jobs also spotted the opportunities associated with personal computing. He stepped into the market, created Apple Mac’s and the Apple business model we all know today.
Who owns Microsoft?
Bill Gate still owns shares in the company, but he has sold or given away the majority of his shres over the years since the company was floated.
In 2014 he sold 4.6 million of them – that left him with 330 million shares, three million fewer than Ballmer.
In 2017, Bill Gates gave away 64 million Microsoft shares in his largest donation since 2000.
Despite this, Bill Gates is still worth is more than $93 billion (as of December 2018). To out that into perspective, if Bill Gates gave everybody in the world $10, he would be left with more than $20 billion.
Although, a long-standing board member, Bill Gates stepped down from the board in early 2020 to devote more time to his ambitious philanthropy projects.
If you want to find more interesting facts and to explore the key milestones in Microsofts histroy take a look at their storyline at Microsoft.
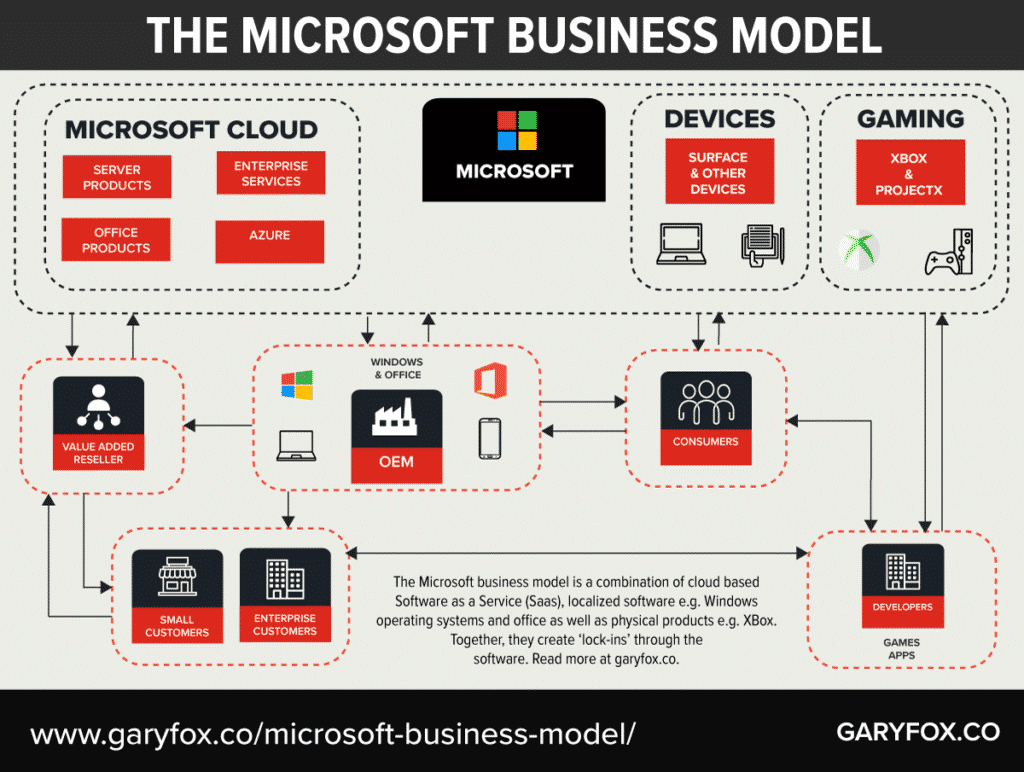
What Is The Microsoft Business Model?
Microsoft provides operating systems and software to businesses and consumers which help people to use easily devices and apps for work and entertainment.
I worked with Microsoft on the launch of the Xbox and developing their retail presence. During that time I learned a lot about Microsoft’s business strategy, long-term focus and the great culture that has propelled Microsoft successfully through its different stages.
