The Apple business model is based on its ecosystem of products and services, which work seamlessly together to deliver an exceptional customer experience.
In this article, I’ll show you how Apple makes money, what underpins its success, and what we can expect to see in the future.
Table of Contents
What is the Apple Business Model?

Apple’s business model has shifted from primarily focusing on products to a more integrated ecosystem that includes services.
Historically, Apple’s products were sold to customers through various retail channels. Now, Apple leverages its devices, such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs, as platforms to distribute services like Apple Music, TV+, and Arcade.
This transition represents a move towards a services-led approach, where Apple encourages users to subscribe to a wide range of experiences through their devices.
The ecosystem Apple is building connects products and integrates services and experiences, creating a subscription-based model that deepens customer engagement.
The focus is no longer on selling physical products but on building long-term relationships with users through service subscriptions that complement their devices.
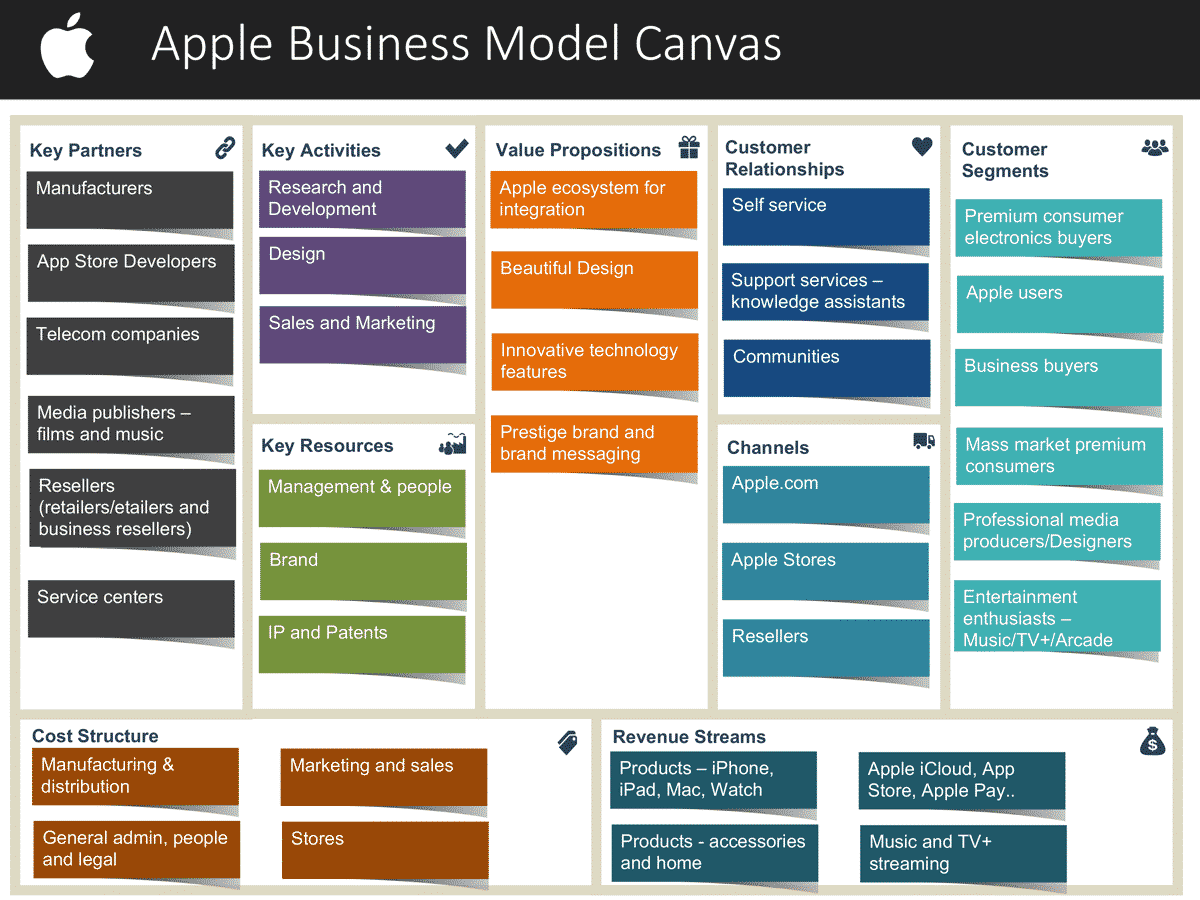
Key Partners:
- Manufacturers
- App Store developers
- Telecom companies
- Media publishers (films and music)
- Resellers (retailers/business resellers)
- Service centers
Key Activities:
- Research and development
- Product design
- Sales and marketing
Key Resources:
- Management and people
- Brand
- Intellectual property and patents
Cost Structure:
- Manufacturing and distribution
- Marketing and sales
- General administration, legal, and operational costs
- Stores
Revenue Streams:
- Product sales (iPhone, iPad, Mac, Watch)
- Accessories and home products
- Digital services (iCloud, App Store, Apple Pay)
- Music and TV+ streaming subscriptions
Value Propositions:
- Integration within the Apple ecosystem
- Distinctive design
- Innovative technology features
- Prestige brand and premium image
Customer Relationships:
- Self-service platforms
- Support services (knowledge assistants)
- Community engagement
Channels:
- Apple website
- Apple Stores
- Resellers
Customer Segments:
- Premium consumer electronics buyersBusiness users
- Entertainment enthusiasts (Music, TV+, Arcade)
- Professional media producers and designers
Key Facts About Apple

Key Facts About Apple
Apple
Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne
April 1, 1976
1976
Tim Cook
Cupertino, California, USA
(FY 2019): 161,000
AAPL
