YouTube’s business model has made it the world’s largest video-sharing platform with over 2 billion active users monthly and 500 hours of video uploaded every minute.
In this article, I’ll examine the YouTube business model and break it down so that you can see what makes it such a dominant player.
Table of Contents
How Does YouTube’s Business Work
The YouTube business model is built around providing a platform for users to upload, share, and view videos. It is essentially a multi-sided market with three key sides.
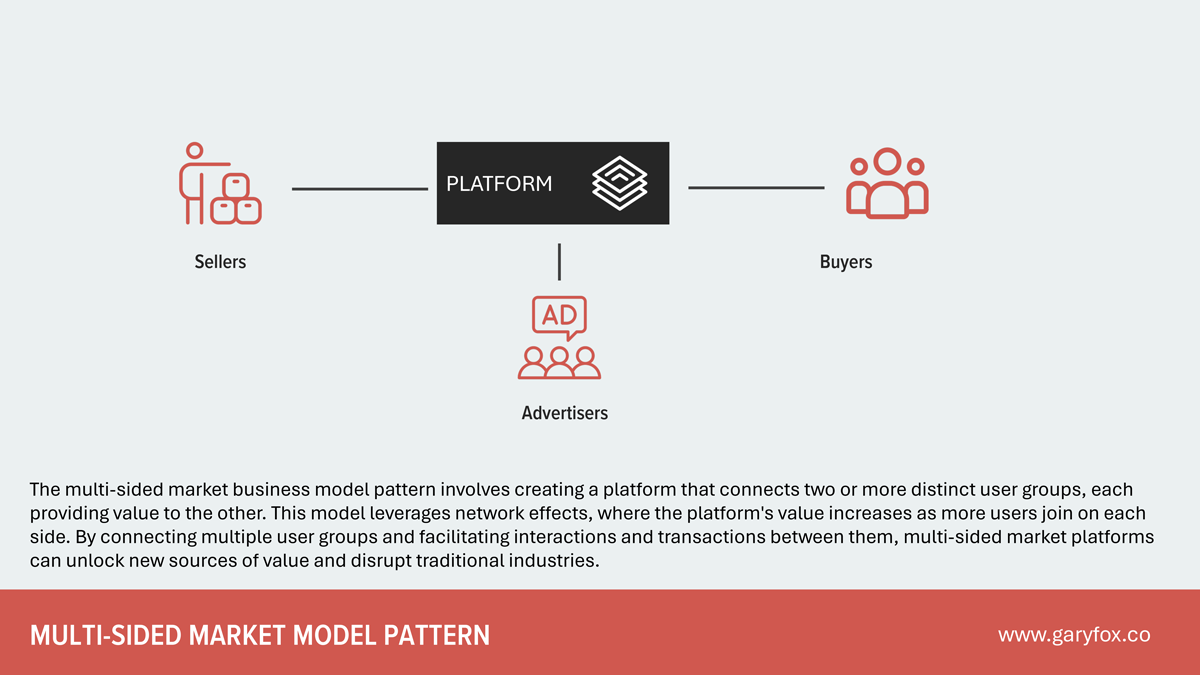
First, there are the audiences that watch the videos. There is no specific customer segmentation for this; it is a general audience, but clearly, there are niche interests and reasons why people search for and watch video content.
Second, content creators generate videos for all sorts of niches and audiences. These content creators range from individuals to large corporations promoting films or songs.
Third, some businesses advertise on YouTube, which is YouTube’s main revenue source (Google).

YouTube hosts a massive library of content, from music videos and movie trailers to educational content and personal vlogs.
Using AI (advanced algorithms), YouTube provides recommendations and personalized content based on people’s viewing history.

