The success of the LEGO business model lies in its ability to adapt and adjust. Digital devices, such as gaming consoles and iPads, became a go-to source of entertainment for kids. This digital shift saw a massive change in the toy industry, with many brands and retailers going into liquidation.
Lego, though, embraced digital technologies at a time when other toy companies failed to do the same.
LEGO Group, a Danish toy company, is a pinnacle of creativity and innovation in the toy market. Founded in 1932 by Ole Kirk Christiansen, the company’s name comes from the Danish phrase “leg godt,” meaning “play well.”
This reflects Lego’s core focus, which is to promote learning and imagination through play.
LEGO’s interlocking brick system, introduced in 1958, revolutionized the toy industry, offering unparalleled durability, versatility, and interoperability.
Table of Contents
A Brief History of Lego
LEGO’s began during a period of economic turmoil, but its founder, Ole Kirk Christiansen, saw an opportunity to bring joy to children through affordable and well-crafted wooden toys.
In 1932, he established the LEGO company in Billund, Denmark. However, it was not until 1958 that LEGO truly revolutionized the toy industry by introducing its patented interlocking brick design.
This ingenious system allowed children to connect and disconnect bricks while building their own creations. It provided kits but children could also use their imagination and build whatever they wanted. Look at what some of the most incredible Lego enthusiasts have built.
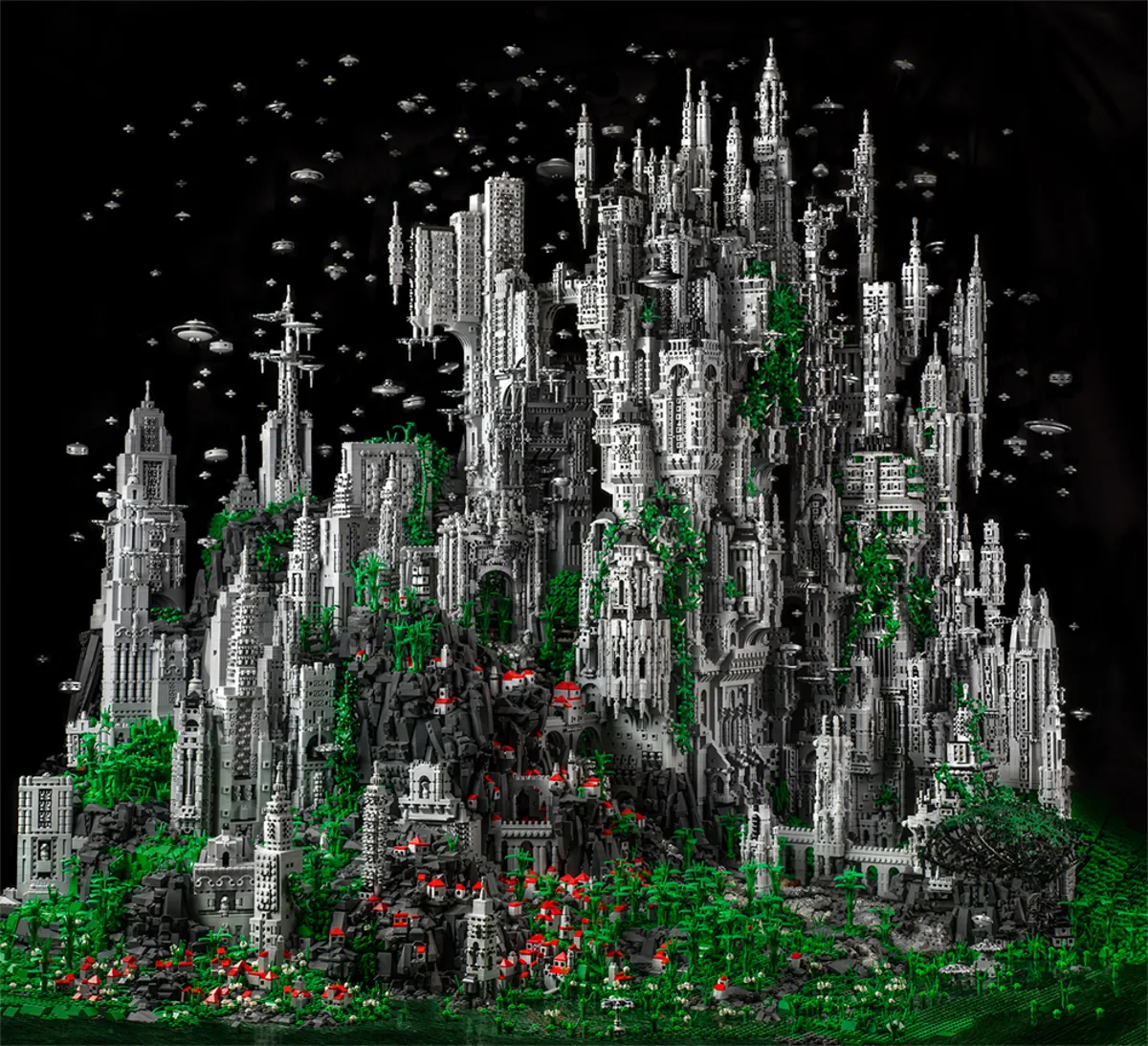

You can begin to see the endless possibilities of using Lego. The LEGO brick became the cornerstone of the brand’s success and remains its most iconic feature today.
