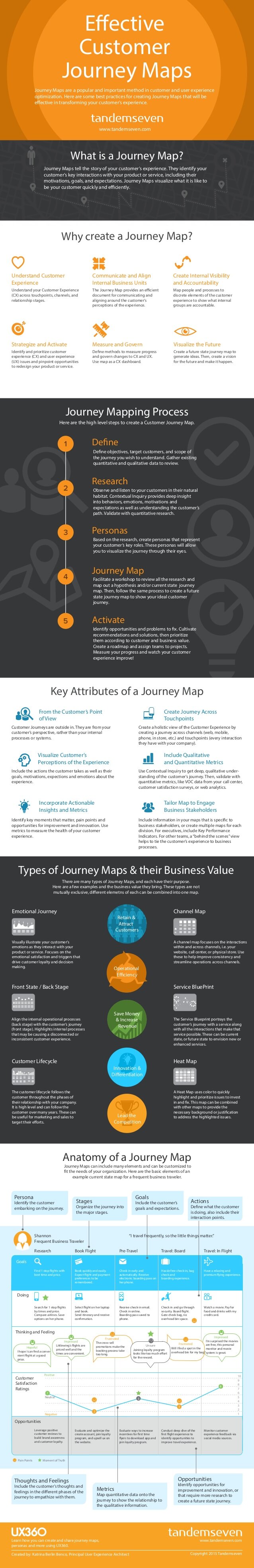
How do you create effective Customer Journey Maps?
Creating effective customer journey maps takes time and a bit of patience.
If they are done well though, they can become a powerful tool for the whole organization to understand how customers interact with and perceive the company.
The Stages of Developing An Effective Customer Journey Map
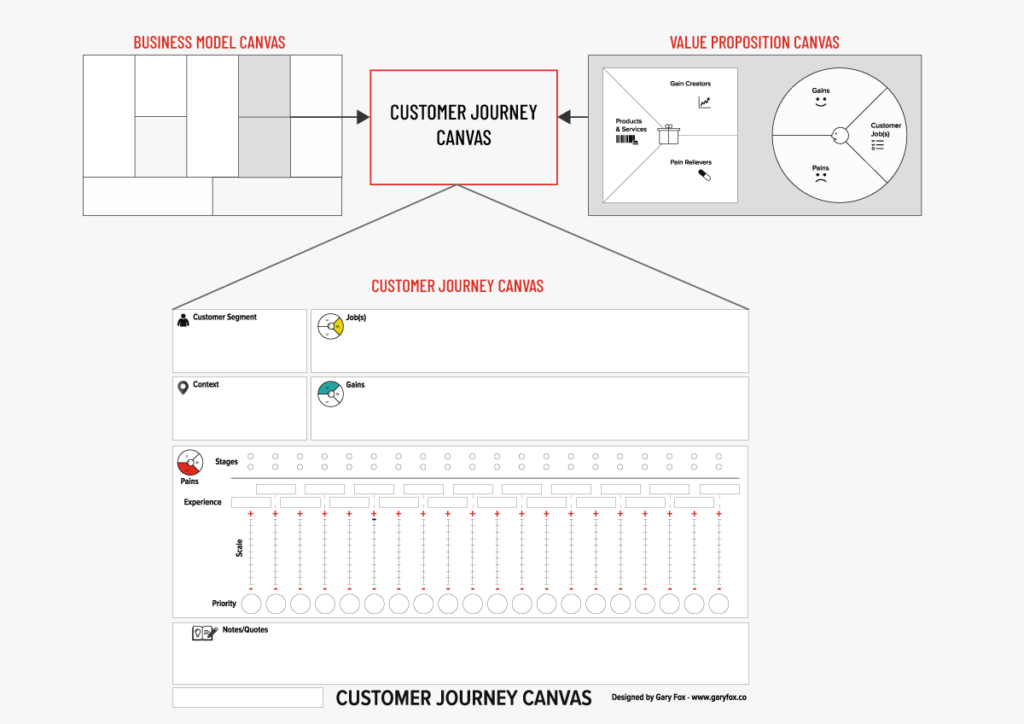
Download a free copy of the customer journey map canvas.
Today, two-thirds of the touch points a consumer has with a brand during product evaluation are customer-initiated.
A typical customer journey may involve searching internet reviews, browsing websites, and getting word-of-mouth recommendations from friends or family.
Customers may also visit stores or compare products with past experiences and available alternatives.
In fact, according to Google, shoppers now use an average of 10.4 sources of information to make a purchase decision.
In a recent study of digital and e-commerce marketers, over 63% rated customer journey analysis as the most valuable method to increasing website purchases.
This makes it one of the best competencies for a company to develop.
But effective customer journey mapping also requires diligence, research, flexibility, and perspective.
Actionable customer journey maps should paint the consumer in his or her full context, requiring teams to consider and account for a significant amount of multi-channel complexity.
Using Data and Observation
Customer journey mapping relies on a blend of data driven insights into how customers feel and emotionally react.
The best approach is to start building your journey map by using your existing knowledge and data about your customers: both qualitative and quantitative.
Audit the data you have and what research and further data you need.
Then you can bridge the gap by defining by what research is needed and ranking its importance. This will often include:
- Collecting first and third party data on customer behavior from market research, consumer surveys, observed actions and other sources
- Analysing your own website, CRM and channel data for insights about who your customer is, why they need your product, and where and how they buy it
- Creating customer personas (use the customer persona canvas), archetypes or ideal buyer profiles
The key is to understand four things about your customer:
- Identity – Who they are, what do they value?
- Situation – When, where and how will your brand present in their life?
- Motivation – Why will they interact with your brand and product? What’s the goal?
- Outcome – What will make them satisfied and mark that goal complete?
Audit touchpoints
Research where and how customers interact with your brand, and build a list (for a quick start, download our content distribution channel checklist).
This should include offline and digital, as well as other important non-marketing interactions like customer service.
It can also be useful to weight and rank the importance of touchpoints to create effective customer journey maps. For example, in physical retail, merchandising and packaging have become increasingly important selling factors, a point often under-appreciated by digital marketers.
Consumers want to look at a product in action and are highly influenced by visual attributes.
According to McKinsey research, up to 40 per cent of customers change their minds because of something they see, learn, or do at the direct point of purchase—observing visual packaging, shelf placement, or interactions with retail employees, for example.
Some important points about creating an effective journey map:
- Don’t rely on generic client demographic data. Determine the segmentation of your customer base. Often, decisions are made on general assumptions about customer behavioural traits that aren’t always true. Most companies don’t regularly gather customer perspectives or share the insights when they do.
- Avoid analysis paralysis. It’s easy to include lots of it. This can result in dizzying complexity. Create customer journeys that represent the largest customer interaction segments to achieve consensus to move forward with design, measurement and optimisation.
- View as a ongoing iterative process. What may be true today may not be true tomorrow. Invest in efforts to maintain a customer journey map that evolves according to the changing needs of the customer.
- Establish key interaction points. Identify points of bottleneck, inefficiency, and positive service levels. Journey events of significant impact have a greater bearing on the customer’s perspective of the company.
- Measure value at key interaction points. Contact Centres are a collection of complex software processes that generate a tremendous amount of interaction data. Most contact centres rely on traditional analysis, such as manual data gathering, text editors and generic log analysis tools in an attempt to understand the data and the customer experience.
Effective Customer Journey Map