A digital business model focuses on harnessing digital technologies to create a value proposition.
Digital technologies change how value is created as well as change the outcome of innovation.
As an example, by attaching sensors to a large wind turbine engineers can create a digital twin and then use this to understand faults in the current design. In this case, digital technologies are tools that provide new ways to innovate.
On the other hand, digital innovations can be new product-service systems like a Fitbit watch. Fitbit uses sensors on a physical watch that generate digital data and help people to understand their heart rate, fitness level and track their performance.
Because of low cost, global digital infrastructure and the ease with which technologies can be integrated, creating a new and innovative digital business model is within reach of most entrepreneurs.
Add to this the no-code movement and you have the ability for most business people to at least create a prototype digital business model.
What’s Driving The Change To Digital Business Models
Compared to physical resources, digital technologies change the way an organization interacts with customers, partners as well as transforming internal processes.
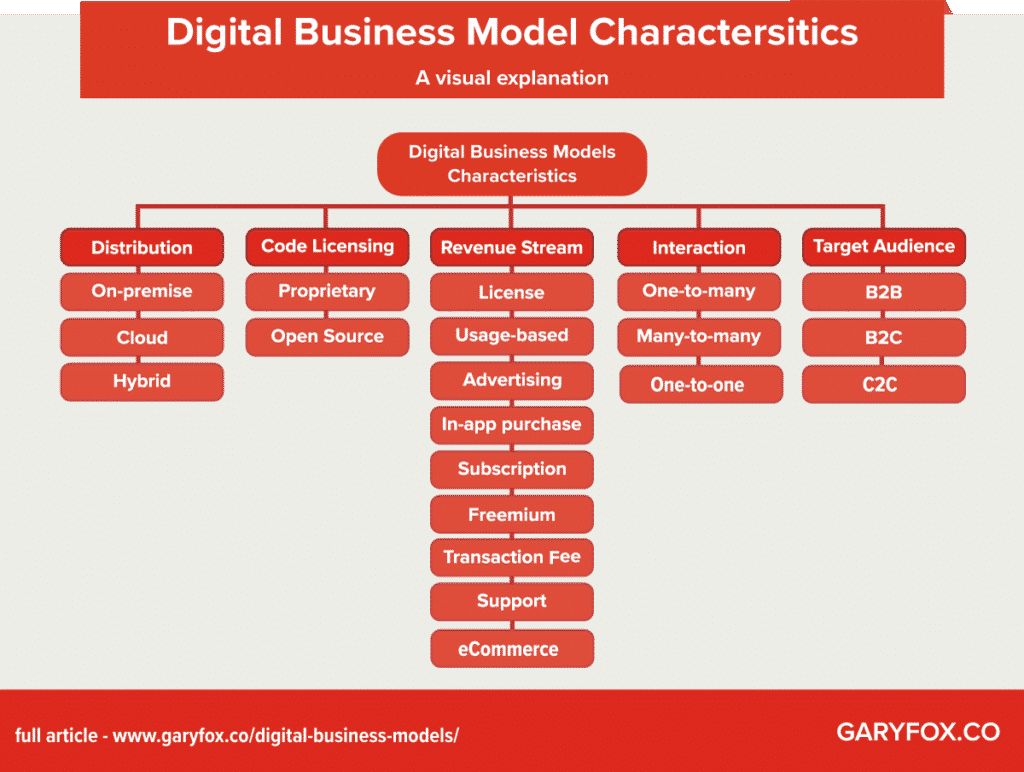
What Is A Digital Business Model?
Digital technologies also present opportunities to identify and realise new and untapped revenue streams, distribution methods and monetization opportunities.
Products and processes that were once physical are now digital. A newspaper used to be printed overnight and then sent in vans to be sold in newsagents and on streets. Now, the news is digital and fluidly distributed globally in seconds.
Likewise, internal processes in a company were once heavily reliant on paper but now digital enables collaborative and social processes, speeding up decisions and saving time.