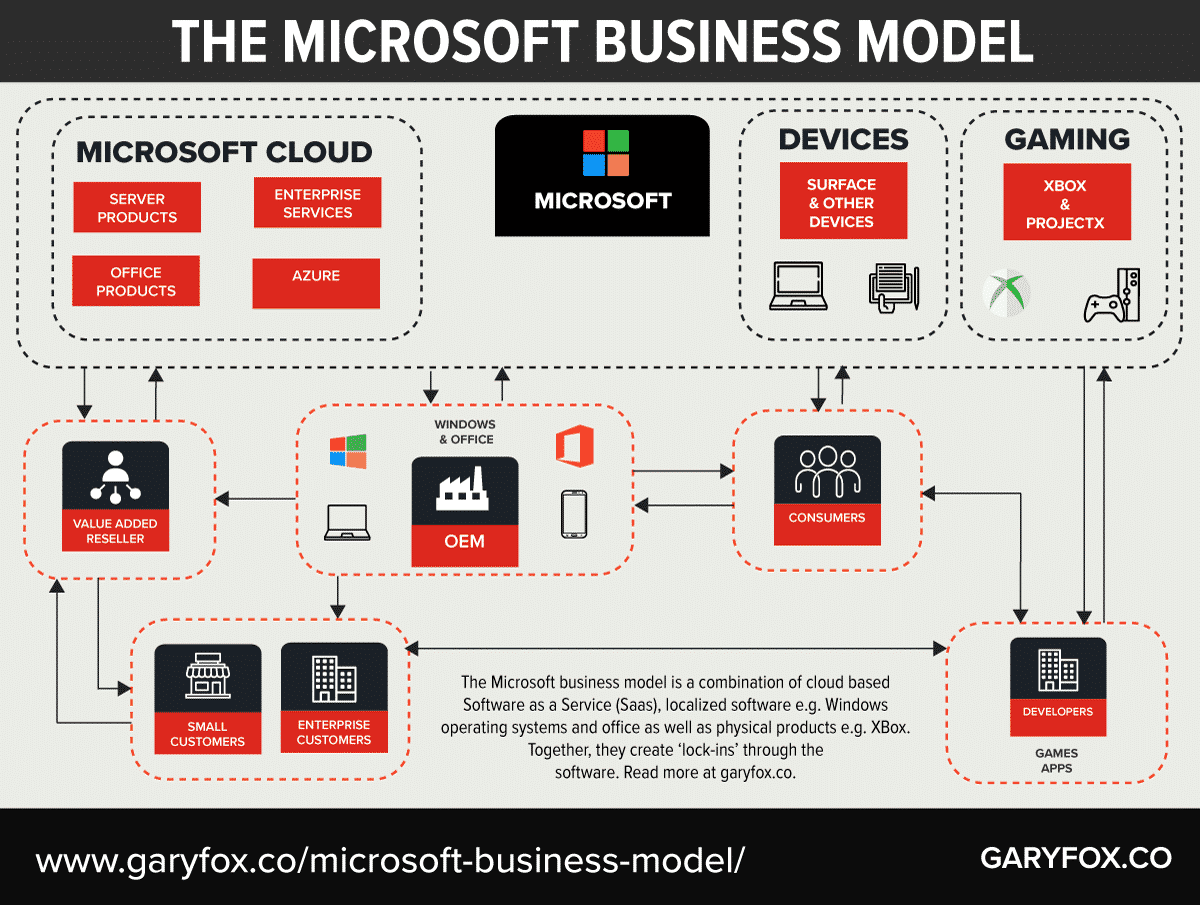
The core business involves the sale, distribution and support of software solutions. Although Microsoft sells hardware this is a relatively small part of the business.
The business model patterns used in the Microsoft business model are:
- Solution Provider: Microsoft provides a full range of solutions for a business to operate e.g. ERP, CRM as well as development platforms for bespoke and customized requirements.
- Razor and Blade: apps and other software won’t work unless specifically developed for the different operating systems. Another example is the Xbox games only working on the Xbox.
- Lock-in: Customers get lock-in to using Microsoft software because of large switching costs.
- Freemium: Linkedin is free to use as a business social network. However, to get the full value from the platform e.g. Linkedin Learning you need to be a premium member.
