The Slack business model is based on the innovative team collaboration platform. Moving from email overload to simple messaging, Slack transformed the way businesses communicate and work together.
Slack has over 12 million daily active users and over 156,000 paying customers.
In this article, I’ll explore Slack’s business model and how this company has redefined team communication.
Table of Contents
The Slack Value Proposition
- An easy-to-use interface with customisable features enables teams to communicate and collaborate efficiently. It reduces the time taken for everyone to stay informed and aligned.
- A vast ecosystem of app integrations. Teams can create effective workflows using multiple integrations and add-ons. Slack automates tasks directly within the platform, boosting productivity and streamlining workflows.
- An easy-to-use and accessible cloud-based platform that helps teams stay connected and productive from anywhere, on any device. It fosters a flexible and agile work environment that adapts to team needs.
Key Facts About Slack
Slack
Stewart Butterfield, Eric Costello, Cal Henderson, and Serguei Mourachov
August 14, 2013
2009
Stewart Butterfield
San Francisco, California, USA
2,500
See Salesforce ticker – CRM
$5.967 billion (2023)
part of Salesforce
reported as part of Salesforce since acquisition
Useful Links for Slack
A Brief History of Slack
Stewart Butterfield, Eric Costello, Cal Henderson, and Serguei Mourachov founded Slack in 2009 as a side project while working on a game called Glitch.
The team realized the potential of the communication tool they had built for internal use and decided to focus on developing it further.
- August 2013: Slack launches publicly as a platform for team communication
- February 2014: Slack reaches $1 million in annual recurring revenue (ARR)
- April 2014: Slack raises $42.75 million in Series C funding
- February 2015: Slack reaches $12 million in ARR and 500,000 daily active users
- April 2015: Slack introduces user groups and expands to 750,000 daily active users
- December 2015: Slack reaches $1 million in paid seats and a $2.8 billion valuation
- January 2017: Slack raises $200 million in Series F funding at a $3.8 billion valuation
- September 2017: Slack reaches 6 million daily active users and 50,000 paid teams
- January 2019: Slack confidentially files for a direct listing on the stock market
- June 2019: Slack goes public through a direct listing on the New York Stock Exchange
- December 2020: Salesforce announces its acquisition of Slack for $27.7 billion
- July 2021: The acquisition of Slack by Salesforce is completed
The Slack Pivot: How It Happened
Slack’s success today can be traced back to a crucial pivot at the right time.
However, this was not the first time Stewart Butterfield, Slack’s founder, had made a strategic shift.
Before Slack, Butterfield co-founded a company called Ludicorp with Caterina Fake.
They developed a game called Game Neverending, which included a feature that allowed players to share photos.
This feature, known as Flickr, became extremely popular.
Recognising the game’s limited financial potential but seeing Flickr’s growing appeal, Butterfield quickly shifted focus from the game to developing Flickr as a standalone photo-sharing platform.
This marked his first successful pivot, which led to Flickr becoming one of the leading photo-sharing apps in the early 2000s.
A similar story unfolded with Slack.
While working on another game called Glitch, Butterfield realised it might not succeed commercially.
However, during this time, his team had developed an internal communication tool to manage their work, which became Slack.
Recognising its potential, Butterfield pivoted again, launching Slack as an instant messaging platform, marking his second major and highly successful pivot.
Understanding Slack’s impact was initially difficult for many, as communication within companies was primarily done through email or direct conversations.
But, over time, it became clear how transformative the tool was. As of now, Slack has been in business for nine years, achieving success beyond expectations.
Who Owns Slack
As of July 2021, Slack is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Salesforce, a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform.
Salesforce’s strategy to expand its offerings and create a more comprehensive platform for businesses drove the acquisition, valued at $27.7 billion.
Before the acquisition, Slack was a publicly traded company. Following its direct listing on the New York Stock Exchange in June 2019, its shares were listed on the exchange.
Overview of Slack Statistics
- Number of Apps on Slack: Slack’s app directory includes over 2,400 apps, allowing users to extend the platform’s functionality.
- Categories of Apps: Apps are organised into categories such as Productivity, Project Management, Developer Tools, and Communication.
- Top Apps in Productivity: Popular productivity apps include Google Drive, Trello, and Asana, which help teams collaborate and manage tasks seamlessly.
- Top Apps in Project Management: Trello, Jira, and Monday.com are widely used in the project management category for team coordination and task tracking.
- Top Apps in Communication: Zoom and Microsoft Teams integrations are frequently used for video conferencing and collaboration.
- Daily Active Users (DAUs): As of 2023, Slack reported over 12 million daily active users globally.
- Monthly Active Users (MAUs): Slack has approximately 18 million monthly active users, reflecting steady growth.
- Enterprise Customers: Slack serves over 750,000 companies globally, including large enterprises and SMEs.
- Messages Sent per Day: Slack users send over 1.5 billion messages daily, highlighting its centrality to workplace communication.
- Countries with Slack Users: Slack has users in over 150 countries, showcasing its wide adoption across diverse geographies.
AI-powered apps in Slack
AI apps integrated with Slack enhance workflow automation by handling repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on high-impact work.
These apps also offer insights, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, improving decision-making and communication efficiency.
By leveraging AI, teams can automate routine processes, streamline collaboration, and accelerate project timelines.
- Troops: Automates CRM updates and provides insights for sales teams directly in Slack.
- Polly: Conducts automated surveys and gathers team feedback efficiently.
- Geekbot: Automates stand-up meetings and status reporting, saving time for teams.
- Statsbot: Provides real-time data analysis and insights from various analytics platforms.
- Automate.io: Connects Slack with other tools to automate workflows like notifications and updates.
- Obie: Delivers knowledge management and automated support by retrieving answers from internal wikis.
- Clara: Automates scheduling and meeting coordination with AI-powered assistance.
- Workbot: Integrates apps and automates workflows within Slack for improved efficiency.
- Ava: Provides automated transcription services, enhancing communication and meeting records.
- Zapier: Automates multi-step workflows across Slack and other business tools, reducing manual tasks.
The Slack Ecosystem