(FY 2023): $383.3 billion.
FY 2023: $97.0 billion
(Feb, 2024): $2.82 Trillion
Apple Products and Services
Apple Key Competitors
Some Frequently Questions About Apple’s Business Model
Apple produces premium consumer electronic products known for their design and ease of use. Its business model is based on combining software, products, and apps to form a complete ecosystem of solutions for customers.
Which type of business model best describes Apple?
Apple’s business model is a platform ecosystem that seamlessly integrates hardware, software, and services to deliver a unified user experience.
Through vertical integration, Apple controls every aspect of its products—from design and manufacturing to software and retail—enhancing quality and fostering customer loyalty.
The company adopts a premium pricing strategy, positioning its products as high-end and leveraging its strong brand identity.
Relevant business model patterns include the subscription business model (e.g., iCloud, Apple Music).
A business model pattern is the lock-in or walled garden model. Apple creates a proprietary ecosystem with tightly integrated hardware, software, and services, encouraging customers to remain within the Apple environment for a seamless experience. This makes it less convenient for users to switch to competitors, fostering brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
What is the Apple Pay business model?
Apple Pay is a mobile payment and digital wallet service by Apple that allows users to make secure payments using their Apple devices. The business model of Apple Pay focuses on enhancing the Apple ecosystem and generating revenue through partnerships with financial institutions.
Revenue Generation:
- Transaction Fees from Banks: Apple earns a small fee from card-issuing banks and financial institutions every time a user purchases using Apple Pay. This fee is typically a fraction of the transaction amount and is negotiated individually with each bank. Users and merchants generally do not pay extra fees for using Apple Pay.
Apple Pay Business Model
Ecosystem Lock-In: Integrating Apple Pay into its devices and services strengthens Apple’s ecosystem. The convenience and security of Apple Pay make users more likely to stay within the Apple environment, increasing customer loyalty and the likelihood of purchasing additional Apple products or services.
Network Effects: As more users adopt Apple Pay, more merchants and banks are incentivized to support it. This creates a positive feedback loop that enhances the service’s value for all participants.