- Subscription model: Linkedin premium membership is a subscription model. Moreover, Office 365 and most of the cloud services provided by Microsoft are in fact, subscription models.
- Hidden Revenue Model: Bing is the search engine that you can use from Microsoft. While it is free advertisers are using the platform to push ads to you based on the keywords you use. A further example is Linkedin, although there is a free version of Linkedin, both free and premium users are shown Ads in their newsfeed. These ads are a significant source of revenue for Linkedin.
- Layer Player: Microsoft provides the core operating system as well as applications that then work with it such as Microsoft Office. Although Microsoft does sell some hardware, e.g. Surface laptops, it is a limited range compared to its software.
- Ingredient Branding: Microsoft branding is built into the use of laptops and PC’s. Although an ingredient, e.g. you buy the PC, Microsoft has already ensured that its brand is prominently shown.
The Evolution Of The Microsoft business model
Operating systems like Mac OS and Windows are unique and apps that work with one operating system will not work the other. That creates a form of lock-in effect making it hard for customers to switch.
This form of lock-in works for developers and customers. Both have to invest time and effort into getting used to the operating system and understand how it works.
A developer does this so he can make money from selling apps that work with Microsoft operating systems. Users need to be able to get work done and use it in their day-to-day life.
Switching costs are a form of competitive advantage because they create barriers to change for customers – in other words, people do not want to invest time to learn something new.
However, the Apple business model lowered the switching costs by making its operating systems easy to use through attention to design.
Despite heavy competition, Microsoft has evolved beyond operating systems and has made some critical changes over its time, not to mention a staggering amount of strategic acquisitions.
Next, I’ll break down how the Microsoft business model and reveal some of the underlying business model principles used.
What is Microsoft’s business strategy?

The Ambitions That Drive Microsoft
To achieve our vision, our research and development efforts focus on three interconnected ambitions:
- Reinvent productivity and business processes.
- Build the intelligent cloud and intelligent edge platform.
- Create more personal computing.
Microsoft produces software solutions for businesses and consumers.
Microsoft’s strategy is heavily focused on integrating platforms and apps and using Artificial Intelligence to drive the next evolution of computing, productivity and business innovation.
The AI capabilities are also echoed in ‘Create more personal computing‘. AI will drive new ways to personalize experiences in real-time as the interface with customers becomes more liquid enabling personalized content and customer journeys.
From distributing software on CD’s, customers now simply download the software or in the case of many enterprise software use it as a SaaS platform.
Customers have moved from buying the software as a single cost transaction to now now ‘renting’ the software through subscription business model.
This shift in the revenue model has resulted in a significant jump in profits (see below) as Microsoft now shifting towards a global platform business.
The Move To Cloud Services
What Is Azure?
Azure is a cloud computing platform that provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Azure offers services such as computing, storage, networking, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
What Is ProjectX?
Microsoft is producing a global platform for gaming that will allow gamers to play a multitude of games on any device, anywhere. Xbox games will also be hosted and delivered to Xbox gamers via Project xCloud. This move gives Microsoft a greater depth and breadth of opportunities to interact and engage with gamers.
The Microsoft Business Model Canvas
You could produce a business model canvas for each of the market offers. To make it simple I’ve just focused on the core business.