Key Facts About YouTube
These are some key facts related to the YouTube business model:
YouTube
Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim
February 14, 2005
2005
Susan Wojcicki (CEO of YouTube)
San Bruno, California, USA
YouTube does not separately disclose its number of employees
Part of Google (Alphabet) GOOGL
$31.5 billion (2023)
Part of Alphabet Inc.
Part of Alphabet Inc.
A Brief History of YouTube

YouTube was founded in February 2005 by three former PayPal employees: Chad Hurley, Steve Chen, and Jawed Karim.
The video streaming platform rapidly grew and was already attracting over 100 million video views per day by 2006. Seeing the huge growth and future potential, Google snapped it up and bought YouTube for $1.65 billion in November 2006.
Key milestones and dates:
- February 2005: YouTube is founded
- April 2005: First video uploaded, “Me at the Zoo“
- December 2005: YouTube receives $3.5 million in funding from Sequoia Capital
- July 2006: 100 million daily video views milestone reached
- October 2006: YouTube launches its first video ads
- November 2006: Google acquires YouTube for $1.65 billion
- May 2007: YouTube launches its Partner Program, allowing creators to monetize their content
- March 2013: YouTube reaches 1 billion monthly active users
- October 2020: YouTube breaks record with over 2 billion monthly active users
Key Competitors of YouTube
Video content was initially difficult and laborious to produce. But fast-forward to today, and there are a ton of tools and apps that allow people to produce videos easily. That’s why video has become one of the dominant forms of social media content.
As of 2024, video content is the most popular form of social media content, with 91% of social media users preferring to watch videos over other types of content – Source: HubSpot.
As a result, YouTube business model now faces competition from various players.
YouTube Competitors
- TikTok: A short-form video platform that has gained significant popularity, particularly among younger audiences – as of 2024, TikTok has over 1.8 billion monthly active users worldwide- source: Statista.
- Netflix: A streaming giant that produces and distributes original video content – as of 2024, Netflix has approximately 238 million monthly active users worldwide – source: Statista.
- Amazon Prime Video: A video streaming service offered as part of Amazon’s Prime membership – as of 2024, Amazon Prime has over 200 million monthly active users worldwide – source: Statista.
- Facebook Watch: A video-on-demand service integrated into the Facebook platform – as of 2024, more than 4 billion video views occur on Facebook every day, which translates to over 120 billion video views per month – source: Social Media Today, TechCrunch.
- Twitch: A live-streaming platform primarily focused on gaming content – as of 2024, Twitch users watch approximately 1.5 billion hours of video content per month – source: TwitchTracker.
- Vimeo: A video hosting and sharing platform geared towards professional creators – As of 2024, Vimeo users watch around 715 million videos per month – source: Vimeo Blog.
- Dailymotion: A video-sharing website that offers a mix of user-generated and professional content
- Hulu: A streaming service that offers a variety of TV shows, movies, and original content – as of 2024, Dailymotion users watch approximately 250 million videos per month – source: Dailymotion Press.
- Disney+: The video streaming platform featuring content from Disney, Pixar, Marvel, Star Wars, and National Geographic – as of 2024, Disney+ has approximately 500 million hours of content watched per month by its users – source: Statista.
- Bilibili: A Chinese video-sharing website that focuses on anime, comics, and gaming content – as of 2024, Bilibili users watch approximately 1.2 billion hours of video content per month – source: Bilibili Investor Relations.
Who Owns YouTube
YouTube is a subsidiary of Google and is owned by Alphabet Inc. Alphabet Inc. was created in 2015 as a restructuring of Google, with Google becoming a subsidiary of the newly formed holding company.
YouTube is now indirectly owned by Alphabet Inc. but remains under Google as its parent company. This ownership structure is most likely due to the common need to personalize content and ads to audiences, similar to how Google operates its search engine.
YouTube Mission Statement
YouTube’s mission statement is “to give everyone a voice and show them the world.”
How Does YouTube Work?
The YouTube recommendation system is a critical part of its business model and is instrumental in keeping audiences engaged with relevant content thus increasing the amount of time spent on the platform. In turn, this leads to more advertising revenue for YouTube and its content creators.
YouTube has also expanded its offerings to include subscription-based services such as YouTube Premium and YouTube TV which provide ad-free content and access to exclusive features.
The Revenue Model of YouTube
The YouTube revenue model is primarily based on income from advertising. YouTube offers various ad formats, including:
- Display ads: Banner ads that appear on the top or side of the video player
- Overlay ads: Semi-transparent ads that appear on the lower portion of the video
- Skippable video ads: Video ads that users can skip after 5 seconds
- Non-skippable video ads: Video ads that users must watch before the main video content
YouTube also uses a subscription business model pattern:
- YouTube Premium: A paid membership that offers ad-free content, offline viewing, and access to exclusive features
- YouTube TV: A live TV streaming service that offers access to cable channels and networks
Key Features of YouTube Business Model
- User-generated content: YouTube relies on its users to create and upload videos, ensuring constant fresh content.
- Advertising revenue sharing: YouTube shares some of its advertising revenue with eligible content creators, incentivizing them to produce high-quality content.
- Personalized recommendations: YouTube’s advanced algorithms suggest personalized content to each user, keeping them engaged and increasing the platform’s overall watch time.
- Continuous innovation: YouTube constantly evolves and introduces new features. Recently it has introduced live streaming, 360-degree videos, and virtual reality support, to stay ahead of the competition.
The YouTube Business Model
I’ve detailed the complete YouTube Business Model into the business model canvas below:

The YouTube Business Model
Customer Segments
The YouTube business model caters to cost-conscious shoppers and other segments including:
- Content creators: Individuals or organizations who upload videos to share with the YouTube community
- Viewers: Users who consume video content on the platform for entertainment, education, or information
- Advertisers: Businesses that leverage YouTube’s advertising options to reach their target audience

Value Propositions
The YouTube business model focuses on the following value propositions:
- Vast content library: Access to an enormous collection of videos spanning various topics and genres
- Easy content creation: User-friendly tools for creating, editing, and uploading videos
- Global reach: Ability to connect with a worldwide audience and build a community around shared interests
- Personalized recommendations: Advanced algorithms that suggest relevant content based on viewing history and preferences
- Free access: No cost for users to watch videos, with optional paid subscriptions for ad-free viewing and exclusive features

Channels
The YouTube business model leverages the following channels to reach and engage with its customers:
- Website: The primary platform where users can upload, watch, and interact with video content
- Mobile apps: Dedicated applications for iOS and Android devices, enabling users to access YouTube on the go
- Social media: Integration with popular social media platforms to share and promote video content
- Partnerships: Collaborations with content creators, media companies, and advertisers to expand reach and offerings
Customer Relationships
The YouTube business model uses methods to minimize costs associated with customer relationships:
- Self-service: Users independently access and utilize the platform and its features.
- Automated services: Algorithms and machine learning provide personalized recommendations and support.
- Co-creation: Content creators actively contribute to the platform, generating diverse content.
- Communities: Users connect and engage through comments, likes, shares, and subscriber interactions.
Key Activities
The YouTube business model includes the following key activities:
- Platform development and maintenance: Ensuring the YouTube platform and its features are functional, user-friendly, and competitive
- Content moderation and curation: Monitoring and managing content to provide a safe and engaging user experience
- Content promotion and optimization: Promoting and optimizing content to attract viewers and advertisers
- Innovation and expansion: Developing new features and offerings to stay ahead of the competition
- Relationship management: Cultivating relationships with content creators, partners, and advertisers
Key Resources
The YouTube business model relies on several key resources to operate effectively and maintain its competitive position:
- Technology infrastructure: Servers, data centers, and content delivery networks that enable seamless video streaming and storage
- Intellectual property: Proprietary algorithms, software, and patents that power YouTube’s platform and features
- Brand equity: The strong reputation and global recognition of the YouTube brand
- Content library: The vast collection of user-generated videos that attract and retain viewers
- Human resources: Skilled employees across various functions, including engineering, marketing, and content moderation
Key Partners
The YouTube business model relies on a diverse network of key partners that play a crucial role in supporting the company’s operations, growth, and success. These partnerships include:
- Content creators: Individual users and organizations that produce videos for the platform
- Advertisers: Businesses that purchase advertising space on YouTube to reach their target audience
- Media companies: Film studios, television networks, and other content providers that distribute their content on YouTube
- Music labels: Record companies that license music for use in videos and share revenue with YouTube
- Technology partners: Companies that provide hardware, software, and services to support YouTube’s infrastructure and operations
Revenue Streams
The YouTube business model generates the following revenue streams:
- Advertising: Display ads, overlay ads, and video ads (skippable and non-skippable) that appear alongside video content
- YouTube Premium: A paid subscription service that offers ad-free viewing, offline playback, and access to exclusive content
- YouTube TV: A live TV streaming service that provides access to cable channels and networks
- Channel memberships: Allows viewers to pay a monthly fee to support their favorite creators and receive exclusive perks
- Super Chat and Super Stickers: Paid features that enable viewers to highlight their messages during live streams