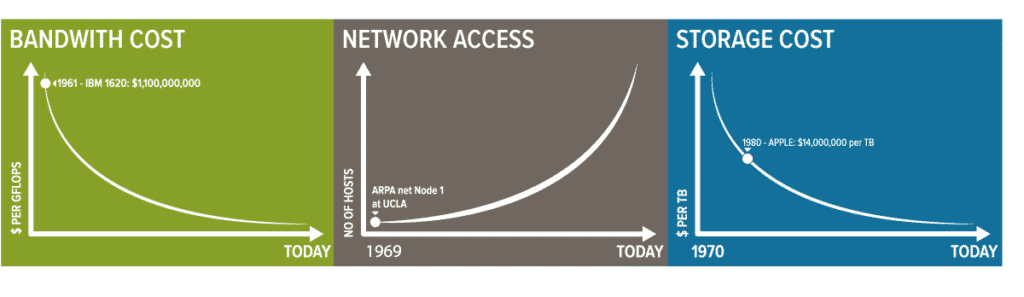
But, digitalization is much more than this. Trying to track and analyse things when everything was physical was difficult and sometimes just impossible. Digital technologies are interwoven and code is ubiquitous.
Just about everything can be digitized to generate data. Smartphones, interactions on social media – virtually anything through sensors. As a result, we are now swamped with data.
The growth in IoT devices is massive. By 2025, there 41.6 billion IoT devices will generate over 79.4ZB.
| Name | Unit | Size (in bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| b | bit | 1/8 byte |
| B | bytes | 1 byte |
| KB | kilobyte | 1,000 |
| MB | megabyte | 1,000,000 |
| GB | gigabyte | 1,000,000,000 |
| TB | terabyte | 1,000,000,000,000 |
| PB | petabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| EB | exabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| ZB | zettabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| YB | yottabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
What types of data can create value?
- Social data e.g. Tweets, posts on Facebook can be tracked to understand brand sentiment – negative or positive.
- Customer data can be used to understand shopping behaviours and characteristics that then enable improved targetting and better conversion rates thus lowering cost of acquisition.
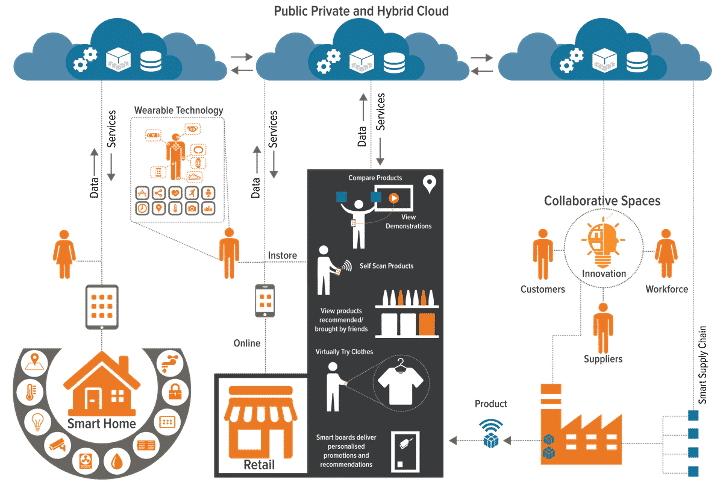
- Sensor data – can help improve logistics, enable better management of infrastructures, help design smarter cities and model new ways of working.
- Transaction data: this is data as a result of a transaction e.g. you buy a bitcoin, sell a bitcoin or buy something from an eCommerce store like Amazon.
- Interactive Data: If you think of smart cities then you will interact with lots of different spaces, environments and systems. Understanding where people go, how they move through a city can help optimize the layout and design.
