Table of Contents
What is customer segmentation?
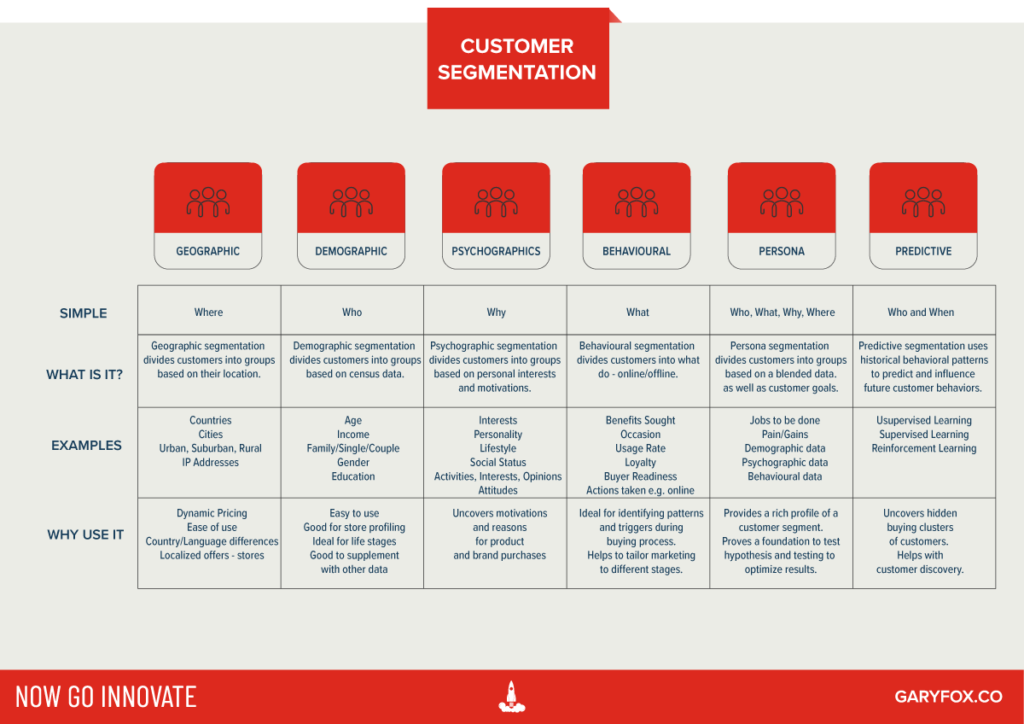
Segmentation is the process of dividing your customers up into different groups, with each group sharing similar characteristics, to improve engagement, sales and loyalty.
However, often finding the best way to segment customers can be far from easy. I’ll cover different insights into how to segment your customers so you can accelerate your growth.
Let’s start by putting into context the importance of data to businesses. In 2018, U.S. companies spent about $19 billion dollars on buying third-party data, and about the same amount on third-party solutions to support that data. Despite this, the majority of the data these information brokers have on consumers isn’t even correct. As an example, it is often out of date.
Why are businesses spending so much money on data and what’s the benefit of segmentation?
Well, Braze (previously Appboy) analyzed their marketing data from over 30,000 campaigns they ran over two years. They found that campaigns that had been sent to well-thought-out customer segments saw 200% greater conversions than those sent to broad audiences.
In other words, there is a clear link between conducting segmentation and then improving sales and profits.
How much do you spend on marketing? Most companies spend about 11-13% of your business’ overall revenue. But according to a report by Rakuten Marketing, marketers expect to waste 26% of their marketing budget on the wrong channels or strategies – this is usually because of poor segmentation.
The upshot is that despite the opportunity to improve sales and profits through segmentation, many marketers are not doing it right and are wasting money.
Meanwhile, customers want and expect personalization:
- 91% of consumers are more likely to shop with brands who provide relevant offers and recommendations.
- 80% of customers are more likely to purchase a product or service from a brand who provides personalized experiences.
- 72% of consumers in 2019 only engage with marketing messages that are customized to their specific interests.
- 80% of those who classify themselves as frequent shoppers say they only shop with brands who personalize their experience
- 63 per cent of consumers, expect personalization as a standard of service.
- 88 percent of surveyed consumers reported not receiving “tailored help.”
— and segmentation is the quickest, simplest (and often most cost-effective) way to cater to that expectation.