Cost Structure
The main costs associated with the YouTube business model include:
- Infrastructure costs: Expenses related to servers, data centers, and content delivery networks
- Content acquisition and licensing: Costs associated with securing rights to music, movies, and other copyrighted material
- Employee salaries and benefits: Compensation for YouTube’s workforce across various departments
- Marketing and advertising: Expenses related to promoting YouTube and its offerings to users and partners
- Research and development: Investments in innovation, new features, and platform improvements
Navigating the Future: Strategic Shifts for YouTube’s Business Model
YouTube’s reign as the digital video king isn’t without its challenges. While advertising remains its bread and butter, user behaviour is always shifting and changing creating new market trends that demand adaptation. Here’s a few areas where YouTube can refine or improve its approach based on recent reports:
1. Combating Ad Fatigue: A Delicate Balancing Act
There’s a growing ad-blocking contingent across the internet. A 2023 Global Web Index report suggests nearly 43% of global internet users use ad-blockers [source: Global Web Index]. This signals a degree of user frustration with ads. Here’s how YouTube can strike a balance:
- Exploring Integrated & Unobtrusive Formats: YouTube can experiment with less disruptive ad formats that align better with user content preferences. Think sponsored segments within videos, championed by creators themselves, or native advertising that blends seamlessly with the content. A 2021 IAB report highlights the effectiveness of native advertising, with 60% of consumers reporting a positive perception [source: Interactive Advertising Bureau].
2. Subscription Evolution: Beyond the Premium Package
YouTube Premium’s ad-free experience offers a solid base, but there’s room for improvement. Here’s my thoughts:
- Tiered Subscription Models: A 2023 report by McKinsey suggests that tiered subscription models can increase customer acquisition and retention across various industries [source: McKinsey & Company]. YouTube tool the idea of ad-free from the Spotify business model. What it could do is offer a business channel – so more B2B content much like Linkedin business model is different to the Facebook business model.
3. AI-Powered Personalization: The Algorithmic Edge
Artificial intelligence is the main game-changer that everyone is talking about. Here’s is how YouTube can further leverage it:
- Enhanced Content Discovery & Recommendations: YouTube can personalize content recommendations to a much deeper level – so think about conversational search, summary of video before watching or producing a list of highlights and moments. Another point is to create recommendations that not only based on past viewing habits, but on adjacent interests. A 2023 study by Accenture found that 91% of consumers are more likely to shop with brands that provide relevant product recommendations [source: Accenture]. This same principle can be applied to content discovery.
4. Empowering the Creator Economy: A Symbiotic Relationship
Creators are YouTube’s source of content. Here’s a few thoughts on what they do to improve:
- Monetization Tools & Support Systems: First, provide creators with a wider range of monetization tools, beyond just ads. Think Super Chat on steroids, or platform-specific merchandise opportunities. Second, support smaller creators who and showcase new talent within niches. A 2022 report by DHG underlines the importance of creator satisfaction, highlighting a correlation between happy creators and a thriving creator economy [source: Digital Hollywood Group].
5. Proactive Regulatory Engagement: Building Trust & Avoiding Roadblocks
Regulatory scrutiny regarding data privacy and competitive practices is on the rise. Here’s what YouTube could do to improve:
- Transparency in Data Use & Ad Targeting: A 2023 report by Pew Research Center highlights a growing public concern about data privacy, with 81% of Americans expressing worry about how companies collect and use their data [source: Pew Research Center]. YouTube can build trust with users and creators alike by being clear and transparent about its practices regarding data usage and ad targeting. This may involve offering users more control over their data and preferences regarding ad targeting.