As LEGO continued to evolve, it expanded beyond just toys.
In 1968, LEGOLAND Park opened its gates in Billund, becoming the world’s first theme park dedicated entirely to LEGO. This marked a milestone for the company as it shifted into experiential offerings and created immersive worlds.
The success of LEGOLAND led to further expansion, with additional parks opening worldwide.
Today, LEGOLAND Parks are located in countries such as Germany, Malaysia, Dubai, Japan, and the United States.
Throughout its history—from its inception in 1932 until now- LEGO has remained committed to inspiring creativity among children and adults alike.
FUN FACT
Lego has produced over 600 billion LEGO bricks since 1932
Lego Products and Services
Lego Sustainability

LEGO bricks and sets are produced in several countries worldwide to meet the global demand for their products. LEGO manufacturing and production facilities are located in:
- Denmark: The original LEGO factory in Billund, where the company was founded, remains a key site for both production and corporate activities.
- Hungary: LEGO has a manufacturing plant in NyÃregyháza, which plays a significant role in supplying the European market.
- Czech Republic: The factory in Kladno is crucial for LEGO’s European operations, focusing on both manufacturing and packaging.
- China: Reflecting LEGO’s commitment to the Asian market, the company operates a factory in Jiaxing, which serves both the local and global markets.
- Mexico: The LEGO factory in Monterrey is pivotal for manufacturing products destined for the Americas.
Who Owns Lego?
LEGO Group remains privately held, predominantly owned by Kjeld Kirk Kristiansen, the grandson of founder Ole Kirk Christiansen, through the Kirkbi A/S investment company.
The ownership by family has been a mjor factor in maintaining LEGO’s commitment to quality and innovation.
Lego Mission Statement
LEGO’s mission statement is “to inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.”
This statement reflects LEGO’s commitment to education, creativity, and fostering a love of learning through play. Their vision extends this ethos, aiming to innovate to benefit children and contribute positively to the world.
However, the concept of creativity has also been harnessed through Lego Serious Play, which is focused on helping businesses unleash their creativity.

Lego Business Model
The LEGO business model is complex. It includes the manufacturing and selling of toy bricks and a broad spectrum of activities designed to engage and retain a very diverse consumer base.
At its core, LEGO’s model is predicated on the physical LEGO brick, a simple yet versatile product that is the foundation for a wide range of sets and themes.
LEGO expands its reach through thematic storytelling, licensing agreements with popular media franchises, and digital gaming. It also has a massive community of enthusiasts who promote the brand through word of mouth and social media.
LEGO also invests in educational initiatives, leveraging its products in schools and educational programs to promote STEM learning.
Key Facts About Lego
Lego
Ole Kirk Christiansen
1932
1932
Niels B. Christiansen (as of the last known update)
Billund, Denmark
20,000 worldwide
Private company
$9,697 million (2022)
$2,010 million (2022)
Private company
How Does Lego Make Money?
The LEGO business model generates several revenue streams including:
- Sales of LEGO sets have various themes and levels of complexity, which are tailored to different age ranges.
- Licensing fees from partnerships with film studios, entertainment properties, and video game developers.
- Revenue from LEGOLAND theme parks and discovery centers operated by Merlin Entertainments under a special agreement.
- Digital gaming, through the sale of video games based on LEGO sets and themes.
- Merchandising, including apparel, books, and accessories tied to LEGO branding.
The Lego Business Model Canvas
Detailed below is the Lego business model canvas showing all nine sections.

Lego Business Model Customer Segments
The Lego business model targets three main customer segments.