You might think that advanced customer segmentation techniques are only for big brands or large corporates. However, that is not the case. In this guide, I’ll help you to discover powerful ways to improve conversions, sales and customer loyalty.
What Are The Benefits of Customer Segmentation?
Why is customer segmentation important? A key focus in marketing is to build relationships with profitable customers. Marketing is not just about a single purchase, a single conversion – the goal is to grow your customer base and to build long term value.
Understanding customers, segmenting them and personalizing marketing campaigns, offers and communications is part of what is broadly known as Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
CRM tools and methods provide the backbone of how you develop a customer segmentation strategy and then implement it.
According to Harvard Business Review, over 30,000 new consumer products are launched each year.
And 95% of them fail for one of these seven reasons:
- Failure to understand consumer needs and wants.
- Fixing a non-existent problem.
- Targeting the wrong market.
- Incorrect pricing.
- Weak team and internal capabilities.
- Prolonged development or delayed market entry.
- Poor execution.
Customer Segmentation Benefits
- helps to detect and exploit new market opportunities.
- improves how to predict customer behaviour.
- Increased customer retention and loyalty.
- improves the perception of a brand through personalization.
- streamlines and improves workflow.
- helps to improve customer lifetime value.
- Email marketers have witnessed a 760% increase in revenue by segmenting their email campaigns.
Consider these statistics:
- 71% of consumers believe personalized experiences would influence their decision to interact with emails.
- 80% of respondents indicating they are more likely to do business with a company if it offers personalized experiences.
- 88% of U.S. marketers reported seeing measurable improvements due to personalization, with more than half reporting a boost greater than 10%.
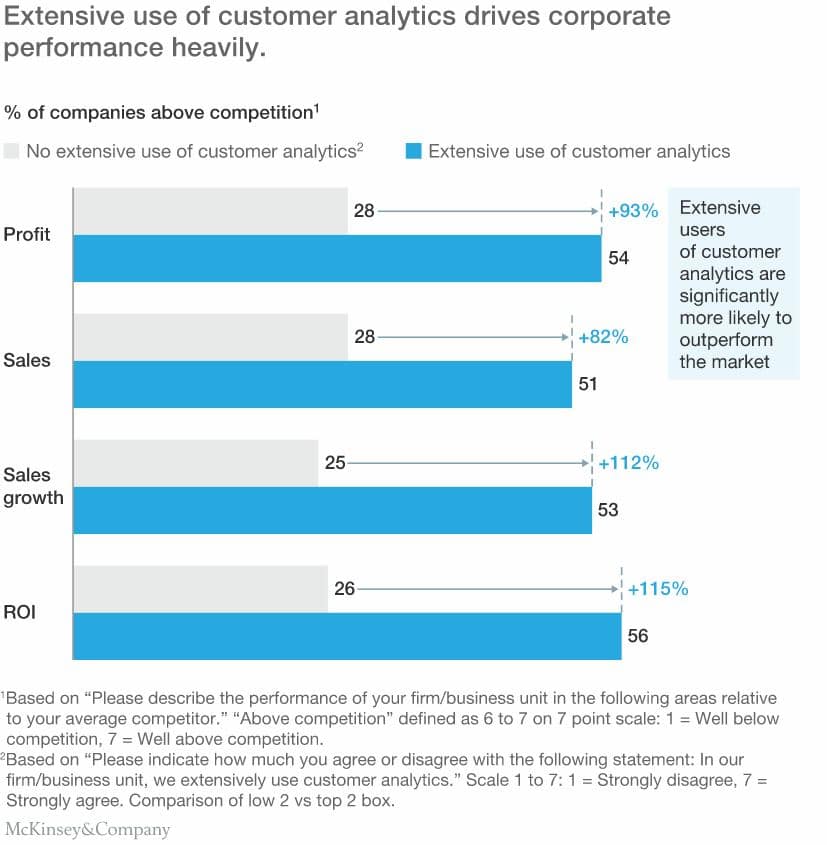
- A recent McKinsey survey found that companies that extensively use customer analytics are reporting 115% higher ROI and 93% higher profits.
What Are The Problems With Customer Segmentation
7 Common Segmentation Mistakes
- Segments aren’t in-line with your business’ goals.
- You’re segmenting based on instincts, not concrete data.
- You’ve created segments based on limited data.
- You’re using ‘dirty data’.