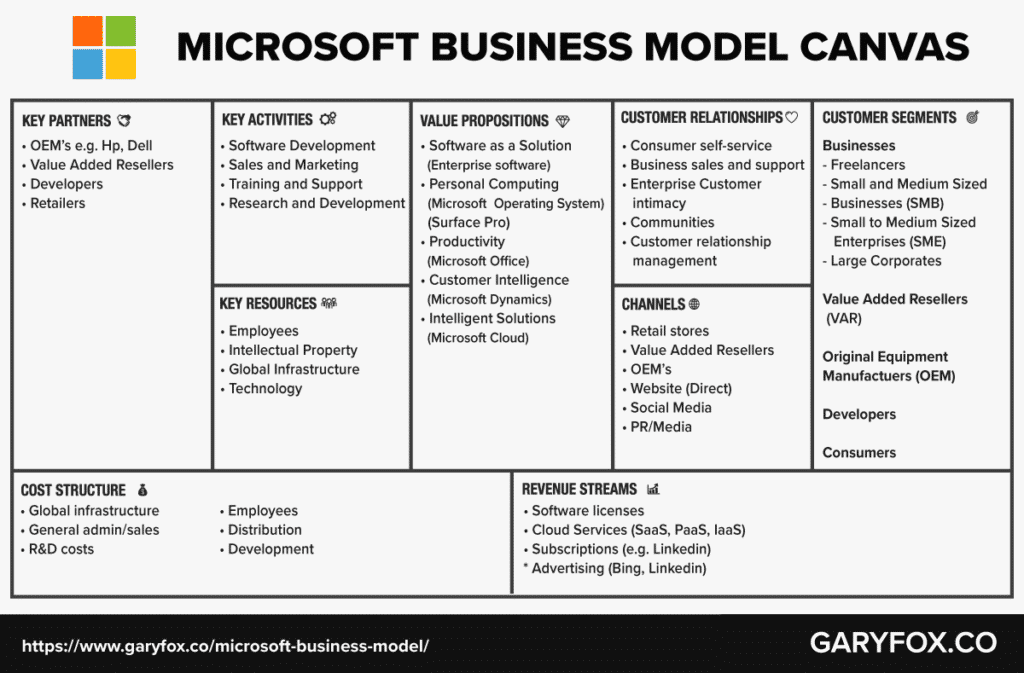
What are Microsoft Customer Segments?
The core customer segments of the Microsoft Business Model are:
- Businesses: Microsoft caters to many different types and sizes of companies, but it is the SME and large corporate market where a large number of its solutions are focused. Smaller businesses are managed through Value Added Resellers, who themselves are a key segment.
- Corporates: These are the companies that have account managers and support teams.
- SMB’s and SME’s: Small to medium-sized businesses will usually deal with VAR’s for support and services.
- Value-Added Resellers: VAR’s distribute and support SMB’s and SME’s in the use of Microsoft products. Many VAR’s have teams of highly trained IT professionals who advise and work with companies. Microsoft supports VAR’s with training and accreditation schemes to ensure that they are able to keep up to date with the latest software releases and technical know-how.
- Original Equipment Manufacturers: OEM’s produce the hardware and install Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Office on the PC/Laptop. Hp, Samsung and Dell are examples of some of the larger OEM clients.