Data Insights (without compromising privacy): While Apple emphasizes user privacy and does not track individual transactions, aggregated data can provide insights into consumer behaviour, helping Apple improve its services.
| Australia | 50% | 39% |
| United States | 58% | 36% |
| Sweden | 48% | 30% |
| Spain | 32% | 17% |
| Italy | 38% | 15% |
| France | 60% | 22% |
| Canada | 64% | 34% |
| Switzerland | 40% | 31% |
| Brazil | 16% | 8% |
| Mexico | 18% | 13% |
| United Kingdom | 66% | 41% |
| China | 11% | 18% |
| Germany | 44% | 17% |
How Does Apple Makes Money?
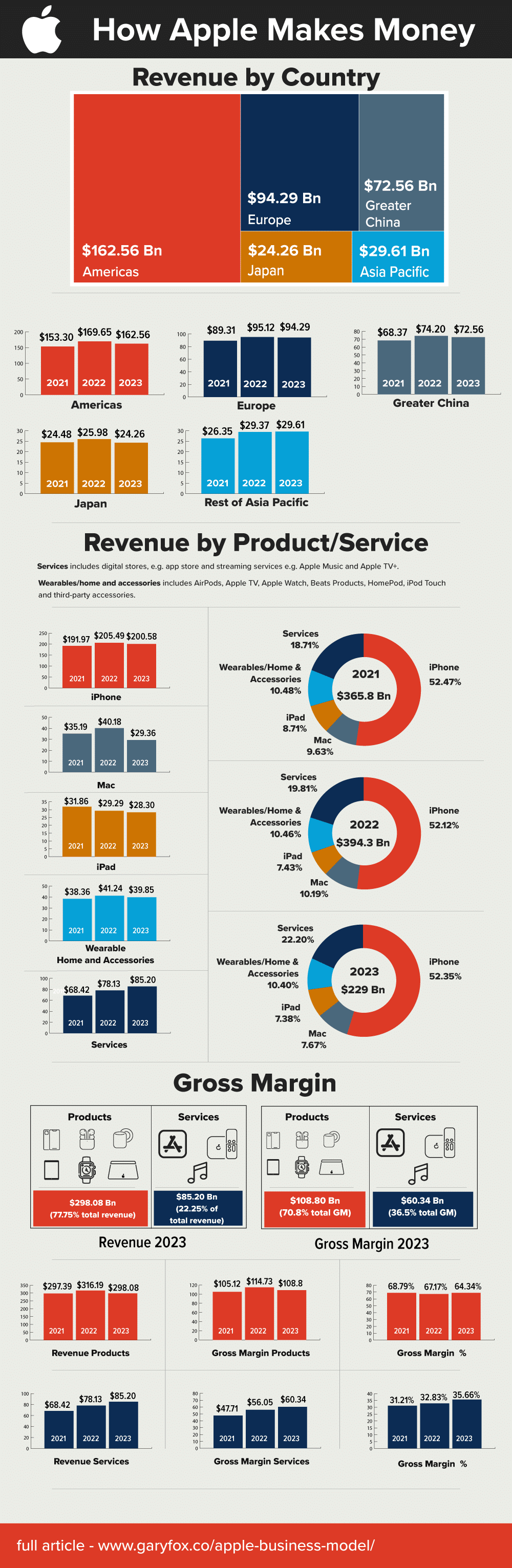
How much revenue does Apple make a year?