- You’re ignoring channels while developing segments.
- You’re not considering the time of engagement and context.
- You’re not tracking segment performance over time.
6 Customer Segmentation Methods
There are lots of ways to segment customers but choosing the best method will depend on the type of business and the market/industry. For instance, B2B segmentation often demands a very different approach to B2C marketing.
A start point for any segmentation method though is data. Making decisions based on customer data is the foundation for any marketing activity and how you effectively develop segmentations that deliver growth.
1. Geographic Segmentation
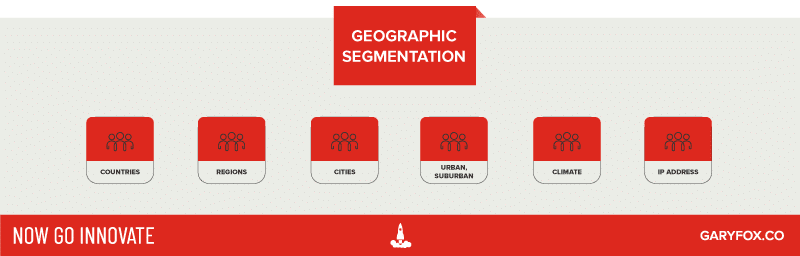
What is Geographic Segmentation?
Geographic segmentation divides customers into groups based on their geography. The most common way of doing this is to use existing boundaries such as Countries, Regions, States and Cities.
More micro-level ways of dividing a market are based on the type of living areas such as rural, suburban, and urban market segments.
Examples of geographic segmentation
- The tourism and travel industry uses geographic segmentation including more nuanced factors like climate.
- IP addresses are used to help online businesses, direct people, to their local sites with localized languages, products and pricing.
- Car manufacturers use climate as a segmentation factor for open-top cars.
Advantages of Using Geographic Segmentation
So what are the advantages of geographic segmentation? Let’s look at some.
- It’s an effective approach for companies with large national or international markets – because different consumers in different regions have different needs, wants, and cultural characteristics that can be specifically targeted.
- It can also be an effective approach for small businesses with limited budgets. They can focus on their defined area and not expend needless marketing dollars on approaches ill-suited for their target geographic segment.
- It works well in different areas of population density. Customers in an urban environment often have different needs, buying patterns and income compared to people in suburban and rural environments. Often, there are also cultural differences between these three areas.
Disadvantages of Geographic Segmentation
- the danger of mixing very heterogeneous tourists from the same country of origin and artificially treating them as one segment e.g. Italians are not all the same.
- sometimes geographic data is used but there is little or no difference in the buying patterns or behaviours which makes targeting obsolete.
2. Demographic Segmentation
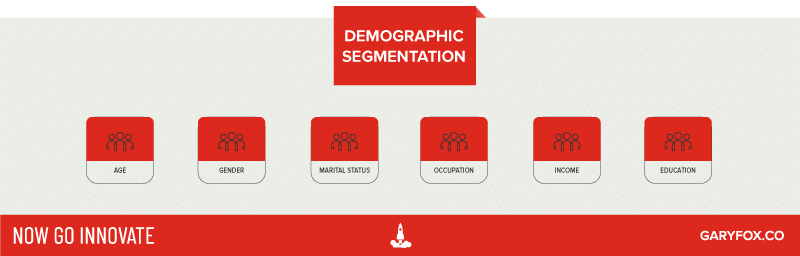
What is Demographic Segmentation?
Demographic data is one of the most commonly used because it’s easy to get through census data, it’s generally updated every 10 years, data analytics such as Google Analytics, consumers through questions and forms such as SurveyMonkey, and through other data sources such as Facebook Insights. Another reason is that also considered to be the cheapest and easiest way to divide a target market.
However, demographic data on its own provides few if any insights into customers. It answers the Who are my customers but not the Why questions – e.g. why customers buy…
Examples of Demographic Segmentation
- Age.
- Gender.
- Race.
- Marital status.
- Number of children (if any)
- Occupation.
- Annual income.
- Education level.
Advantages of Using Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic data is typically easier to collect and measure versus those of other segmentation techniques.
- Targeting is typically more straightforward when using demographics as a metric, e.g. you can target a consumer group such as men between the ages of 35 and 45.
- Demographic data, when blended with other data sets, provides an easy way to analyse differences amongst customers.
- Ideal for monitoring trends and social shifts.