Slack Mission Statement
“Make work life simpler, more pleasant, and more productive.”
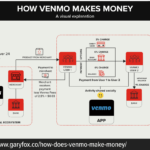
How Does Slack Make Money

The Slack Revenue Model
The Slack business model generates money through its subscription-based pricing model, offering different plans tailored to the needs and sizes of various teams and organisations.
- Paid subscriptions: Slack offers paid plans, such as Pro and Business+, which provide additional features, storage, and support for a monthly or annual fee.
- Add-ons and extras: Customers can purchase additional features, such as extra storage or priority support, to enhance their Slack experience.
- Slack for Enterprise: Slack offers customized solutions for large organizations, providing advanced security, compliance, and IT administration features for a premium price.
Key Features of Slack’s Business Model
- Freemium pricing: Slack’s freemium model allows teams to start using the platform for free, driving widespread adoption and encouraging upgrades to paid plans as needs grow.
- Channel-based communication: Slack organizes conversations into dedicated channels, ensuring focused and easily accessible communication.
- Extensive app integrations: Slack’s vast app directory enables teams to integrate with essential tools and services, centralizing work and streamlining workflows.
- Customizable and scalable: Slack offers customizable features and scalable pricing plans, catering to the diverse needs of teams and organizations of all sizes.
Slack Business Model Patterns
Slack Business Model Canvas

The Slack Business Model
Slack Customer Segments
The Slack business model caters to cost-conscious shoppers and other segments including:
- Teams: Small to large teams within organizations of all sizes
- Enterprises: Large corporations with complex communication needs
- Startups: Fast-paced, agile teams requiring efficient collaboration tools
- Education: Academic institutions, including universities and schools
- Non-profits: Organizations with limited budgets seeking affordable communication solutions

Slack Value Propositions
The Slack business model focuses on the following value propositions.
- Seamless communication: Centralized platform for efficient team interaction
- Customizable workspace: Tailor Slack to fit unique team requirements
- Integrations: Connect with a vast ecosystem of third-party apps and services
- Productivity enhancement: Streamline workflows and reduce communication clutter
- Accessibility: Available across multiple devices and platforms

