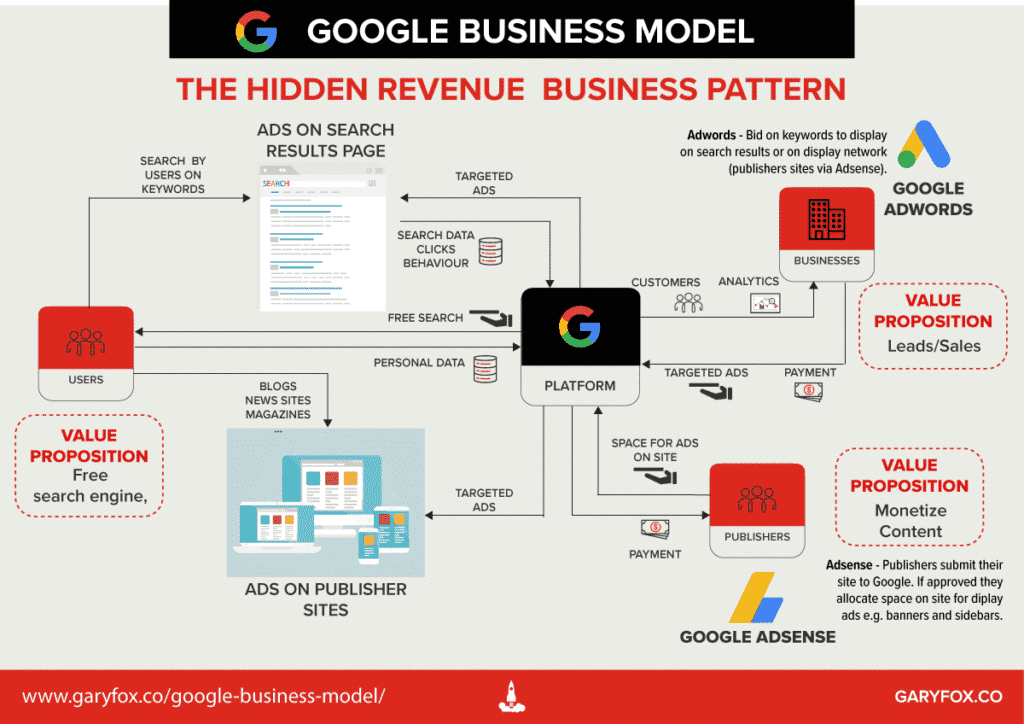
The Google business model is based on a hidden business model pattern.
A hidden business model is interesting because the user doesn’t pay for the service. Instead, third parties. such as businesses pay.
In the case of the Google business model, businesses pay to advertise either on the search results page or on its display network.
This is just one of many different business model patterns that Google uses in different parts of its business. In this article, I’ll break some of the other powerful models that Google uses to drive its growth.
Advertisers use Google because of the massive volume of people that use it globally. Here are a few mind-blowing stat about the scale of Google search engine:
- Google is the most visited site in the world with over 80 billion searches per year – source: Similarweb.