Disadvantages of Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic data changes quickly; age changes every year (of course), people’s’ incomes, their marital status, education level, occupation, the list goes on.
- Descriptive only – little understanding of the consumer themselves.
- Assumes that consumers in the same demographic group have similar needs and lifestyle – which is unlikely, all 30 year olds are unlikely that have the same needs, for example.
- When collecting data people often lie about their age or other elements of data e.g. income.
- For some products and services demographic is of little use. Take Spotify for example, music is such a subjective topic Spotify tracks behaviour and listening preferences rather than demographics. For Spotify, demographic data is too vague to create any meaningful marketing content or communications that are effective.
Grocery stores typically use demographic data to target their customers. They know that families buy more goods per annum than single people or couples.
3. Psychographic Segmentation
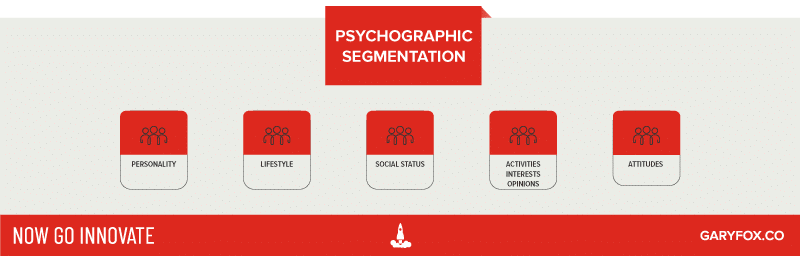
Psychographic segmentation is the use of people’s attitudes and interests, often studied in conjunction with typical demographic data, to build and target customers.
Unlike demographics, transactional, or behavioural data, psychographics gives us an idea of Why a certain customer chose to buy a product.
Together with this market research, you could use methods like Facebook Pixel to keep track of everything your customers like, view, or share online.
Examples of Psychographic Segmentation
- Interests
- Personality
- Lifestyle
- Social Status
- Activities, Interests, Opinions (AIO)
- Attitudes
Tools like Brandwatch help you collect details about your audience and then use it to divide your market based on attitudes, interests, activities, and personality traits.
Advantages of Psychographic Segmentation
- Provides insight into customers lifestyles and their needs.
- Helpful for uncovering motivations and reasons for product and brand purchases.
- Often better helpful for developing promotional campaigns.
Disadvantages of Psychographic Segmentation
- Requires market research – usually a mix of qualitative and quantitative – which can be expensive.
- As a result of the research cost, probably more suitable for larger firms/brands.
- Sometimes qualitative market research is still open to different interpretations of the findings.
- Psychographic segments may not be as easy to reach via promotional methods or to identify in-store.
4. Behavioural Segmentation
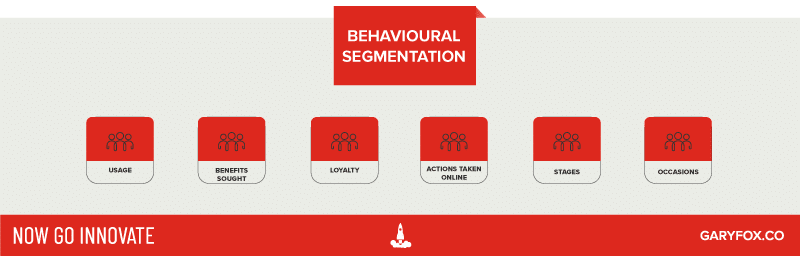
Behavioural segmentation is based on What your customers do and therefore likely to do again. Behavioural segmentation principally focuses on the buying process of customers, and then groups customers with similar buying behaviours together into one ‘segment’. Businesses can then target companies, customers, and potential customers based on their buying behaviours.
Trying to identify a consumer’s buyer journey stage based on just one or two of their behaviours can easily lead to a wrong assumption.
Customers in various stages still interact and engage with content in other stages, across a variety of channels, at all different times, and in no particular order. Therefore, single customer behaviour or interaction is not enough to pinpoint which journey stage they exist.
To improve accuracy, you must leverage all of their behavioural data across various touchpoints and channels so that you can build weighted algorithms based on patterns of behaviour over time.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 25% of marketing departments will have a dedicated behavioural scientist or ethnographer as part of their full-time staff. Understanding human biases are, therefore, key to understanding behaviour.