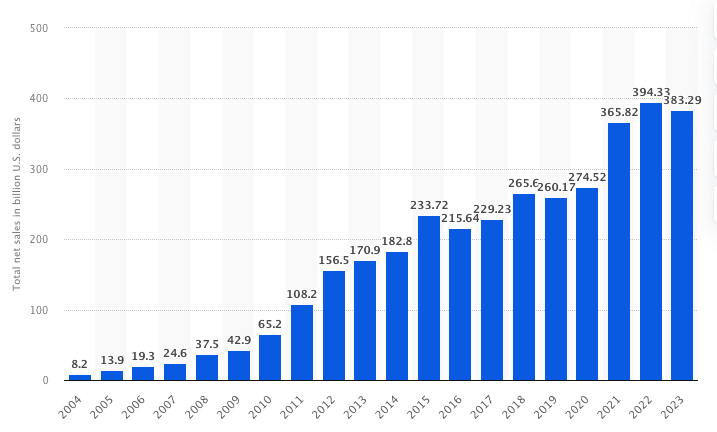
Apple’s total net sales amounted to 383.29 billion U.S. dollars in their 2023 financial year, a decrease from the historical record of 394.33 billion U.S. dollars in financial year 2022. Apple’s annual revenue quadrupled in the last ten years.
Apple generates its revenue primarily through the sale of products and services, with a recent strategic shift towards services as a key growth area. While products like the iPhone continue to be the main revenue driver, services are growing rapidly and generating higher margins.
Revenue from Products
Apple’s products include hardware like the iPhone, Mac, iPad, wearables, and accessories. Historically, these items have accounted for the majority of Apple’s revenue. In 2023, products generated a gross margin of $108.8 billion, contributing 64.34% to the total gross margin. However, the product gross margin as a percentage of total gross margin has been declining since 2021, indicating a relative shift in the company’s focus and profitability sources.
Services as a Growing Revenue Stream
Services, including the App Store, Apple Music, iCloud, AppleCare, and Apple Pay, have seen significant growth over recent years. The services segment generated a gross margin of $60.3 billion in 2023, constituting 35.66% of Apple’s total gross margin. This marks an increase from previous years, reflecting Apple’s strategic emphasis on developing high-margin, recurring revenue streams. With a gross margin percentage of 70.8% in 2023, services are far more profitable than products (36.5% gross margin), primarily due to lower direct costs associated with service delivery and the scalability of digital offerings.
Strategies for Services Expansion
Apple’s strategies to grow its services revenue include leveraging its vast installed user base, enhancing integration across its ecosystem, and introducing new services to drive subscription-based income. By developing a seamless user experience across its devices and services, Apple encourages users to engage more deeply within its ecosystem, leading to higher retention and cross-selling opportunities. Services like Apple Music, Apple TV+, and iCloud are designed to keep users tied to Apple hardware, further solidifying revenue streams from both products and services.
Challenges and Competitive Pressures
While Apple’s services segment has been a growth engine, it faces challenges from regulatory scrutiny, competition, and the need for continual innovation. Regulatory issues, such as antitrust investigations and legal battles related to the App Store’s policies, present potential hurdles that could impact service profitability. Furthermore, Apple’s competitors in the services space, such as Spotify (for music) and Netflix (for streaming), necessitate constant product enhancement and innovation. The company also faces margin pressure from pricing competition in its product categories and the high cost of developing original content for services like Apple TV+.
Regional and Market Trends
Regional markets play a significant role in Apple’s revenue, with growth dynamics varying by geography. The Americas remain the largest market for Apple, but regions like Greater China and Europe are key to Apple’s growth strategy. Market-specific factors, such as economic conditions, regulatory environments, and local competition, influence sales patterns and performance in each region. Additionally, as Apple continues to explore new regions, it adapts its product and services strategy to cater to local preferences and regulatory requirements.
How many people use Apple products?
As of 2024, there are over 2.2 billion active Apple devices worldwide, including iPhones, iPads, Macs, and other Apple products. This figure illustrates the extensive reach of the Apple ecosystem, driven by strong demand for hardware and services. Among these, the iPhone remains Apple’s most popular product, accounting for a significant portion of its active devices and sales.
In terms of individual users, it’s estimated that around 1.5 billion people use iPhones, with millions more relying on other Apple devices such as iPads, MacBooks, and Apple Watches.