- Google dominates the Search Engine Market, it has commands over 91% of all search – source: Statcounter.
- 81% of people search online before making a major purchase – source: CSA.
The hidden revenue model concept separates the idea of ‘revenue and customer’.
Interesting Fact: Google is owned by its parent company Alphabet, which is valued at 1.3 trillion dollars.
Table of Contents
The Google Business Model
In 2019, Google earned over 160 billion dollars, 88% of which came from advertising.
If you’re wondering about that other 12% and are curious about how does Google make money, then click on that link and you’ll get a full breakdown of its latest results.
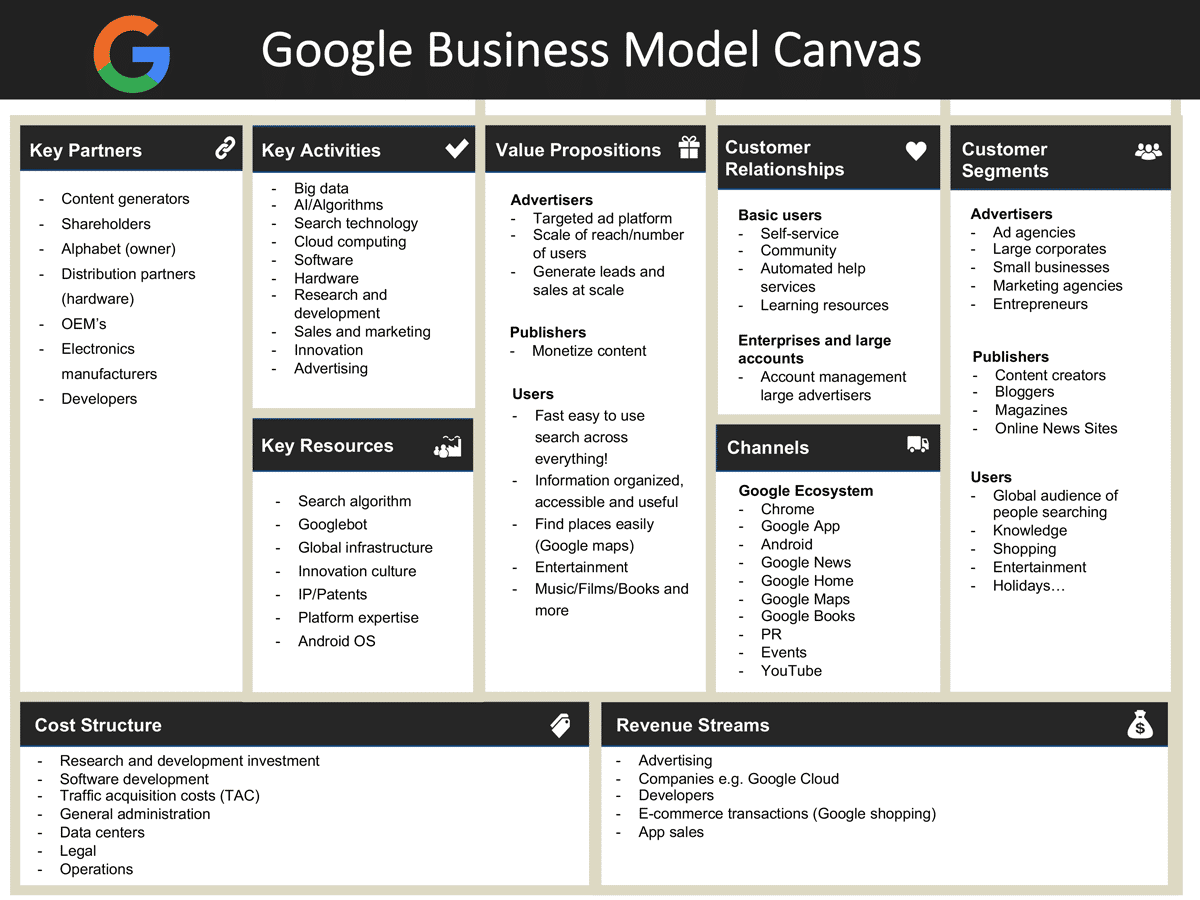
Google Business Model Canvas
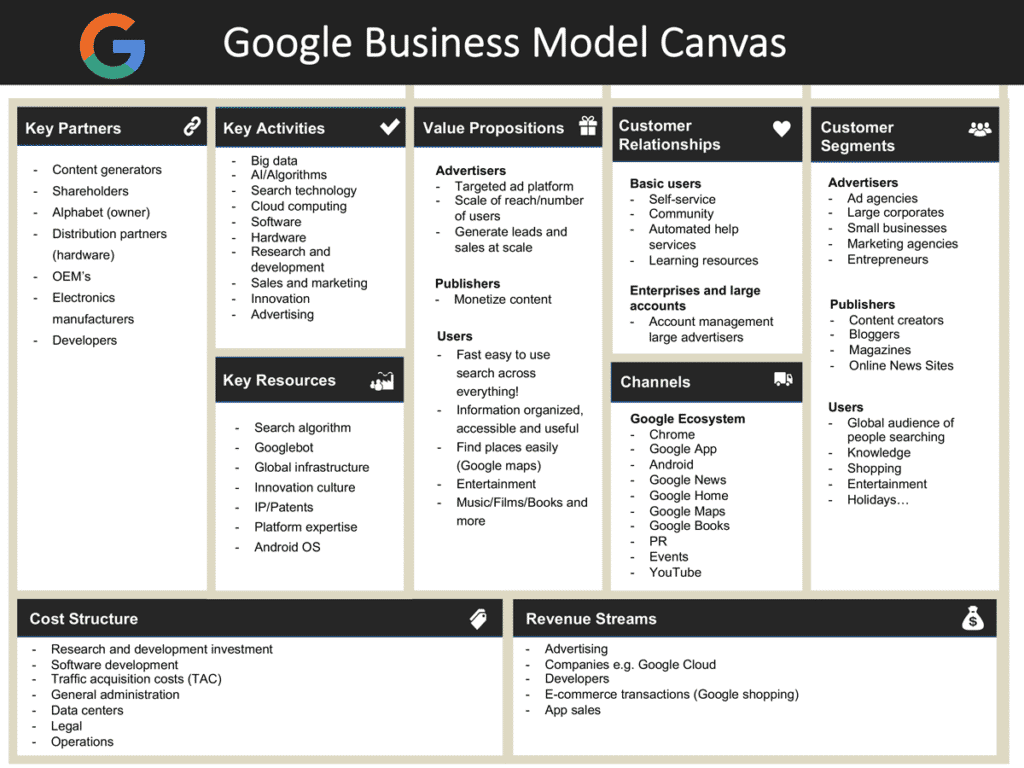
Google has several types of business. The Google Business Model Canvas focuses mainly on the core Google Business Model which is the hidden revenue model.
Customer Segments