Digital Business Models Examples
Digital Platforms
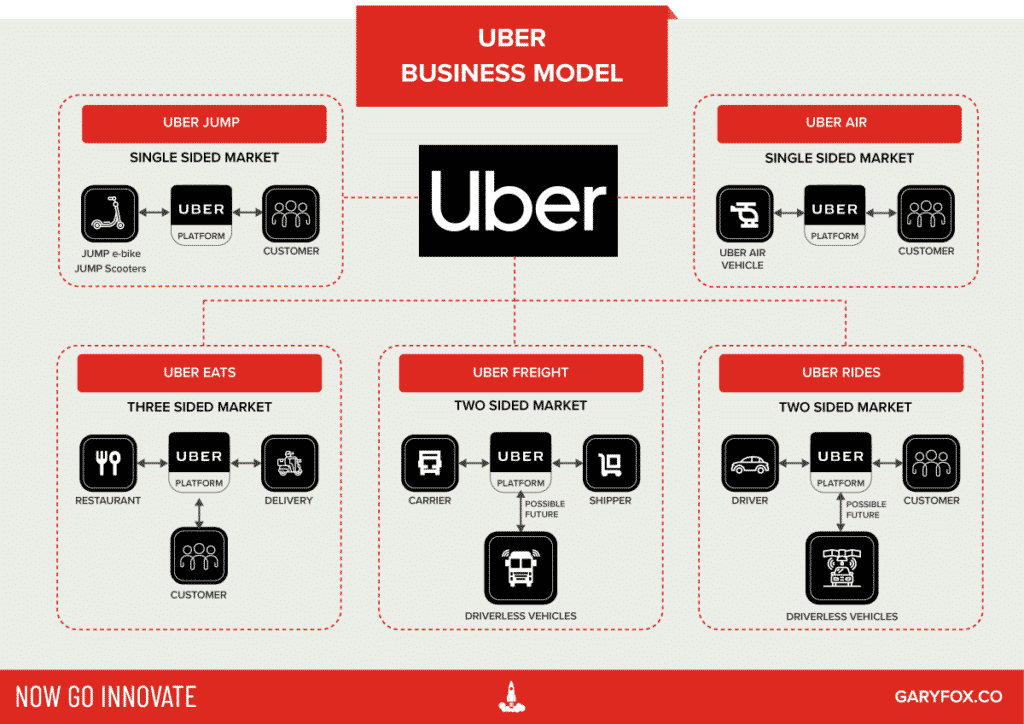
Platforms like Uber run on large scale infrastructures with a global reach. Moreover, they harness the power of mobile devices and apps to connect customers with drivers.
Open Digital Models
Another familiar open-source business model is WordPress. WordPress is freely available and can be installed by anyone as long as they use it on a hosting service e.g. Bluehost. However, for those that want a more simple solution, they offer a premium ready-hosted solution on WordPress.com that is subscription-based and has other premium features.
ECommerce
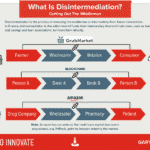
Ecommerce stores like Amazon have transformed how we shop. Moreover, the AI and machine learning process Amazon employ help with personalized suggestions. Without digital technologies, the whole supply chain of Amazon would disintegrate.