Apple’s robust service offerings, such as iCloud, Apple Pay, and Apple Music, further support this growing user base and keep users engaged across the ecosystem.
Where does Apple make most of its revenue?

In 2023, 52% of Apple’s total revenue came from iPhone sales. Despite diversifying its product lines and services, the iPhone remains Apple’s largest revenue driver, contributing more than half of its overall income. However, Apple is gradually increasing its focus on services like iCloud, Apple Music, and Apple Pay, which have been growing as additional revenue sources.
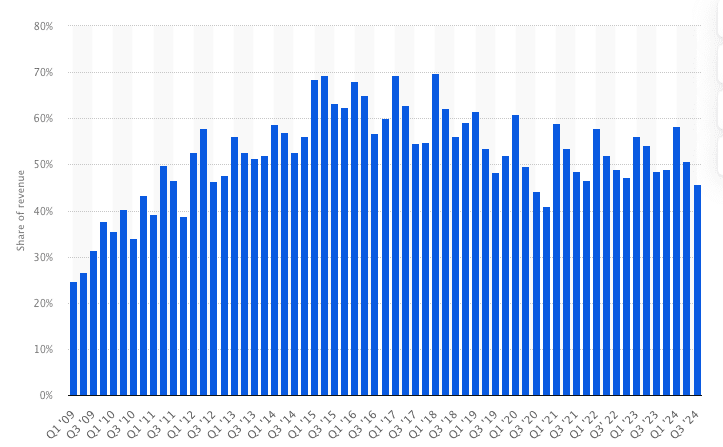
How much is Apple worth?
As of September 2024, Apple is valued at $3.38 trillion in market capitalization, making it the most valuable company in the world. This valuation reflects the total value of all outstanding Apple shares in the stock market.
FUN FACT: The Apple Watch outsold the Swiss watch industry by sales volume in 2019.
Apple’s Revenue By Category In 2023
Despite Apple’s lack of growth, many investors are still excited about its future. Below, I’ll explain why in a review of Apple’s business model.
The following table presents the revenue and gross margin (as a proxy for profitability since net profit by line is not provided) for Apple Inc.’s product and service lines for FY 2023:
- iPhone: $200.6 billion – iPhone: $200.6 billion
- Wearables, Home, and Accessories: $39.8 billion – 10.3% of total revenue
- Mac: $29.3 billion – 7.6% of total revenue
- iPad: $28.3 billion – 7.3% of total revenue
- Services: $85.2 billion –
What Are Apple Services?
Apple Services refers to the digital and subscription-based products and offerings that complement Apple’s hardware ecosystem. These services have become a significant revenue stream for the company and include various categories:
- iCloud: Apple’s cloud storage solution allows users to store files, photos, and backups and access them across multiple devices. It also includes services for syncing data such as contacts and calendars.
- Apple Music: A music streaming service that offers access to millions of songs, curated playlists, and exclusive content. It competes with platforms like Spotify and Amazon Music.
- Apple TV+: A video streaming service that offers original TV shows, movies, and documentaries. Apple has invested heavily in creating original content to compete with platforms like Netflix and Disney+.
- Apple Arcade: A gaming subscription service offering access to premium games across iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple TV. It is aimed at users who prefer ad-free gaming experiences.
- Apple News+: A subscription service that provides access to premium news and magazine content from various publishers. It offers curated stories across different topics like business, technology, and entertainment.
- Apple Pay: A mobile payment service that allows users to make secure payments using their Apple devices. It supports both in-store contactless payments and online transactions.
- Apple Fitness+: A fitness service that provides guided workout routines and classes, designed to integrate with Apple Watch, offering real-time metrics and personalized workout suggestions.
- App Store: Although not a subscription service, the App Store is a key component of Apple’s services revenue. Apple earns from in-app purchases and a percentage of sales from third-party apps.
- AppleCare+: A subscription-based extended warranty program for Apple devices, providing coverage for repairs and support beyond the standard warranty.