Slack Channels
The Slack business model leverages the following channels to reach and engage with its customers:
- Website: Primary platform for accessing Slack and its features
- Mobile apps: iOS and Android apps for on-the-go communication
- Desktop apps: Native apps for Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Partnerships: Collaborations with other companies to expand Slack’s reach
- Events: Conferences, webinars, and workshops to showcase Slack’s capabilities
Slack Customer Relationships
The Slack business model uses methods to minimize costs associated with customer relationships:
- Customer support: Dedicated support team to assist users
- Community building: Encouraging users to share ideas and best practices
- User feedback: Actively seeking and incorporating user input for improvements
- Onboarding: Guided setup and training to ensure smooth adoption
- Education: Resources and tutorials to help users maximize Slack’s potential
Slack Key Activities
The Slack business model includes the following key activities:
- Product development: Continuously improving and expanding the Slack platform
- Customer acquisition: Attracting new users through marketing and partnerships
- User engagement: Fostering a loyal and active user community
- Integration ecosystem: Building and maintaining a robust app integration marketplace
- Customer support: Providing timely and effective assistance to users
Slack Key Resources
The Slack business model relies on several key resources to operate effectively and maintain its competitive position:
- Talent: Skilled workforce, including developers, designers, and support staff
- Technology: Proprietary software and infrastructure powering the Slack platform
- Brand: Strong brand recognition and reputation in the team collaboration market
- Data: Valuable user data and insights for product improvement and innovation
- Partnerships: Strategic alliances with other companies to expand Slack’s capabilities
Slack Key Partners
The Slack business model relies on a diverse network of key partners that play a crucial role in supporting the company’s operations, growth, and success. These partnerships include:
- App developers: Third-party developers creating integrations for the Slack platform
- Technology providers: Companies supplying infrastructure, security, and other essential services
- Strategic alliances: Partnerships with complementary companies to expand Slack’s capabilities
- Resellers: Partners offering Slack as part of their product or service portfolio
- Investors: Venture capital firms and other investors supporting Slack’s growth
Slack Revenue Streams
The Slack business model generates the following revenue streams:
- Subscriptions: Slack generates revenue primarily through paid subscription plans for its platform. Users pay for access to advanced features and increased functionality.
- Freemium Model: Slack offers a free version with limited features to attract users, who may eventually convert to paid plans for enhanced capabilities.
- Enterprise Grid: Large organisations often opt for the enterprise-grade version, which offers customised solutions, security, and compliance features at a higher price point.
- App Integrations: Slack earns revenue from app integrations and partnerships, providing third-party tools and software integrations for a fee.
- Consulting and Support Services: Slack offers premium support and consulting services to businesses, which are charged separately from the subscription fees.
- Marketplace: Slack has an app marketplace where businesses can buy third-party tools, and Slack earns revenue through commissions on these transactions.

Slack Cost Structure
The main costs associated with the Slack business model include:
- Research and development: Investing in continuous product improvement and innovation
- Talent acquisition: Attracting and retaining top talent across various functions
- Infrastructure: Maintaining and scaling Slack’s technology infrastructure
- Sales and marketing: Promoting Slack and acquiring new customers
- Customer support: Providing high-quality assistance to Slack’s user base
The Future of the Slack Business Model
The Slack business model has shown resilience and adaptability.
As of 2023, Slack’s valuation stood impressively at $26.51 billion, highlighting its growth trajectory and market acceptance since its acquisition by Salesforce for approximately $27.7 billion in 2012.
Financially, Slack has demonstrated solid performance, with reported revenue of over $273.4 million in Q1 of 2022, marking a 36% year-over-year increase.
This is supported by a significant user base and projection to hit 47.2 million daily active users by 2025.
This projection is based on Slack’s high penetration in the United States market, where it remains the tool of choice for many businesses.
However, challenges remain as Slack faces fierce competition from major players like Microsoft SharePoint, which holds a larger market share.
To put the market into perspective, the collaborative software market is projected to grow to $16.2 billion by 2028. To maintain its competitive edge, Slack’s strategy involves expanding its ecosystem, integrating AI features (think automation), and enhancing user experience.