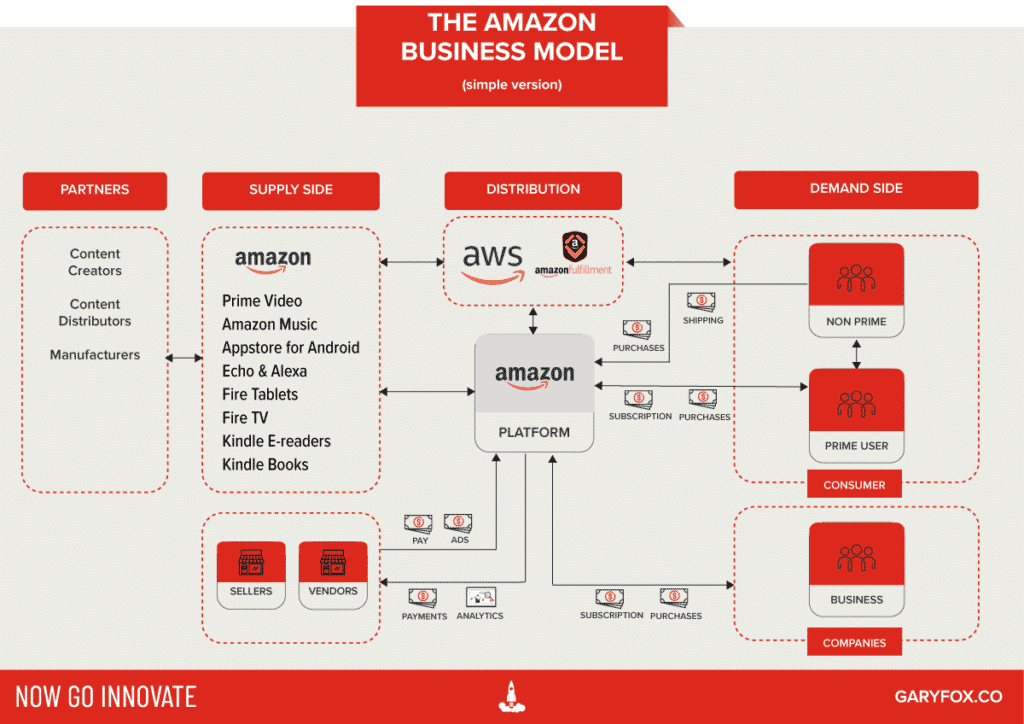
Software as a Service Business Model
Software as a Service (SaaS) companies typically uses subscription models. A good example is Salesforce.com. This digital business model lowers initial barriers to entry and also require less commitment long-term. To improve cash flow and lock-in customers many companies offer discounted rates for annual buy-in e.g. get two months free if you pay for twelve.
Both B2C- and B2B-facing organizations can benefit from subscription economics, assuming revenue and retention outweigh customer acquisition costs (CACs).
On-Demand model
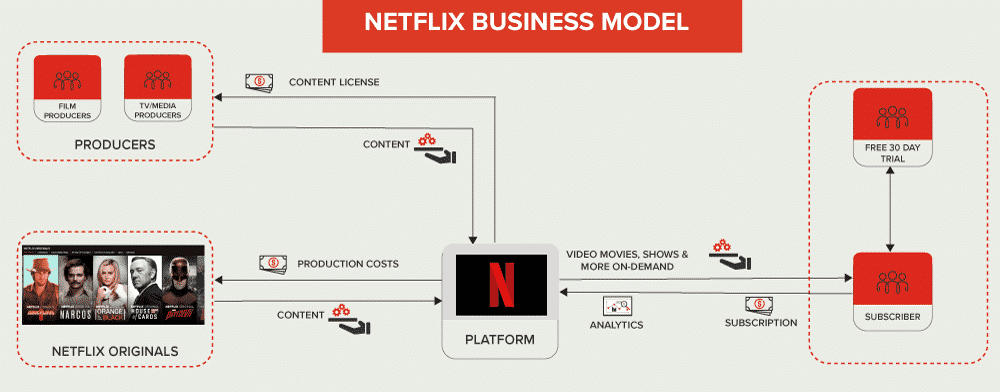
The on-demand business model is defined by fulfilling customer demand via the immediate provisioning of goods and services.
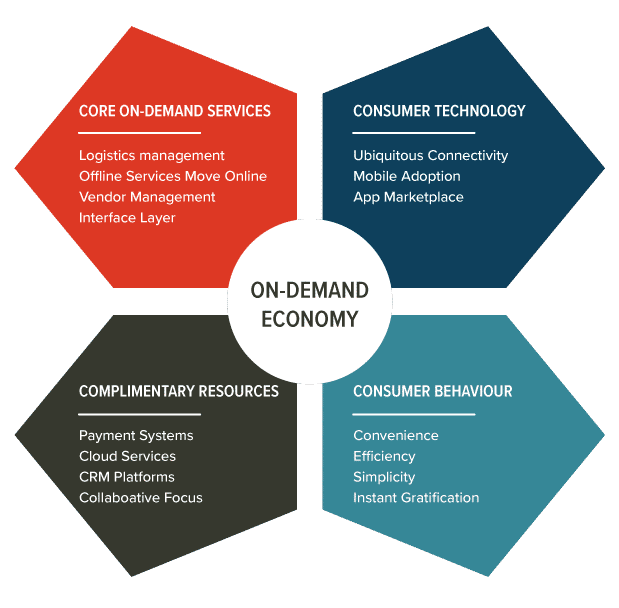
Characteristics Of DIGITAL BUSINESS MODELS
If we focus on the different types of digital business models as they are now we can see how they will change. The diagram below shows the current digital business model characteristics.