Examples of Behavioural Data
- Online shopping habits: You might consider a users’ online shopping habits across all sites, as this may correlate with the likelihood they will make an online purchase on your website.
- Timing-based behaviour: Consider segmenting customers based on when they purchase — occasion segmentation, the time of year, seasonally, one-off purchases, quarterly patterns etc.
- Actions taken on a website: You can track actions users take on your online properties to better understand how they interact with them. You might look at how long someone stays on your site, whether they read articles all the way to the end, the types of content they click on and more.
- Benefits sought: This refers to the need a customer is trying to meet by purchasing a product.
- Usage: You can categorize users based on usage rate. Your messaging will be different depending on whether someone is a heavy user, medium user, light user or non-user of your product.
- Loyalty: After using a product for some time, customers often develop brand loyalty. You can categorize customers based on how loyal they are to your brand and tailor your messaging accordingly.
- Product Reviews/Feedback – Seeing how people actually experienced a product, the challenges they had or they things they enjoyed most is a useful insight. You don’t need to limit this to your product; you can see competitors, complements and comparables
Advantages of Behavioural Segmentation
- Helps align marketing and sales teams because both have a focus on the sale.
- Focuses on stages within the buying process and therefore creates more contextual communications.
- Identify customers with similar behaviours and needs.
- Brand loyalty can be further built upon those customers who have shown as an affinity towards a brand. Thus behavioural segmentation helps to improve customer loyalty.
Disadvantages of Behavioural Segmentation
- Customer behaviour changes with time, location, occasion, requirement etc and it can not always be predicted correctly. Behavioural segmentation can only give a framework on personality traits and behaviour.
- Mostly, behavioural segmentation would be done on the basis of qualitative data and not completely quantitative data. Hence, making forecasts, budgets, expenses etc would all depend on certain assumptions.
5. Persona Segmentation
A well-defined persona will help you to build a better marketing plan and help you target your marketing campaigns and offers to the right groups of prospective consumers. Marketing personas put a face to your customer and help you identify their needs and wants.
I’ve put together a persona canvas to help people understand how to develop a marketing persona.
Examples of Persona Segmentation
Marketing personas are extremely powerful customer segmentation method. Particularly, when used with research on customer goals.
Also, research demonstrates that using customer personas improves marketing results.
However, effective personas are not made up. They are part of a bigger data-driven strategy that requires a much deeper understanding of what data to collect, how it relates to your business goals and how to effectively use the data to make decisions.
Advantages of Persona Segmentation
- Gain a deeper understanding of customer goals, needs and jobs to be done.
- Builds a richer profile of knowledge of how and why customers buy.
- Helps teams to have a consistent understanding of customer segments.
- Improves how teams produce creative and innovative solutions.
Disadvantages of Persona Segmentation
- Takes time to produce.
- Requires multiple sets of data in order to create a powerful profile.
6. Predictive Segmentation
What Is Predictive Analytics?
Predictive models are used in lots of business and in everyday life. Examples include politics, fraud detection, and financial modelling. In marketing, it used to predict individual customer behaviour and to group customers into the most actionable and meaningful ways. For example, using predictive analytics, you can predict whether and when a customer may be planning to buy next.
Using predictive analytics you can predict what specific product a customer may buy next and recommend these products to your customers proactively.
Examples of predictive segmentation
- Unsupervised learning: Unsupervised learning finds hidden patterns in data, without explicitly trying to estimate or predict an outcome.
- Supervised learning: Supervised learning is used to estimate an output given an input, by training it with sample inputs and target.
- Reinforcement learning: Supervised learning is used to estimate an output given an input, by training it with sample inputs and target.
Marketers now have access to hundreds of different types of data, such as brand preference, discount preference, time spent on site, browsing behaviour, length of call, purchase history, products viewed… It is just not feasible for a person to go through hundreds of types of data to find the relationships between each variable, but for today’s powerful computers and algorithms it is easy to analyse.
Customer segmentation is moving from a manual process to an AI automated process.
Unsupervised Learning: The difference between clustering and segmentation
Segmentation is the process of manually putting customers into groups based on similarities. Clustering though is different, it is an automated/statistically rigorous process of finding similarities in customers so that they can be grouped.
Clustering is a method to automatically discover segments in your customer base by using already known factors about your customers. Clustering algorithms, such as k-means and apriori algorithms, can analyze hundreds of customer attributes and previous customer interactions to reveal insights into customer behaviours and the forces driving those behaviours.