For its core advertising business, Google has three main groups of customers.
Advertisers

Advertisers are a mix of different types of businesses and individuals (e.g. entrepreneurs) who want to market their products or services. Some of these are global advertising giants like BBDO while others
Examples of advertisers include:
- Amazon is the biggest advertiser in the world and a considerable amount of that is on Google ads.
- Large advertising agencies e.g. Omnicom, Interpublic, Publicis.
- Small and Media sized business.
- Ad, web and other marketing agencies.
- Search Marketing agencies.
- Small businesses.
Publishers

Publishers normally have valuable content that they have created and need a way to monetize it. As an example, many bloggers who have built up organic traffic over time can use Adsense to place banners on their site.
The space they allocate to banners is then used by Google for display ads that match the interests of the audience.
Publishers include:
- Bloggers
- Online news sites
- Magazine sites
Users
Users are everybody that searches on Google – the billions of people that search for everything from cars to holidays and more.
Without users, Google wouldn’t be able to have advertisers. That’s why Google has to continually invest in the quality of the search results and user experience.
Channels

Google uses its own channels to promote its services. With 91% of search engine market Google itself is the channel.
The Google business model uses its other services to reinforce its advertising ecosystem. As an example, an increasing trend is a move to voice search through smart speakers such as Google Home.
- Google GSuite (including Gmail)
- Chrome
- Google Maps
- Google Analytics
- Google Adwords
- Google Developer
- Google Cloud
- Android Devices
- Google Home
Customer Relationships

Google is principally a self-service operation. However, if you are an advertiser they are more proactive and often you will have an account manager call you to guide you in the initial stages of setting up your AdWords campaigns. This is often referred to as onboarding new customers.
Much larger enterprise and corporate accounts have dedicated account managers or whole teams in place depending on the size of their budget.
Value Proposition

Google has three main value propositions that fit to their customer segments:
1. Users
The main value proposition for users is the free use of the Google Search Engine.
2. Advertisers
Advertisers can target customers online with a high degree of accuracy based on keywords. Additionally, filters allow advertisers to refine their targeting.
When comparing Facebook ads vs Google ads, one of the key points of difference is that online searches often show a high degree of intent. In other words, people are searching to buy something.
3. Content Producers
The main value proposition for content producers is that they can monetize their content.
Producing content takes time and effort and is costly on a commercial basis e.g. newspapers have salaries to pay, infrastructure.
Many newspapers that survived the shift to digital now rely on Adsense and advertising more generally for their revenue.
However, even influencers and bloggers use Adsense to make money, but to make any significant amount of money you need a lot of traffic.
The Google ads business model is the key driver for the huge income Google generates.
Key Partners

Google relies on a lot of hardware, not just software to power its global infrastructure. Many manufacturers are involved in producing servers and other network hardware for its gigantic data centres.
Other partners include:
- Content generators – bloggers, online magazines…
- Shareholders – investors in Google.
- Alphabet (owner) – the parent company of Google.
- Distribution partners (hardware) – partners for the distribution of hardware products like Google Pixel.
- OEM’s – manufacturers of servers and other essential infrastructure technology.
- Electronics manufacturers – chip manufacturers such as Intel.
- Developers – developers who create the Amazon Cloud services such as Google Maps.
Key Activities

Google is technology company that focuses on advertising but also has its eye on the next wave of technology. It invests heavily in research and development to maintain its competitive position as well as invest in future bets.
Other key activities of the Google business model:
- Big data – managing and using the massive amount of data from billions of searches.
- AI/Algorithms – AI to optimise the delivery of search results.
- Search technology – the technology that delivers the rapid response to any search query.
- Cloud computing – the global infrastructure.
- Software – the many different services developers can use.
- Hardware – hardware such as Google Pixel, Google Home, Fitbit…
- Sales and marketing – to promote Google products and services.
- Innovation – coming up with new ideas and solving problems.
- Advertising – advertising online.
Key Resources