- Children (6-12 years): The primary target, with sets designed to inspire creativity and imaginative play.
- Teenagers and Adults (13+ years): With more complex sets, including Technic and Architecture, catering to advanced builders and collectors.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and programs focused on STEM education, utilizing LEGO products for hands-on learning.
Lego Business Model Value Propositions
The Lego business model offers the following value propositions:
- Creativity and Imagination: Encourages users to imagine, create, and build, offering endless possibilities.
- Educational Value: Promotes STEM skills through problem-solving and design.
- Quality and Durability: High-quality, durable bricks that last for generations.
- Interoperability: All bricks are compatible, allowing for continual expansion and use.
Lego Business Model Channels
- Retail Stores: LEGO branded stores and third-party retailers worldwide.
- Online Sales: Direct-to-consumer sales through LEGO’s website.
- Theme Parks: LEGOLAND parks serving as immersive brand experiences.
- Educational Partnerships: Distribution through educational programs and schools.
Lego Business Model Customer Relationships
The Lego business model relies on maintaining engaged communities of users by:
- Community Engagement: Active online communities and forums for sharing ideas and creations.
- Customer Service: Robust support for product information, replacement parts, and building instructions.
- Brand Loyalty Programs: VIP programs offering rewards, early access to sets, and exclusive promotions.
- Educational Support: Resources and kits for teachers and educators incorporating LEGO into curriculum.
Lego Business Model Key Activities
The Lego business model focuses on the following key activities:
- Product Development: Designing and developing new LEGO sets.
- Manufacturing and Distribution: Producing and distributing products globally.
- Marketing and Branding: Promoting the LEGO brand and products.
- Community and Educational Engagement: Supporting educational initiatives and community building.
Lego Business Model Key Partners
The Lego business model relies on a range of external partners to innovate and produce the value propositions:
- Media Franchises: Partnerships for thematic sets (e.g., Star Wars, Harry Potter).
- Retail Partners: Distribution through major retailers and LEGO stores.
- Educational Institutions: Collaborations for STEM education programs.
- Merlin Entertainments: Operator of LEGOLAND parks under a partnership agreement.
Lego Business Model Cost Structure
The Lego business model cost structure is based on its global production and distribution of physical products and engagement online for digital products and services:
- Manufacturing and Materials: Costs associated with producing LEGO bricks and sets.
- Research and Development: Investment in new product design and innovation.
- Marketing and Sales: Advertising, promotions, and retail operations expenses.
- Operational and Administrative: The company’s costs include staff and facilities.
Lego Competitors
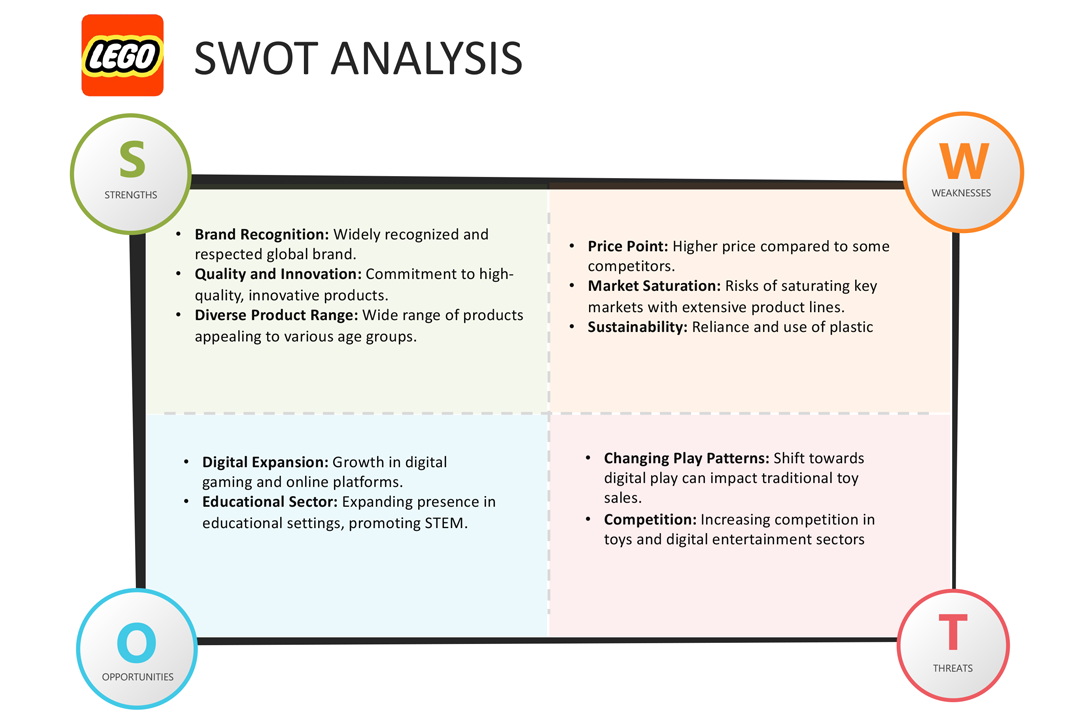
The SWOT analysis of the Lego business model demonstrates the overall competitive position of Lego and what it needs to consider for its strategic future.