Digital Business Model Transformation
The core of future business models is the value proposition that solves a customer problem or satisfies a customer need.
Digital business models are both easy and complex to understand. So let’s start with the easy and look at how digital transforms the business model. We can use the business model canvas to do this.
Various trends and drivers determine the transformation of business models.
The complexity, speed and effectiveness of these influences make it increasingly difficult for companies to master the challenges of transformation.
digital business models – Value Propositions
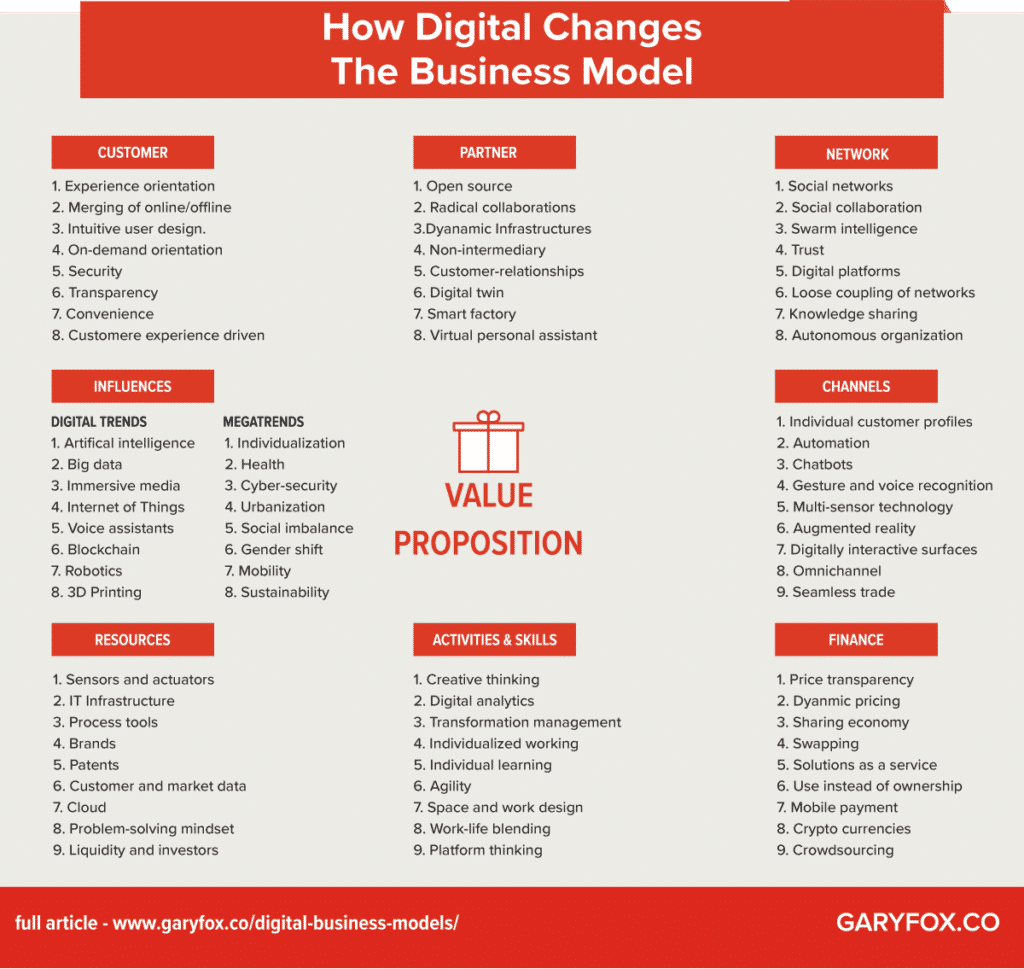
Various megatrends, as well as digital and technological trends, will fundamentally change the value proposition of the future.