Google is a technology giant and therefore patents and general intellectual properties are an essential part of its resources.
Surprisingly Google is lacking behind other tech giants when it comes to patents, coming in at 15th in 2019.
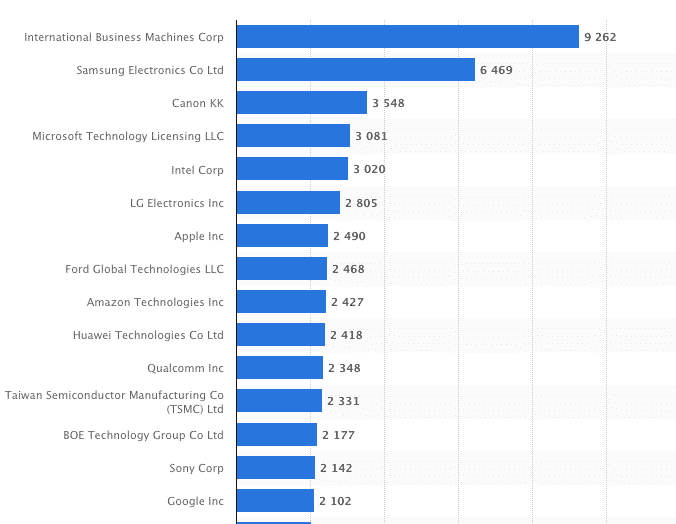
Other key resources for the Google business model include:
- Search algorithm – the Google search algorithm
- Googlebot – the Googlebot that checks sites and indexes their content.
- Global infrastructure – the global technology infrastructure.
- Innovation culture – the culture and way of being Google.
- IP/Patents – its patents and intellectual property.
- Platform expertise – expertise in technology.
- Android OS – the operating system for mobiles.
Cost Structure
- Research and development investment
- Software development
- Traffic acquisition costs (TAC)
- General administration
- Data centres
- Legal
- Operations
Revenue Streams
The Google revenue model is primarily driven by online advertising – display network, pay per click and cost per impressions.
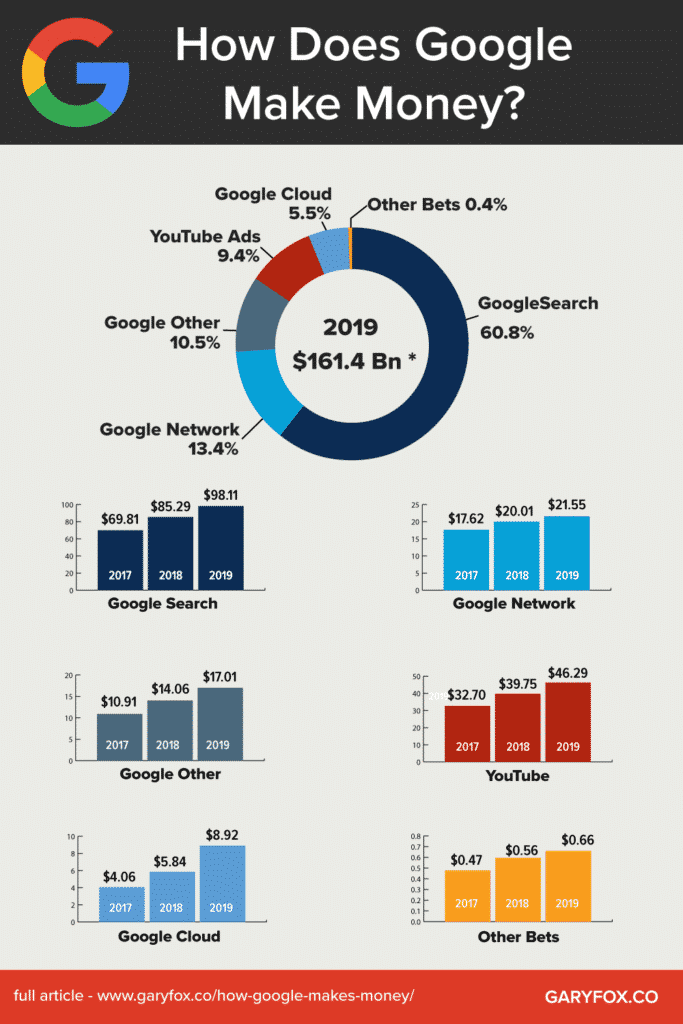
Google Innovation Strategy
Here are a few notes on how the Google business model differs across its portfolio.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud is a subscription business model. Companies pay based on the amount of resources they use e.g. the number of processes, bandwidth and other services. While Google Cloud isn’t as large as the Amazon Business model of AWS, it is rapidly growing and is used by a significant number of major corporates.
YouTube Business Model
With YouTube content creators have a platform to display their videos and viewers have a seemingly limitless supply of entertainment.
A perfect two-sided platform. But the revenue came from advertising. Even before being purchased by Google, YouTube declared it was making 15 million dollars per month. Fast-forward and in 2019 YouTube advertising amounted to over $46 billion – that’s $3.8 billion. month
Google’s Top Acquisitions
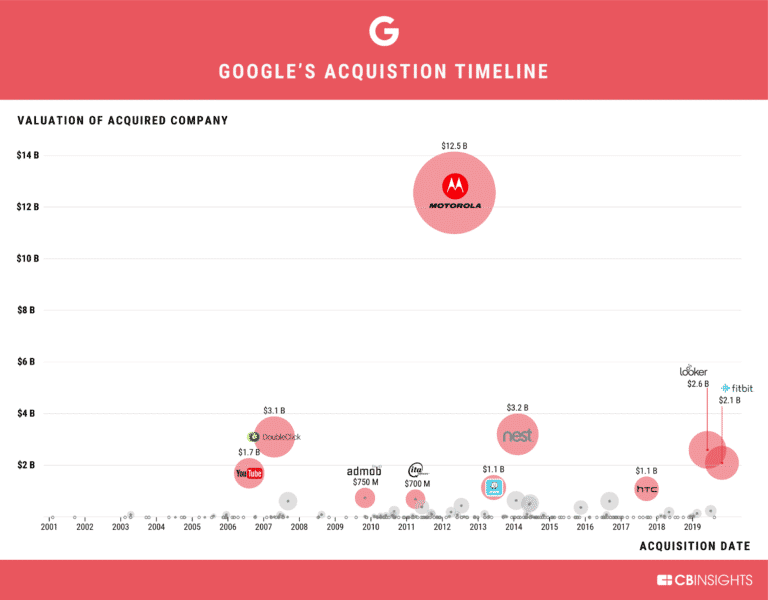
1. Motorola Mobility ($12.5B, 2012) is Google’s largest acquisition to date. In October 2014, Motorola was sold to Lenovo for less than a quarter of its acquisition price (approximately $2.9B).
2. Nest Labs ($3.2B, 2014) was Google’s entry into the smart home space. Google acquired the connected home developer to increase its household footprint, while also providing expansion opportunities for its Android ecosystem.