Apple’s Performance Products and Services
Many might think a two per cent revenue decline is a blip in Apple’s performance. However, the Apple SWOT analysis takes a much deeper look at the problems and opportunities Apple is now facing.
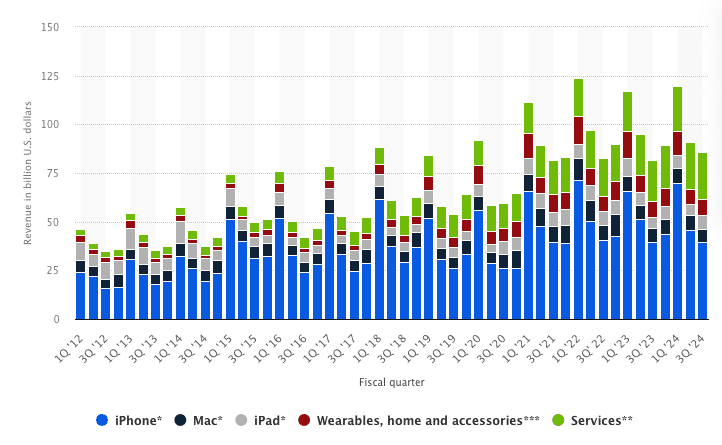
Apple’s Regional Performance

There is no question that Apple’s user growth is slowing. Much of this is due to Apple running out of premium smartphone users in key markets like China and India.
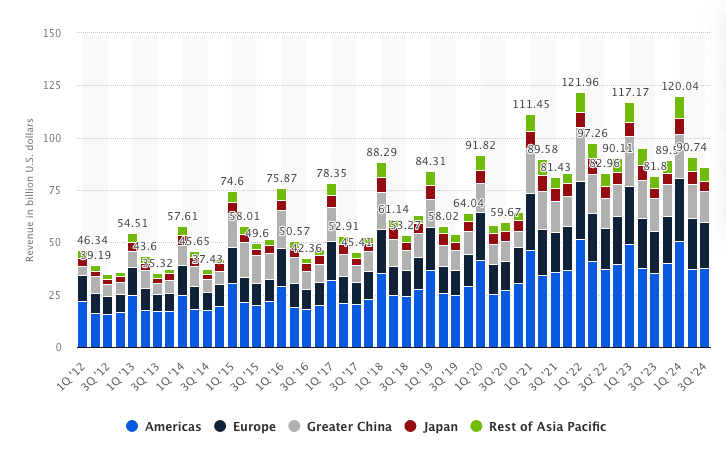
Apple’s revenue performance in China, Japan, and the Rest of Asia Pacific has shown mixed trends in recent years:
- China: Revenue from China has been fluctuating. After peaking in earlier years, Apple saw a decline in sales from 2015 to 2019. In 2021, Apple experienced a recovery, with China contributing significantly to iPhone sales, but revenue from China slightly dropped again in 2023 to $72.5 billion. This represents a minor decline from previous years but remains a key market for Apple.
- Japan: Revenue from Japan has remained relatively stable but also experienced a slight decline in 2023 to $24.2 billion, down from earlier peaks(Business of Apps)(CompaniesMarketCap). Japan continues to be a smaller yet crucial market due to its consistent demand for premium products like the iPhone.
- Rest of Asia Pacific: This region also saw a slight decline in revenue, dropping to $29.6 billion in 2023. While the Rest of Asia Pacific represents growing markets like India, Apple has faced challenges in expanding its footprint across the region compared to its dominance in other parts of the world.
Apple must have lower-priced products like iPhones in countries like India and Brazil. However, it is the wearable technology that may become the biggest opportunity, if Apple can deliver an accessible price point may not be the best tools to bring new users into the ecosystem.
Is The Apple Business Model Under Threat?
Apple is introducing lower-cost, smaller iPhones in a mad dash to stave off the competition. But will it be enough?