This is different from customer segmentation in the sense that most segmentation utilizes one or two factors, such as age or income in non-statistical ways to group customers together.
Supervised Learning: Propensity Models
propensity models make true predictions about a customer’s future behaviour by learning from examples from the past. Examples include the likelihood of a customer to buy a product or the likelihood of a prospect to engage with a website.
As an example, propensity models are used to predict how much money a customer would spend throughout their lifetime to generate a predicted lifetime value model. This type of model can be used to predict future prospect or customer behaviour.
Reinforcement Learning and Collaborative Filtering
The common marketing application for collaborative filtering models is recommendations.
Collaborative filtering models can recommend products, content, or just about anything else. These recommendation models were made famous by Amazon with their “customers who liked this product, also liked …” suggestions.
Other Customer Segmentation Methods
- Value segmentation: Some businesses will split up a market based on the “transactional worth” of their customers — how much they’re likely to spend on their products. To determine a customer’s transactional worth, you can look at previous purchase data such as how many purchases they make, how often they make purchases and the value of the items they purchase.
- Firmographic segmentation: Business-to-business (B2B) companies may use firmographic segmentation to divide up the businesses in a market. This is similar to demographic segmentation with individual consumers but instead looks at the characteristics of companies that may become customers. Examples of data to look at include industry, revenue, number of employees and location.
- Generational segmentation: Businesses may segment consumers by generation and group them into categories that include Gen Z, Millenials, Generation X, Baby Boomers and the Silent Generation. These generations are believed to share certain preferences, behaviors, personality traits and beliefs. Of course, not every member of a generation is the same, but generational segmentation can give you some additional insight into your audience.
- Lifestage segmentation: You can also segment your market into groups based on where they are in their lives. Going to college, getting married and having children are examples of key life events to consider. People at different stages of life need different things. For instance, soon-to-be college students may need apartment furniture. New parents will be looking to purchase baby food.
- Seasonal segmentation: Similarly to how people buy different products in different periods of their lives, people also buy different items at different times of the year. Major holidays such as Christmas and Hanukkah also significantly impact purchasing behaviors.
How To Do Customer Segmentation for Beginners
Step 1: Select the right measurements
To give you a basic idea of how to start with customer segmentation here is a four-step guide.
Step 2: Select the right tools .For Customer Segmentation
Google Analytics
- Google Analytics allows you to create detailed customer segments. You can find plenty of demographic statistics under the audience tab, as well as some information about the (other) interests of your visitors. Click “add segment” to add any segment you’d like and keep track of…
- Google Analytics allows you to analyze your traffic and website flow. The tabs behaviour and acquisition are a great place to find out exactly where, when, and how long your visitors are spending time on your website. You can spend some time playing around with it to see what is attracting your audience and keeping them interested – and identify the areas that could improve.
- Google Analytics allows you to set specific goals and test solutions. Once you have a basic idea of the parts of your website that need improvement, you can head over to the conversion tab and create new goals for yourself. There are four categories: destination (visits to a single page), duration (time spent on page), pages/screens per session (click-through rate), and events (specific actions on a page). For a best practice, try matching micro-conversion goals to macro conversion goals.
- If you’re looking to invest in more in-depth analysis, you might try out some alternatives like Mixpanel, Kissmetrics, or Amplitude.
Facebook Insights
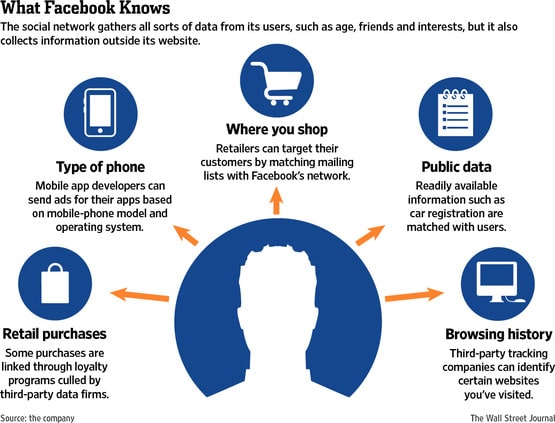
Facebook audience insights give you lots of useful demographic and psychographic data. Furthermore, if you use the Facebook pixel on your website you can track behavioural data as well. Here are some of the types of Facebook data you can use for your customer segmentation:
- Demographics.