3. DoubleClick ($3.1B, 2007), an ad serving company was purchased to complement Google’s existing ad business. The deal has been instrumental in giving Google a foothold in the lucrative display advertising industry, allowing the company to facilitate programmatic ad-buying through its own ad exchange.
4. Looker ($2.6B, 2019) is a California-based business intelligence platform whose recent acquisition further signals Google’s current focus on growing its cloud offerings.
5. Fitbit ($2.1B, 2019), a global leader in consumer health wearables, is the most recent of Google’s top 10 acquisitions. In 2018, Fitbit sold 14M devices and had nearly 30M active users worldwide. Google expects the acquisition to strengthen its Wear OS efforts as it attempts to catch up with Apple.
6. YouTube ($1.7B, 2006), a leading video-sharing platform, was Google’s first $1B+ acquisition. Through this purchase, Google anticipated the shift from traditional media like TV to online viewing, while also increasing its traffic and growing its ad business.
7. Waze ($1.15B, 2013), an Israel-based mapping service startup, brought social traffic data that helped Google improve Google Maps functions such as accurately predicting travel time and suggesting navigation routes.
8. HTC – Pixel Smartphone Division ($1.1B, 2017) is a Taiwan-based consumer electronics manufacturer. While the acquisition did not include any production facilities, it left Google with a significant part of HTC’s smartphone team (underlining the Android maker’s focus on competing with iPhone maker Apple) and helped Google establish a manufacturing presence in Taiwan.
9. AdMob ($750M, 2009), a mobile advertising company founded in 2006, was purchased by Google in anticipation of the massive proliferation of mobile ads.
10. ITA Software ($700M, 2011), a US-based airline IT and services provider, was acquired by Google to expand the tech giant’s search capabilities and to power Google Flight Search.
Key Points For the Google Business Model
- Google has spent nearly $29B on its top 10 acquisitions.
- These top deals reflect Google’s strategy evolution, from adtech (AdMob, DoubleClick) in the late 2000s to mobile (Motorola Mobility, Apigee) and wearables (Fitbit) in the 2010s.