If we use disruption theory, we can see that Apple is ripe for disruption.
So why is Apple’s stock price still high? Why do investors still think the Apple business model has a strong future?
What Is The Future For Apple?
Apple’s recent growth has come from the growth in its streaming services—TV+ and Music—and the success of Apple Watch.
The more substantial margin contribution and moving from selling products (one-off transactions) to a subscription business model (streaming TV and Music) provide a more profitable and recurring revenue.
The big play, though, is in the healthcare market worth an estimated $3 trillion dollars.
The Apple Watch opens up new possibilities for further digital subscription models based on the collection and use of data. Turning the Big Data into personalized services fits to the future trend of healthcare and open up new revenue streams for Apple.
Apple recently acquired AI startup Voysis to boost its natural language capabilities with Siri. However, this AI capability can be applied to a much broader set of uses, including AI.
Geographic Customer Segments
Apple operates globally, but that doesn’t necessarily mean it has the same mix of customers in each market. In developing countries, the affluent are mainly the ones who can afford Apple prices because average wages are lower.
Demographic, Psychographic and Behavioural Segments
Teenagers in the US have the highest uptake of Apple iPhones, but older generations are the highest spenders. However, the complexities of breaking down segments vary by Country, age, lifestyle, income, personality, and behaviours, e.g., lifestyle.
For example, in examining single households, there are significant differences in spending based on age.
The Apple Business Model Value Propositions
Apple’s core value proposition revolved around the products and operating systems that formed its main revenue streams. More recently, Apple has expanded into services such as music streaming and TV+. These services build on the core value propositions but also have their own distinct ones.
- Think different
- Tech that works
- Your privacy is safe with us.
Think Different
“Think different” is Apple’s invitation to be creative. Since its early days, the Mac has been associated with designers, and Apple has used that association to foster and encourage creativity through its devices.
Tech that works
The promise is simplicity, ease of use and seamless integration across devices.
Even in the early days, Apple used to attack its competitor, Microsoft, based on this simple value proposition.
I can easily use my iPad as a second screen with my MacBook—no configuration or settings are required; it’s just there as an option. That ease of use has led to Apple’s status as a technology built around the user.
Your privacy is safe with us.
Google’s business model is based on selling your search behaviour to bidders. For example, if you were looking for a new car, you would see an ad for one on each search page. Google collects your data, refines your search based on your preferences, and uses this to optimize ad clicks.
Apple doesn’t rely on ad revenue and uses this as part of its value proposition. Furthermore, the iOS software provides options for users to use ad blockers.
Music streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music accounted for 80 percent of all recorded music revenue in 2019 in the US and close to 50% globally. The value proposition for music streaming relies on on-demand service, breadth of music and quality. Apple’s ecosystem of devices is ideally placed to help integrate and sell its music offer.
Apple Arcade

Apple’s Distribution Channels

Business model channels are the routes you use to reach, communicate, and convert your customers – they don’t just refer to distribution.
How you reach and communicate is equally important.
Your marketing channels are the mechanisms for creating brand awareness, developing customer relationships, offering customer service, and acquiring customers.
Apple’s Distribution Channels

- Apple Stores.
- Apple’s website – (see the ecommerce business model pattern)
- Third-Party Stores (Many of these also act as service centers forApple).
- Resellers (resellers sell to B2B clients).
- Telecom Companies (the majority of iPhones are sold bundled with a mobile package to spread costs).
Apple’s Marketing Channels
Apple has over many years created a devoted fan base. From the legendary figure of Steve Jobs through to the innovative products, people talk about Apple. Add to this their famous minimalist branding and status and you have the perfect recipe for PR.
Apple’s Customer Relationships
The customer relationship block defines the type of relationship the business wants with its customers. This, in turn, determines the level and type of resources needed to deliver the customer experience.
Of course, the obvious benefit of creating beautifully designed products and software is that it reduces support costs.