- Developers: Microsoft Azure is a platform that provides developers with the capabilities to design and develop applications. Other developers produce apps for operating systems such as Microsoft Windows phones and Xbox games. The increasing focus on developers is one of the reasons that Microsoft purchased GitHub.
- Consumers: Home users of PC’s, laptops and cloud services such as Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Office and Xbox gaming.
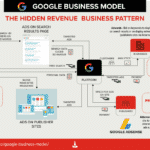
The Bing Advertising Business Model
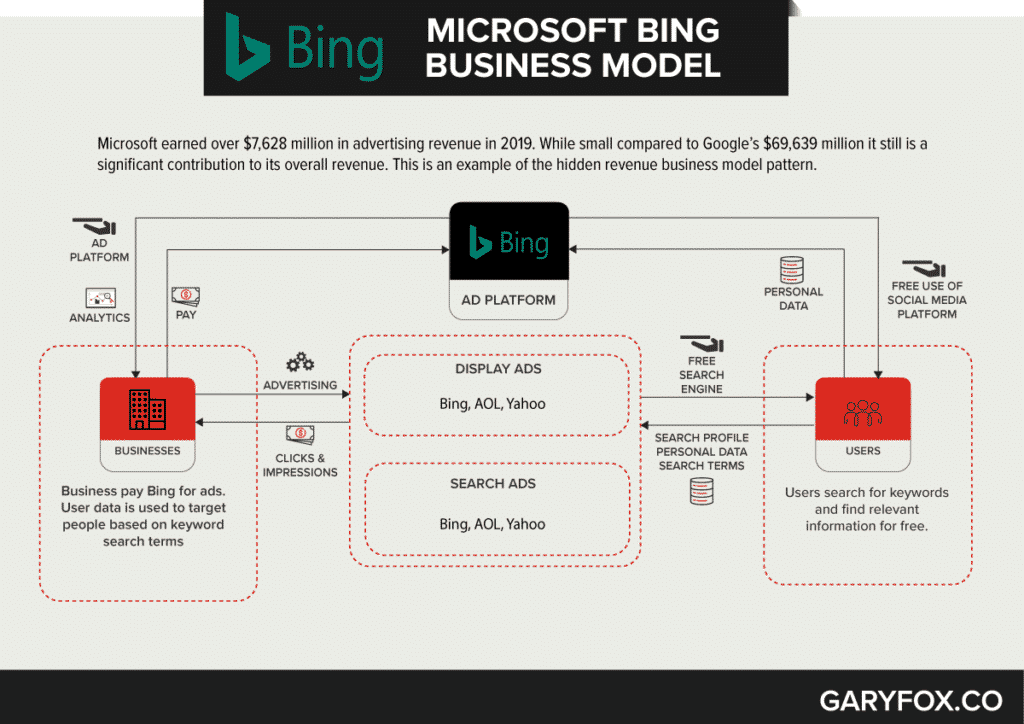
Bing is a web search engine owned and operated by Microsoft. The service has originally was Microsoft’s search engine MSN Search. Bing is the third largest search engine globally, with a query volume of 4.58%.
The Bing business model is based on the hidden revenue model. Users can search on Bing for free while advertisers can use Bing to promote products or services.
The Linkedin Business Model
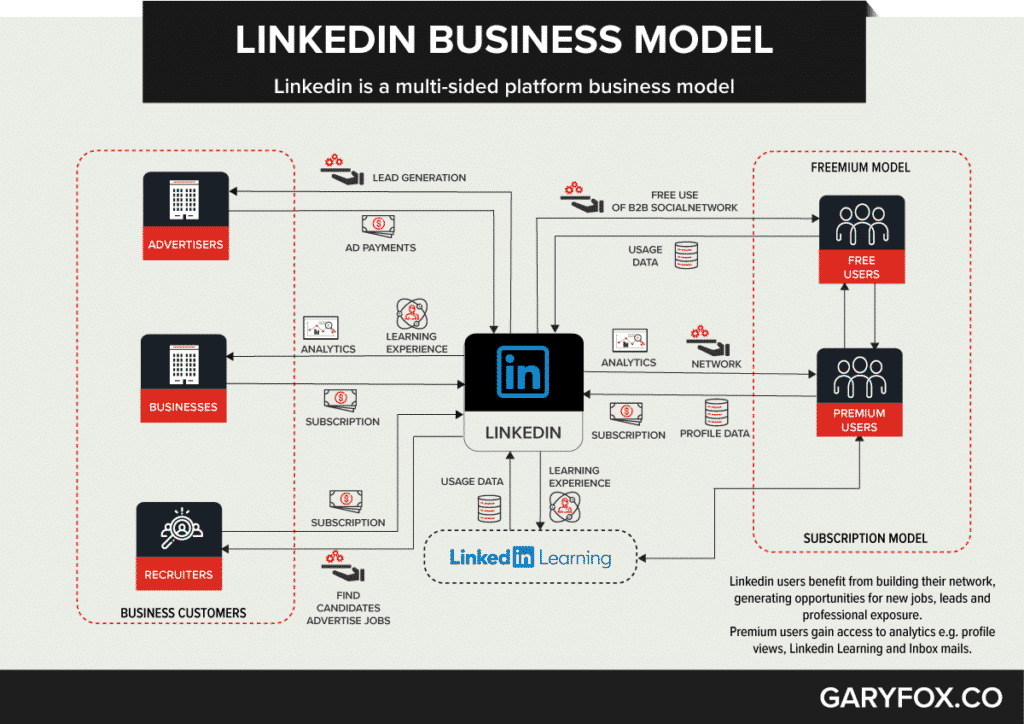
LinkedIn is the number one social network for business professionals with more than 645 million members and growing.