Trends and technologies do not exist in isolation. They build on and reinforce one another to create the digital world. Combinatorial innovation explores the way trends combine to build this greater whole. Individual trends and related technologies are combining to begin realizing the overall vision embodied in the intelligent digital mesh.
Some statistics from Gartner that demonstrate the speed and impact of digital business models:
- By 2022, at least 40% of new application development projects will have artificial intelligence co-developers on the team.
- By 2024, most cloud service platforms will provide at least some services that execute at the point of need.
- By 2023, blockchain will be scalable technically and will support trusted private transactions with the necessary data confidentiality.
Technology innovation leaders must adopt a mindset and new practices that accept and embrace perpetual change. That change may be incremental or radical and may be applied to existing or new business models and technologies.
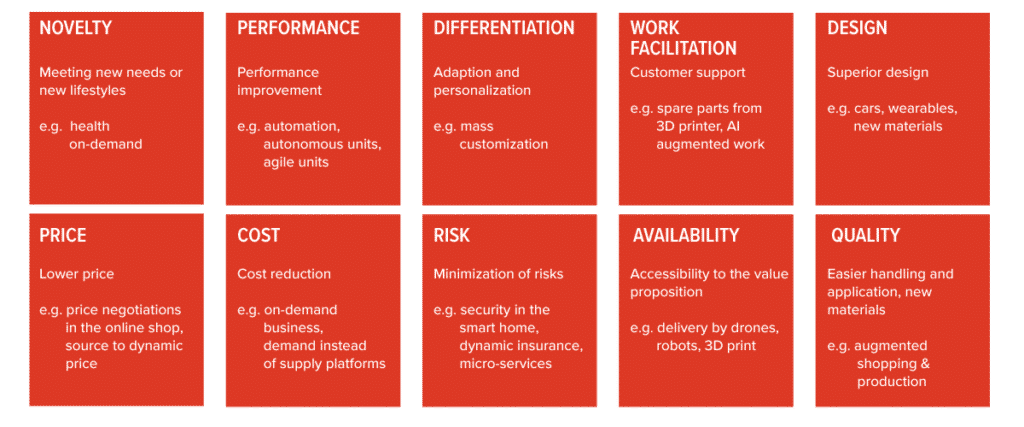
DIGITALLY ENABLED VALUE PROPOSITIONS
Of course, each person is built differently and will need to examine how it creates value using digital business models. These ten building blocks for value proposition design are just some of the ways that digital technologies transform the value chain.
Digital Business Models: Trends Accelerating Innovation
There are four trends that relate to the democratization of technology which will, in turn, ignite new levels of innovation:
- Democratization of Application Development. AI is now offered as a Platform as a Service (PaaS) providing access to sophisticated AI tools to leverage custom-developed applications. As a result, developers can harness powerful AI-model-building tools, APIs and associated middleware. Additionally, PaaS providers have quickly established valuable training and knowledge sharing communities, including pre-built modules. These processes and resources are accelerating the development of digital business models. New solutions include vision, voice, and general data classification and prediction models of any type. digital business models
- Democratization of Data and Analytics. The tools used to build AI-powered solutions are expanding. New tools are built for the professional developer community (AI platforms and AI services) and the general data specialist. These tools enable rapid new modelling and testing and speed up innovation cycles.
- Democratization of Design. In addition, low-code or in some cases no-code, application development platform tools exist to build AI-powered solutions. In turn, these are built on and have new AI-driven capabilities that assist professional developers to automate tasks. This expands on the low-code, no-code phenomenon with automation of additional application development functions to empower the citizen developer.