- Geographics.
- Gender.
- Time user is active.
- Device.
- Interests.
Step 3: Derive insights from your data
This brings me to my next point and perhaps the most important one of all. While psychographics has received its fair share of buzz, there’s still one part that most people working with psychographics tend to overlook:
Make your insights actionable by linking back to psychological theory. Take a deep dive into your dataset.
- Do you recognize any behavioural patterns?
- Can you connect them to specific consumer traits?
- Can you match those traits and patterns to any relevant psychological principles?
Think about how you can encompass those principles in your copy.
Investigate if your assumptions are correct by setting up experiments. Of course, it goes without saying that you can only tell if something works by trying it out. Make adjustments to your website based on your new action plan and see what sticks (if you want to know how you can support your findings with marketing psychology, read this guide).
Step 4: Test, test, test
So, you did your groundwork, tested out a few new strategies on your website, and learned a bit more about your customers.
While there is plenty of evidence that suggests at least part of our psychological tendencies are hardwired, most of our human behaviour is dynamic. The way we think, act, or feel can change over time and across different situations. This variation results in different shopping states, another factor to take into account during your analysis.
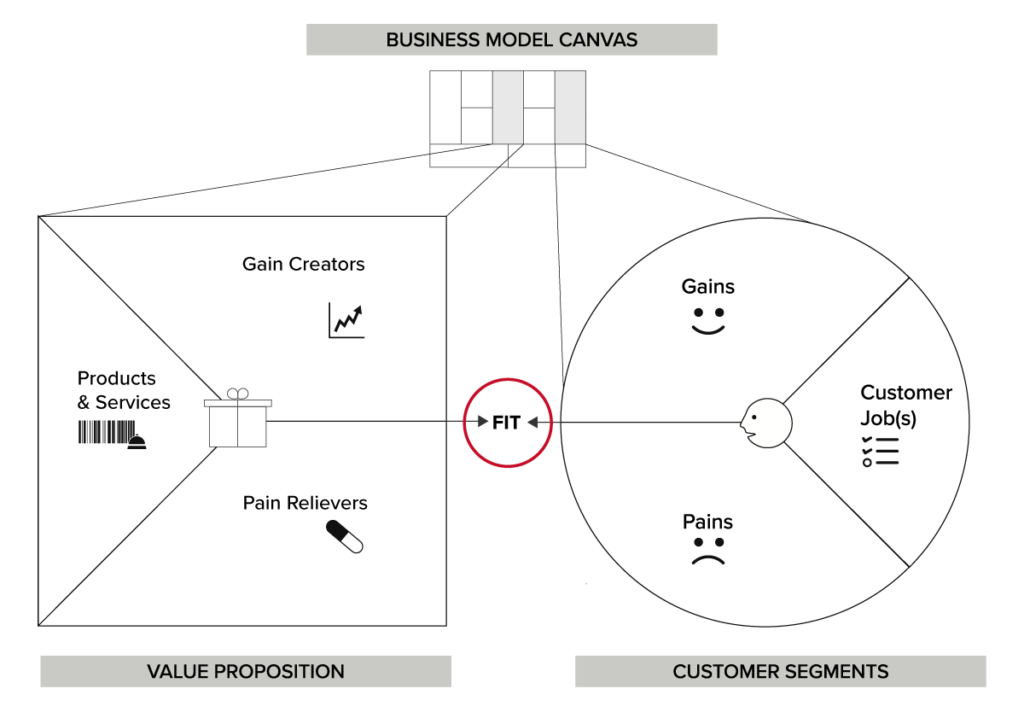
Business Model Canvas and Customer Segments
By now you’ll understand the importance of customer segments and the different ways to segment customers.
It’s probably no surprise that the first block of the business model canvas is customer segments.
The second block is the Value Proposition.
In a nutshell, at the heart of every great business is the same principle of producing something that customers want, in other words offering them value. Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur were so convinced of the importance of these two blocks that they subsequently released a further book called the Value Proposition Canvas.
In this guide, I’ll cover mone on how to fill in the Value Proposition Canvas.
Final Point On GDPR
Final note: make sure your data gathering and analysis efforts are appropriate, valuable, actionable, non-intrusive and GDPR compliant – that way, everybody wins!