The platform has three main propositions:
- Talent Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Premium Subscriptions
Talent Solutions is comprised of two elements: Hiring, and Learning and Development. Hiring is a service for recruiters to help them attract, recruit, and hire talent. Learning and Development provide subscriptions to enterprises and individuals to access online learning content (Linkedin Learning).
Marketing Solutions enables companies to advertise to LinkedIn’s member base.
Premium Subscriptions enables professionals to manage their professional identity, grow their network, and connect with talent through additional services like premium search. Premium Subscriptions also includes Sales Solutions, which helps sales professionals find, qualify, and create sales opportunities and accelerate social selling capabilities.
How Does Microsoft Make Money?
Microsoft employs a number of different revenue models through its operations. In this section, I’ll show you where the Microsoft business model makes money and how it generates its profits.
How is Microsoft growing?
Microsoft is expanding and growing its cloud offers. The revenue for cloud services, which includes Office 365 Commercial, Azure, the commercial portion of LinkedIn, Dynamics 365, and other commercial cloud properties, was $38.1 billion in 2019.
Key growth areas in FY 2019 as reported by Microsoft:
- Productivity and Business Processes
- Revenue increased $6.0 billion or 20%.
- Office Commercial revenue increased $2.4 billion or 11%.
- Office Consumer revenue increased $382 million or 11%.
- Dynamics revenue increased by 13%.
- Intelligent Cloud
- Revenue increased $6.8 billion or 21%.
- Server products and cloud services revenue, including GitHub, increased $6.5 billion or 25%.
- More Personal Computing
- Revenue increased $3.4 billion or 8%.
- Windows revenue increased $877 million or 4%.
- Surface revenue increased $1.1 billion or 23%.
- Gaming revenue increased $1.0 billion or 10%, driven by Xbox software and services.
- Search advertising revenue increased by $616 million or 9%.
How much money does Bing make?
Search advertising revenue, excluding traffic acquisition costs, increased by 13%. In 2019, Bing accounted for $7.63 billion.
How much money does Linkedin make?
In 2019, Linkedin revenue was $5.3 billion, up from LinkedIn revenue increased $3.0 billion the previous year.
How much revenue does Microsoft make a year?
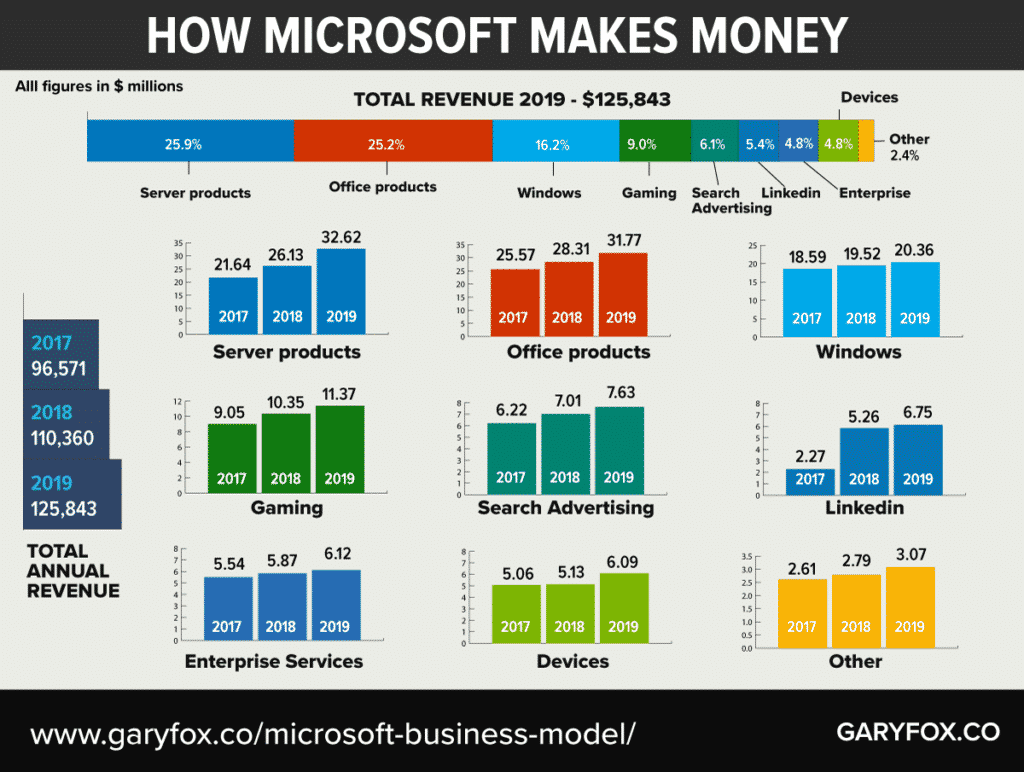
Microsoft business model relies heavily on the core revenues from operating systems, servers products and Microsoft Office.