Lego SWOT Analysis
Lego Sustainability
LEGO’s commitment to sustainability is a cornerstone of its corporate ethos, reflecting a profound understanding of its responsibility towards the environment, society, and future generations.
The company’s sustainability statement emphasises its dedication to making a positive impact, with a clear focus on reducing carbon emissions, sustainable packaging, and responsible sourcing of materials. LEGO aims to inspire children through play while ensuring that its operations and products leave a minimal environmental footprint.
Lego Sustainability Initiatives
- Planet Promise: LEGO aims to positively influence future generations by enhancing the sustainability of its products, packaging, and operations, thereby minimising its environmental impact targets.
- Carbon Emission Reduction: LEGO continues to work towards its science-based target of reducing absolute carbon emissions by 37% by 2032, compared to 2019. This effort acknowledges that 98% of its carbon emissions originate outside its operations, necessitating supplier collaborations.
- Sustainable Packaging: LEGO has committed to making its packaging 100% sustainable by the end of 2025, including eliminating single-use plastic and adopting Forest Stewardship Council-certified paper and cardboard. In 2022, the company started introducing paper-based bags into its boxes.
- Innovation in Sustainable Materials: The company is exploring new sustainable materials for LEGO bricks and elements, including a prototype brick made from recycled plastic bottles (rPET) and bio-PE LEGO elements, now found in over half of LEGO sets.
- Zero Waste to Landfill: LEGO is focused on achieving zero waste to landfill. Its future carbon-neutral sites in Vietnam and the U.S. will match energy needs with onsite or nearby solar panels and aim for LEED Gold certifications.
- Community Engagement: LEGO has collaborated with organizations such as Save the Children and UNICEF to bring Learning through Play to children and families in need, reaching over 9.8 million in 2022. Initiatives supported by LEGO employees include the ‘Build and Talk’ series to discuss digital well-being and the ‘Build the Change’ programme, which expanded to Mexico and China, engaging 900,000 children.
- LEGO Replay Programme: This programme has kept over 66 million bricks in play and circulation in 2022 by encouraging people in the U.S. and Canada to donate their unused LEGO bricks to children’s charities.
Lego Sustainability Issues
- Dependency on Plastic: Despite strides towards sustainable materials, LEGO’s core products remain predominantly plastic-based, posing challenges in terms of long-term sustainability and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensuring the sustainability and ethical standards of the supply chain remains a complex issue, particularly with global operations and sourcing.
- End-of-Life Product Management: Due to their durability and mixed materials, LEGO products present ongoing challenges for circularity in terms of recyclability and disposal.
Lego Sustainability Criticisms
- Bioplastic Transition Challenges: Reports have highlighted LEGO’s challenges in transitioning to bioplastics, with concerns about the scalability, environmental impact, and performance of alternative materials.
- Packaging Criticisms: Despite efforts to improve, LEGO has faced criticism over the amount of packaging used for its products, which activists argue contributes to waste and environmental pollution.
Lego Improvements for Sustainability and Circularity
- Enhanced Recycling Programs: LEGO could develop more robust programs for customers to return or recycle old LEGO bricks, facilitating a more circular product lifecycle.
- Investment in Alternative Materials Research: Increasing investment in research and development of alternative materials that are sustainable and maintain the quality and durability LEGO is known for.
- Supply Chain Innovation: Further innovation in supply chain management to improve transparency, reduce emissions, and ensure all materials are sourced responsibly and ethically.
Conclusion
The company’s proactive stance on environmental responsibility showcases its commitment to play and the planet. However, the path to true sustainability and circularity in the toy industry is complex, requiring continued innovation, collaboration, and stakeholder engagement.