The relationships between the products and services are quite different. Products which are transactional relationships aim to keep costs to a minimum and operate a self-service model.
- Genius bars in Apple shops – these provide a physical place where people can explore how to use devices and software. The relative coverage is low though and this is primarily to onboard and showcase products to potential new customers.
- Customer Support – This is where Apple provides a range of self-support options. In cases of damage or repair, you are pointed to either official Apple stores or Service Centres.
- Telephone customer support
- Chat support
- Communities: Given the number of Apple fans out there, it’s no surprise that you can easily connect with them across channels such as YouTube to find help and support, lessons on software, and much more.
Apple’s Key Activities
The key activities section reflects the core strategic capabilities of Apple. In simple terms, what it does best and resources.
Apple’s distinctive activities encompass innovation, marketing, quality, strong customer service, simplicity, and strong financial performance.
- Design
- Research and development
- Branding
Apple Design
Apple has been the leader in designing consumer electronics for many years. However, more recently other companies have started to focus on design. Additionally, Jony Ive left Apple to set up his own design company – on the day that was announced Apple value on the stock market dropped by $9 billion. Jony Ive’s new company has already got its first customer though – Apple!
Research and Development
This shows a consistent increase in R&D spending yearly, indicating Apple’s ongoing commitment to innovation and the development of new technologies and products.
- 2021: $21,914 million
- 2022: $26,251 million
- 2023: $29,915 million
Design and innovation are two sides of the same coin.
New technologies enable new ways to design products and services that change how people communicate, interact with media, and much more.
Apple has continually invested in research and development that pushes the boundaries and limits of technologies. Apple invests in research and development to maintain its position and acquires companies to accelerate technology capabilities.
Branding
This trinity of capabilities—R&D, design, and technology—provides the fuel that continues to propel Apple’s marketing into new markets.
Apple Business Model – Key Partnerships
The Apple business model, key partnerships block, defines the services Apple needs to deliver its overall business.

The activities that Apple doesn’t view as strategically core it outsources. In other words, Apple has a network of broad set partnerships that help it to deliver manufacture and supply the enormous number of products and services it offers.
Here is a sample of some of the many different types of business partners Apple relies on to deliver its operations and services globally:
| Type of Partner | Partner |
|---|---|
| Operations (ICT) | Cisco |
| Business (Consultancy) | Accenture |
| Qualcomm | Semi-conductors |
| Cloud Services | Amazon/Google |
| Memory | Samsung |
| Apple Watch | Texas Instruments |
| IOT | General Electric |
| AT&T | Partners who distribute and bundle Apple products with their telecom services |
Apple Business Model – Key Resources
Apple business model resources are listed below:
- The legacy of Steve Jobs – he was the fearless leader who pioneered new products, new services and made the Apple brand as recognizable as Coca-Cola.
- Brand – The power and strength of the Apple brand – worth billions in PR, word of mouth – let alone the fanatical fans that provide a powerhouse of evangelists.
- Intellectual Property and Research – the patents that secure Apple’s future and provide it with unique technologies that maintain its position in the market.
- People – Apple attracts recruits, trains, and retains some of the best talent in the world. parts of its business.
- Management Team – Apple’s top management team continues to steer the company toward growth and profits.
Apple Business Model – Cost Structure
Apple stores are in prime positions in the most expensive capital cities worldwide. Additionally, they are known for the outstanding level of design that goes into the store. Add the staff, training, and equipment to this, and you will have a hefty bill just for your retail division.
Costs related to business operations include:
- Manufacturing/distribution is the main reason physical products have a lower margin than services.
- Selling – people, systems, and marketing
- General and administrative – departments, systems, people and operations that underpin the delivery of the business.
Apple Business Model – Revenue Streams
The primary revenue streams have been covered earlier in this article.
What remains to be seen is if Apple can reinvigorate its growth with its next set of products.