- Democratization of Knowledge. Non-IT professionals increasingly have access to powerful tools and expert systems that empower them to exploit and apply specialized skills beyond their own expertise and training. Dealing with the issues around “shadow AI” in this user-led environment will be a challenge.
Blockchain Model
Blockchain has the potential to reshape industries by enabling trust, providing transparency and enabling value exchange across business ecosystems. There is a huge potential to lower costs, reduce transaction settlement times and improve cash flow. digital business models
Moreover, in combination with IOT technologies, assets can be traced and tracked from their origin to the point of production or purchase. Often it is the combination of blockchain and other digital technologies that produces more radical digital business models.
As a result, blockchain significantly improves supply logistics and reduces risks associated with counterfeit goods.
Another area in which blockchain has potential is identity management. Smart contracts can be programmed into the blockchain where events can trigger actions; for example, payment is released when goods are received.
The Blockchain Value Proposition
A key component of digital business models is the realization of value. Blockchain potentially drives value in a number of different ways:
- Blockchain removes business and technical friction by making the ledger independent of individual applications and participants and replicating the ledger across a distributed network to create an authoritative record of significant events. Everyone with permission access sees the same information, and integration is simplified by having a single shared blockchain model.
- Blockchain also enables a distributed trust architecture that allows parties that do not know or inherently trust one another to create and exchange value using a diverse range of assets.
- With the use of smart contracts as part of the blockchain, actions can be codified such that changes in the blockchain trigger other actions.
Development of a digital business model
Despite the proliferation of technology, it is essential to put people at the centre of your technology strategy. Digital business models need to be evaluated but it is in the generation stage that modelling needs to be aligned to potential solutions.
Solutions must be assessed as to how they impact your customers, employees, business partners, society or other key constituencies. digital business models
A people-centric approach should start with understanding these key target constituencies and the journey they undertake to interact with or support your organization.
Digital technologies enable new forms of interaction and therefore creative visioning and thinking is essential. The boundaries, methods and approaches to business are changing and demand new mindsets to innovate.
Some useful tools:
Personas (See the persona canvas)
A persona is a useful tool to describe a target individual or group. The persona highlights the set of motivations, preferences, biases, needs, wants, desires and other characteristics that can be used to evaluate how applications of technology might impact that group. digital business models
Personas have been used for many years and have gained broadest adoption in design and marketing areas, where understanding the motivations of a target audience are particularly important.
The persona sets the context for evaluating the potential impact on people and the resulting business outcome. Personas can be used to anticipate the valuable business moments that emerge as people traverse technology-enabled smart spaces.
Persona-based analysis is a powerful tool that helps leaders diagnose and take action against digital-business-disruption opportunities. Enterprise architecture and technology innovation leaders can help business and IT leaders to consider the human side of digital business strategy decisions with personas.
Journey Maps (See the Customer Journey Map Canvas)
A second useful tool is “journey maps.” A journey map is a model that shows the stages that target personas go through to accomplish a task or complete a process.
Customer journey maps diagram the stages a customer goes through to buy products, access customer service, or complain about a company on social networks. It can be linked to the jobs to be done framework and as such provides a compelling method to identify customer problems (pains and gains).
An alternative approach is to use a journey map to diagram the stages employees go through in onboarding or in adopting new systems. Journey maps look at how multiple constituencies interact around a provide a powerful way to identify improvements.
For example, a journey map for a customer purchase might consider not only the customer view but also that of a salesperson or a fulfilment group.
Journey maps provide even more concrete context for digital business model innovation. Executives and innovation teams should consider the pain points, inefficiencies, gaps, and opportunities to delight and create new digital business moments for all the relevant constituents.
Digital Business Models
Digital technologies are complex and organizations need to understand the recombination effect as well as the digital ecosystem. Subscribe to find out more about digital business models and how you can take advantage of the democratization of digital.