How Profitable Is Microsoft?
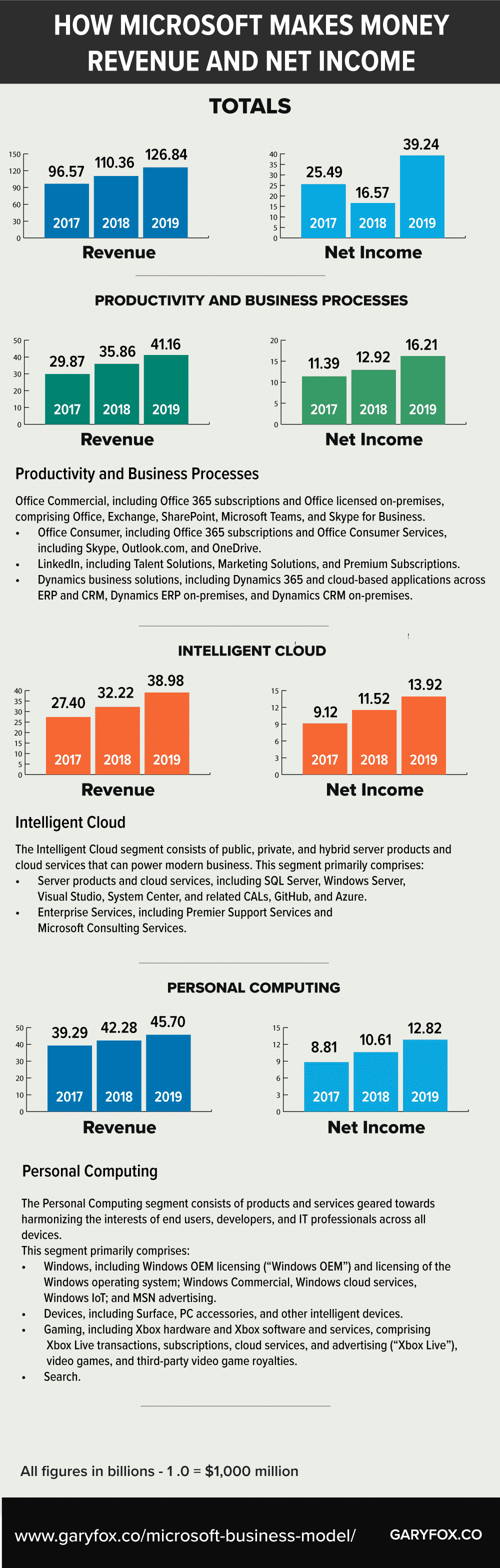
Microsoft’s profits are increasingly being driven by its cloud services which offer a scalable set of resources with a high level of efficiencies.
240 Acquisitions Later!
To understand more about the future of Microsoft and its plans, it is worth looking at its recent acquisitions. I’ll explore this shortly in the next post on Microsoft.
Microsoft bought Linkedin on December 8 2016, for $26.2-billion – Linkedin Business Model for more details.
Microsoft bought GitHub on June 4, 2018, for $7.5 billion in stock.